Evaluates the real inverse complementary error function erfc-1 (x).
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_erfc_inverse (float x)
The type double procedure is imsl_d_erfc_inverse.
Required Arguments
float x
(Input)
Point at which the inverse complementary error function is to be
evaluated. The argument x must be in the range
0 < x < 2.
Return Value
The value of the inverse complementary error function.
Description
The inverse complementary error function y = erfc-1 (x) is such that x = erfc (y) where
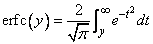

Figure 9- 4 Plot of erfc-1 (x)
Example
Evaluate the inverse complementary error function at x = 1/2.
#include
<imsl.h>
main()
{
float x = 0.5;
float ans;
ans =
imsl_f_erfc_inverse(x);
printf("inverse erfc(%f) = %f\n",
x, ans);
}
Output
inverse erfc(0.500000) = 0.476936
Alert Errors
IMSL_LARGE_ARG_UNDERFLOW The argument x must not be so large that the result underflows. Very approximately, x should be less than
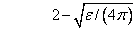
where ɛ is the machine precision.
Warning Errors
IMSL_LARGE_ARG_WARN
|x| should be less than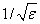 where ɛ is the machine precision, to
prevent the answer from being less accurate than half precision.
where ɛ is the machine precision, to
prevent the answer from being less accurate than half precision.
Fatal Errors
IMSL_ERF_ALGORITHM The algorithm failed to converge.
IMSL_SMALL_ARG_OVERFLOW
The computation of
must not overflow.
IMSL_REAL_OUT_OF_RANGE The function is defined only for 0 < x < 2.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |