Computes the sample variance-covariance or correlation matrix.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_covariances (int n_observations, int n_variables, float x[], ¼, 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_covariances.
Required Arguments
int
n_observations (Input)
The number of
observations.
int
n_variables (Input)
The number of variables.
float x[]
(Input)
Array of size n_observations ´ n_variables containing
the matrix of data.
Return Value
If no optional arguments are used, imsl_f_covariances returns a pointer to an n_variables ´ n_variables matrix containing the sample variance-covariance matrix of the observations. The rows and columns of this matrix correspond to the columns of x.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_covariances (int
n_observations, int
n_variables,
float
x[],
IMSL_X_COL_DIM, int
x_col_dim,
IMSL_VARIANCE_COVARIANCE_MATRIX,
IMSL_CORRECTED_SSCP_MATRIX,
IMSL_CORRELATION_MATRIX,
IMSL_STDEV_CORRELATION_MATRIX,
IMSL_MEANS, float
**p_means,
IMSL_MEANS_USER, float
means[],
IMSL_COVARIANCE_COL_DIM, int
covariance_col_dim,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
covariance[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_X_COL_DIM, int x_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of array x.
Default: x_col_dim = n_variables
IMSL_VARIANCE_COVARIANCE_MATRIX, or
IMSL_CORRECTED_SSCP_MATRIX, or
IMSL_CORRELATION_MATRIX, or
IMSL_STDEV_CORRELATION_MATRIX
Exactly
one of these options can be used to specify the type of matrix to be
computed.
|
Keyword |
Type of Matrix |
|
IMSL_VARIANCE_COVARIANCE_MATRIX |
variance-covariance matrix (default) |
|
IMSL_CORRECTED_SSCP_MATRIX |
corrected sums of squares and crossproducts matrix |
|
IMSL_CORRELATION_MATRIX |
correlation matrix |
|
IMSL_STDEV_CORRELATION_MATRIX |
correlation matrix except for the diagonal elements which are the standard deviations |
IMSL_MEANS, float **p_means
(Output)
The address of a pointer to the array containing the means of the
variables in x.
The components of the array correspond to the columns of x. On return, the
pointer is initialized (through a memory allocation request to malloc), and the array
is stored there. Typically, float *p_means is declared;
&p_means is
used as an argument to this function; and free(p_means) is used to
free this array.
IMSL_MEANS_USER, float means[]
(Output)
Calculate the n_variables means and
store them in the memory provided by the user. The elements of means correspond to
the columns of x.
IMSL_COVARIANCE_COL_DIM, int
covariance_col_dim (Input)
The column dimension of array
covariance, if
IMSL_RETURN_USER
is specified, or the column dimension of the return value otherwise.
Default:
covariance_col_dim = n_variables
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
covariance[] (Output)
If specified, the output is stored
in the array covariance of
size n_variables ´ n_variables provided
by the user.
Description
The function imsl_f_covariances computes estimates of correlations, covariances, or sums of squares and crossproducts for a data matrix x. The means, (corrected) sums of squares, and (corrected) sums of crossproducts are computed using the method of provisional means. Let
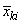
denote the mean based on i observations for the k-th variable, and let cjki denote the sum of crossproducts (or sum of squares if j = k) based on i observations. Then, the method of provisional means finds new means and sums of crossproducts as follows:
The means and crossproducts are initialized as:
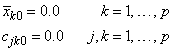
where p denotes the number of variables. Letting xk,i+1 denote the k-th variable on observation i + 1, each new observation leads to the following updates for
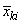
and cjki using update constant ri+1:
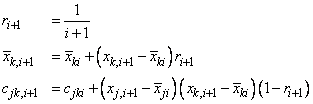
Usage Notes
The function imsl_f_covariances uses the following definition of a sample mean:
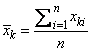
where n is the number of observations. The following formula defines the sample covariance, sj k, between variables j and k:
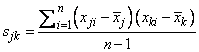
The sample correlation between variables j and k, rjk, is defined as follows:
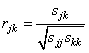
Examples
Example 1
The first example illustrates the use of imsl_f_covariances for the first 50 observations in the Fisher iris data (Fisher 1936). Note in this example that the first variable is constant over the first 50 observations.
#include <imsl.h>
#define
N_VARIABLES 5
#define N_OBSERVATIONS
50
main()
{
float *covariances;
float x[] = {1.0, 5.1, 3.5, 1.4, .2,
1.0, 4.9, 3.0, 1.4,
.2,
1.0, 4.7, 3.2, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 4.6, 3.1, 1.5,
.2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.6, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 5.4, 3.9, 1.7,
.4,
1.0, 4.6, 3.4, 1.4, .3, 1.0, 5.0, 3.4, 1.5,
.2,
1.0, 4.4, 2.9, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 4.9, 3.1, 1.5,
.1,
1.0, 5.4, 3.7, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 4.8, 3.4, 1.6,
.2,
1.0, 4.8, 3.0, 1.4, .1, 1.0, 4.3, 3.0, 1.1,
.1,
1.0, 5.8, 4.0,
1.2, .2, 1.0, 5.7, 4.4, 1.5,
.4,
1.0, 5.4, 3.9, 1.3, .4, 1.0, 5.1, 3.5, 1.4,
.3,
1.0, 5.7, 3.8, 1.7, .3, 1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.5,
.3,
1.0, 5.4, 3.4, 1.7, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.7, 1.5,
.4,
1.0, 4.6, 3.6, 1.0, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.3, 1.7,
.5,
1.0, 4.8, 3.4, 1.9, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.0, 1.6,
.2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.4, 1.6, .4, 1.0, 5.2, 3.5, 1.5,
.2,
1.0, 5.2, 3.4, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 4.7, 3.2, 1.6,
.2,
1.0, 4.8, 3.1, 1.6, .2, 1.0, 5.4, 3.4, 1.5,
.4,
1.0, 5.2, 4.1, 1.5, .1, 1.0, 5.5, 4.2, 1.4,
.2,
1.0, 4.9, 3.1, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.2, 1.2,
.2,
1.0, 5.5, 3.5, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 4.9, 3.6, 1.4,
.1,
1.0, 4.4, 3.0, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.4, 1.5,
.2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.5, 1.3, .3, 1.0, 4.5, 2.3, 1.3,
.3,
1.0, 4.4, 3.2, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.5, 1.6,
.6,
1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.9, .4, 1.0, 4.8, 3.0, 1.4,
.3,
1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.6, .2, 1.0, 4.6, 3.2, 1.4,
.2,
1.0, 5.3, 3.7, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.3, 1.4, .2};
covariances = imsl_f_covariances (N_OBSERVATIONS, N_VARIABLES, x,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix ("The default case:
variances/covariances",
N_VARIABLES, N_VARIABLES,
covariances,
IMSL_PRINT_UPPER,
0);
}
Output
The default case:
variances/covariances
1
2
3
4
5
1 0.0000
0.0000 0.0000
0.0000
0.0000
2
0.1242 0.0992
0.0164
0.0103
3
0.1437 0.0117
0.0093
4
0.0302
0.0061
5
0.0111
Example 2
This example illustrates the use of some optional arguments in imsl_f_covariances. Once again, the first 50 observations in the Fisher iris data are used.
#include <imsl.h>
#define
N_VARIABLES 5
#define N_OBSERVATIONS
50
main()
{
char *title;
float *means,
*correlations;
float
x[] = {1.0, 5.1, 3.5, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 4.9, 3.0, 1.4,
.2,
1.0, 4.7, 3.2, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 4.6, 3.1, 1.5,
.2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.6, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 5.4, 3.9, 1.7,
.4,
1.0, 4.6, 3.4, 1.4, .3, 1.0, 5.0, 3.4, 1.5,
.2,
1.0, 4.4, 2.9, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 4.9, 3.1, 1.5,
.1,
1.0, 5.4, 3.7, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 4.8, 3.4, 1.6,
.2,
1.0, 4.8, 3.0, 1.4, .1, 1.0, 4.3, 3.0, 1.1,
.1,
1.0,
5.8, 4.0, 1.2, .2, 1.0, 5.7, 4.4, 1.5,
.4,
1.0, 5.4, 3.9, 1.3, .4, 1.0, 5.1, 3.5, 1.4,
.3,
1.0, 5.7, 3.8, 1.7, .3, 1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.5,
.3,
1.0, 5.4, 3.4, 1.7, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.7, 1.5,
.4,
1.0, 4.6, 3.6, 1.0, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.3, 1.7,
.5,
1.0, 4.8, 3.4, 1.9, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.0, 1.6,
.2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.4, 1.6, .4, 1.0, 5.2, 3.5, 1.5,
.2,
1.0, 5.2, 3.4, 1.4,
.2, 1.0, 4.7, 3.2, 1.6,
.2,
1.0, 4.8, 3.1, 1.6, .2, 1.0, 5.4, 3.4, 1.5,
.4,
1.0, 5.2, 4.1, 1.5, .1, 1.0, 5.5, 4.2, 1.4,
.2,
1.0, 4.9, 3.1, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.2, 1.2,
.2,
1.0, 5.5, 3.5, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 4.9, 3.6, 1.4,
.1,
1.0, 4.4, 3.0, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.4, 1.5,
.2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.5, 1.3, .3, 1.0, 4.5, 2.3, 1.3,
.3,
1.0, 4.4, 3.2, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.5, 1.6,
.6,
1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.9, .4, 1.0, 4.8, 3.0, 1.4,
.3,
1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.6, .2, 1.0, 4.6, 3.2, 1.4,
.2,
1.0, 5.3, 3.7, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.3, 1.4, .2};
correlations = imsl_f_covariances (N_OBSERVATIONS,
N_VARIABLES-1, x+1,
IMSL_STDEV_CORRELATION_MATRIX,
IMSL_X_COL_DIM,
N_VARIABLES,
IMSL_MEANS,
&means,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Means\n", 1, N_VARIABLES-1,
means, 0);
title = "Correlations with Standard Deviations
on the Diagonal\n";
imsl_f_write_matrix (title,
N_VARIABLES-1, N_VARIABLES-1,
correlations, IMSL_PRINT_UPPER,
0);
}
Output
Means
1
2
3
4
5.006
3.428
1.462 0.246
Correlations with
Standard Deviations on the
Diagonal
1
2
3
4
1 0.3525
0.7425 0.2672
0.2781
2
0.3791 0.1777
0.2328
3
0.1737
0.3316
4
0.1054
Warning Errors
IMSL_CONSTANT_VARIABLE Correlations are requested, but the observations on one or more variables are constant. The corresponding correlations are set to NaN.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |