ad_normality_test
Performs an Anderson‑Darling test for normality.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float imsls_f_ad_normality_test (int nobs, float x[], … , 0)
The type double function is imsls_d_ad_normality_test.
Required Arguments
int nobs (Input)
Number of observations. nobs must be greater than or equal to 3.
Number of observations. nobs must be greater than or equal to 3.
float x[] (Input)
Vector of length nobs containing the observations.
Vector of length nobs containing the observations.
Return Value
The p‑value for the Anderson‑Darling test of normality.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
float imsls_f_ad_normality_test (int nobs, float x[],
IMSLS_STAT, float *adstat,
IMSLS_N_MISSING, int *nmiss,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_STAT, float *adstat (Output)
The Anderson‑Darling statistic.
The Anderson‑Darling statistic.
IMSLS_N_MISSING, int *nmiss (Output)
The number of missing observations.
The number of missing observations.
Description
Given a data sample {Xi, i = 1 .. n}, where n = nobs and Xi = x[i-1], function imsls_f_ad_normality_test computes the Anderson-Darling (AD) normality statistic A = adstat and the corresponding Return Value (p‑value) P = P == {probability that a normally distributed n element sample would have an AD statistic > A}. If P is sufficiently small (e.g. P < .05), then the AD test indicates that the null hypothesis that the data sample is normally-distributed should be rejected. A is calculated:
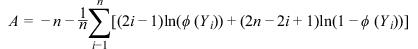
where and and s are the sample mean and standard deviation respectively. P is calculated by first transforming A to an “n‑adjusted” statistic A*:
and then calculating P in terms of A* using a parabolic approximation taken from Table 4.9 in Stephens (1986).
Example
The following example is taken from Conover (1980, pages 364 and 195). The data consists of 50 two‑digit numbers taken from a telephone book. The AD test fails to reject the null hypothesis of normality at the .05 level of significance.
#include <imsls.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int nobs = 50, nmiss;
float p_value, adstat;
float x[] = {
23.0, 36.0, 54.0, 61.0, 73.0, 23.0, 37.0, 54.0, 61.0, 73.0,
24.0, 40.0, 56.0, 62.0, 74.0, 27.0, 42.0, 57.0, 63.0, 75.0,
29.0, 43.0, 57.0, 64.0, 77.0, 31.0, 43.0, 58.0, 65.0, 81.0,
32.0, 44.0, 58.0, 66.0, 87.0, 33.0, 45.0, 58.0, 68.0, 89.0,
33.0, 48.0, 58.0, 68.0, 93.0, 35.0, 48.0, 59.0, 70.0, 97.0};
p_value = imsls_f_ad_normality_test (nobs, x,
IMSLS_STAT, &adstat,
IMSLS_N_MISSING, &nmiss,
0);
printf ("Anderson-Darling statistic = %11.4f \n", adstat);
printf ("p-value = %11.4f\n", p_value);
printf ("# missing values = %4d\n", nmiss);
}
Output
Anderson-Darling statistic = 0.3339
p-value = 0.5024
# missing values = 0
Informational Errors
IMSLS_PVAL_UNDERFLOW | The p‑value has fallen below the minimum value of # for which its calculation has any accuracy; ZERO is returned. |
Fatal Errors
IMSLS_TOO_MANY_MISSING | After removing the missing observations only 2 observations remain. The test cannot proceed. |