poisson_cdf
Evaluates the Poisson distribution function.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_poisson_cdf (int k, float theta)
The type double function is imsl_d_poisson_cdf.
Required Arguments
int k (Input)
Argument for which the Poisson distribution function is to be evaluated.
Argument for which the Poisson distribution function is to be evaluated.
float theta (Input)
Mean of the Poisson distribution. Argument theta must be positive.
Mean of the Poisson distribution. Argument theta must be positive.
Return Value
The probability that a Poisson random variable takes a value less than or equal to k.
Description
The function imsl_f_poisson_cdf evaluates the distribution function of a Poisson random variable with parameter theta. The mean of the Poisson random variable, theta, must be positive. The probability function (with θ = theta) is
f(x) = e-q θx/x!, for x = 0, 1, 2, …
The individual terms are calculated from the tails of the distribution to the mode of the distribution and summed. The function imsl_f_poisson_cdf uses the recursive relationship
f(x + 1) = f(x)q/(x + 1), for x = 0, 1, 2, …, k - 1
with f(0) = e-q.
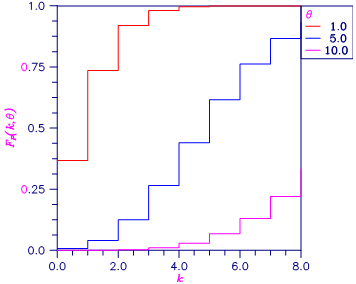
Figure 24, Plot of Fp(k, θ)
Example
Suppose X is a Poisson random variable with θ = 10. This example evaluates the probability that X ≤ 7.
#include <imsl.h>
int main()
{
int k = 7;
float theta = 10.0;
float p;
p = imsl_f_poisson_cdf(k, theta);
printf("Pr(x <= 7) = %6.4f\n", p);
}
Output
Pr(x <= 7) = 0.2202
Informational Errors
IMSL_LESS_THAN_ZERO | The input argument, k, is less than zero. |