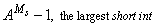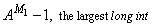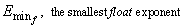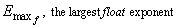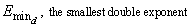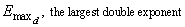Returns integer information describing the computerís arithmetic.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
int imsl_i_machine (int n)
Required Arguments
int n
(Input)
Index indicating which value is to be returned. It must be between 0
and 12.
Return Value
The requested value is returned. If n is out of range, then NaN is returned.
Description
The function imsl_i_machine returns information describing the computerís arithmetic. This can be used to make programs machine independent.
imsl_1_machine(0) = Number of bits per byte
Assume that integers are represented in M-digit, base-A form as
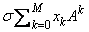
where σ is the sign and 0 ≤ xk < A for k = 0, ľ, M. Then,
|
n |
Definition |
|
0 |
C, bits per character |
|
1 |
A, the base |
|
2 |
Ms, the number of base-A digits in a short int |
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
Ml, the number of base-A digits in a long int |
|
5 |
|
Assume that floating-point numbers are represented in N-digit, base B form as
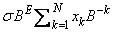
where σ is the sign and 0 ≤ xk < B for k = 1, ľ, N for and E$ ≤ E ≤ E". Then,
|
n |
Definition |
|
6 |
B, the base |
|
7 |
Nf, the number of base-B digits in float |
|
8 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
10 |
Nd, the number of base-B digits in double |
|
11 |
|
|
12 |
|
Example
This example prints all the values returned by imsl_i_machine on a machine with IEEE (Institute for Electrical and Electronics Engineer) arithmetic.
#include
<imsl.h>
main()
{
int n,
ans;
for (n = 0; n <= 12; n++)
{
ans =
imsl_i_machine(n);
printf("imsl_i_machine(%d) = %d\n", n, ans);
}
}
Output
imsl_i_machine(0) = 8
imsl_i_machine(1) =
2
imsl_i_machine(2) = 15
imsl_i_machine(3) = 32767
imsl_i_machine(4) =
31
imsl_i_machine(5) = 2147483647
imsl_i_machine(6) =
2
imsl_i_machine(7) = 24
imsl_i_machine(8) = -125
imsl_i_machine(9) =
128
imsl_i_machine(10) = 53
imsl_i_machine(11) =
-1021
imsl_i_machine(12) = 1024
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |