Returns the value of various mathematical and physical constants.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_constant (char name, char unit)
The type double function is imsl_d_constant.
Required Arguments
char *name
(Input)
Character string containing the name of the desired constant. The
case of the character string name does not matter.
The names PI,
Pi, pI, and pi are equivalent.
Spaces and underscores are allowed and ignored.
char *unit
(Input)
Character string containing the units of the desired constant. If
NULL, then
Systθme International dUnitιs (SI) units are assumed. The case of the character
string unit does
not matter. The names METER, Meter and meter are equivalent.
unit has the
form U1*U2*...
*Um/V1/.../Vn, where Ui and Vi are the names of
basic units or are the names of basic units raised to a power. Basic units must
be separated by * or /. Powers are
indicated by ^,
as in m^2 for
m2. Examples
are, METER*KILOGRAM/SECOND,
M*KG/S, METER, or M/KG^2.
Return Value
By default, imsl_f_constant returns the desired constant. If no value can be computed, NaN is returned.
Description
The names allowed are listed in the following table. Values marked with a are exact (to machine precision). The references in the right-hand column are indicated by the code numbers: [1] for Cohen and Taylor (1986), [2] for Liepman (1964), and [3] for precomputed mathematical constants.
|
Name |
Description |
Value |
Reference |
|
Amu |
Atomic mass unit |
1.6605655 ΄ 10-27 kg |
1 |
|
ATM |
Standard atm pressure |
1.01325 ΄ 105 N/m2 |
2 |
|
AU |
Astronomical unit |
1.496 ΄ 1011 m |
|
|
Avogadro |
Avogadro's number, N |
6.022045 ΄ 1023 1/mole |
1 |
|
Boltzman |
Boltzman's constant, k |
1.380662 ΄ 10-23 J/K |
1 |
|
C |
Speed of light, c |
2.997924580 ΄ 108 m/s |
1 |
|
Catalan |
Catalan's constant |
0.915965Ό |
3 |
|
E |
Base of natural logs, e |
2.718Ό |
3 |
|
ElectronCharge |
Electron charge, e |
1.6021892 ΄ 10-19 C |
1 |
|
ElectronMass |
Electron mass, me |
9.109534 ΄ 10-31 kg |
1 |
|
ElectronVolt Euler |
ElectronVolt, ev Euler's constant, g |
1.6021892 x10 -19J 0.577Ό |
1 3 |
|
Faraday |
Faraday constant, F |
9.648456 ΄ 104 C/mole |
1 |
|
FineStructure |
Fine structure, a |
7.2973506 ΄ 10-3 |
1 |
|
Gamma |
Euler's constant, g |
0.577Ό |
3 |
|
Gas |
Gas constant, R0 |
8.31441 J/mole/K |
1 |
|
Gravity |
Gravitational constant, G |
6.6720 ΄ 10-11 N m2/kg2 |
1 |
|
Hbar |
Planck's constant/2p |
1.0545887 ΄ 10-34 J s |
1 |
|
PerfectGasVolume |
Std vol ideal gas |
2.241383 ΄ 10-2 m3/mole |
1 |
|
Pi |
Pi, p |
3.141Ό |
3 |
|
Planck |
Planck's constant, h |
6.626176 ΄ 10-34 J s |
1 |
|
ProtonMass |
Proton mass, Mp |
1.6726485 ΄ 10-27 kg |
1 |
|
Rydberg |
Rydberg's constant, R΅ |
1.097373177 ΄ 107/m |
1 |
|
Speedlight |
Speed of light, c |
2.997924580 ΄ 108 m/s |
1 |
|
StandardGravity |
Standard g |
9.80665 m/s2 |
2 |
|
StandardPressure |
Standard atm pressure |
1.01325 ΄ 105 N/m2 |
2 |
|
StefanBoltzman |
Stefan-Boltzman, s |
5.67032 ΄ 10-8W/K4/m2 |
1 |
|
WaterTriple |
Triple point of water |
2.7316 ΄ 102 K |
2 |
The units allowed are as follows:
|
Unit |
Description |
|
Time |
day, hour = hr, min, minute, s = sec = second, year |
|
Frequency |
Hertz = Hz |
|
Mass |
AMU, g = gram, lb = pound, ounce = oz, slug |
|
Distance |
Angstrom, AU, feet = foot, in = inch, m = meter = metre, micron, mile, mill, parsec, yard |
|
Area |
acre |
|
Volume |
1 = liter=litre |
|
Force |
dyne, N = Newton |
|
Energy |
BTU, Erg, J = Joule |
|
Work |
W = watt |
|
Pressure |
ATM = atmosphere, bar |
|
Temperature |
degC = Celsius, degF = Fahrenheit, degK = Kelvin |
|
Viscosity |
poise, stoke |
|
Charge |
Abcoulomb, C = Coulomb, statcoulomb |
|
Current |
A = ampere, abampere, statampere |
|
Voltage |
Abvolt, V = volt |
|
Magnetic induction |
T = Telsa, Wb = Weber |
|
Other units |
I, farad, mole, Gauss, Henry, Maxwell, Ohm |
The following metric prefixes may be used with the above units. The one or two letter prefixes may only be used with one letter unit abbreviations.
|
a |
atto |
10-18 |
|
d |
deci |
10-1 |
|
f |
femto |
10-15 |
|
dk |
deca |
102 |
|
p |
pico |
10-12 |
|
k |
kilo |
103 |
|
n |
nano |
10-9 |
|
|
myria |
104 |
|
u |
micro |
10-6 |
|
|
mega |
106 |
|
m |
milli |
10-3 |
|
g |
giga |
109 |
|
c |
centi |
10-2 |
|
t |
tera |
1012 |
There is no one letter unit abbreviation for myria or mega since m means milli.
Examples
Example 1
In this example, Eulers constant γ is obtained and printed. Eulers constant is defined to be
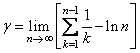
#include <stdio.h>
#include
<imsl.h>
main()
{
float
gamma;
/* Get gamma */
gamma = imsl_f_constant("gamma",
0);
/* Print gamma */
printf("gamma = %f\n", gamma);
}
Output
gamma = 0.577216
Example 2
In this example, the speed of light is obtained using several different units.
#include <stdio.h>
#include
<imsl.h>
main()
{
float
speed_light;
/* Get speed of light in meters/second */
speed_light =
imsl_f_constant("Speed Light", "meter/second");
printf("speed of light = %g meter/second\n",
speed_light);
/* Get speed of light in miles/second */
speed_light =
imsl_f_constant("Speed Light", "mile/second");
printf("speed of light = %g mile/second\n",
speed_light);
/* Get speed of light in */
/* centimeters/nanosecond */
speed_light =
imsl_f_constant("Speed Light", "cm/ns");
printf("speed of
light = %g cm/ns\n", speed_light);
}
Output
speed of light = 2.99792e+08 meter/second
speed of
light = 186282 mile/second
speed of light = 29.9793 cm/ns
Warning Errors
IMSL_MASS_TO_FORCE A conversion of units of mass to units of force was required for consistency.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |