.p>.CMCH4.DOC!FCN_DERIVATIVE;fcn_derivative
Computes the first, second, or third derivative of a user-supplied function.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_fcn_derivative (float fcn(), float x, …, 0)
The type double procedure is imsl_d_fcn_derivative.
Required Arguments
float fcn(float x)
(Input)
User-supplied function whose derivative at x will be
computed.
float x
(Input)
Point at which the derivative will be evaluated.
Return Value
An estimate of the first, second or third derivative of fcn at x. If no value can be computed, NaN is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
imsl_f_fcn_derivative (float fcn(), float x,
IMSL_ORDER, int order,
IMSL_INITIAL_STEPSIZE, float
stepize,
IMSL_RELATIVE_ERROR, float tolerance,
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA,
float fcn(), void *data,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_ORDER, int order
(Input)
The order of the desired derivative (1, 2 or 3).
Default: order = 1.
IMSL_INITIAL_STEPSIZE, float stepsize
(Input)
Beginning value used to compute the size of the interval for
approximating the derivative. Stepsize must be chosen small enough that fcn is defined and
reasonably smooth in the interval
(x - 4.0*stepsize, x + 4.0*stepsize), yet large
enough to avoid roundoff problems.
Default: stepsize = .01
IMSL_RELATIVE_ERROR, float tolerance
(Input)
The relative error desired in the derivative estimate. Convergence is
assumed when (2/3) |d2 - d1| < tolerance, for two
successive derivative estimates,
d1 and d2.
Default:
tolerance =
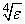
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA, float fcn
(float x, void *data), void *data (Input)
User
supplied function whose derivative at x will be computed,
which also accepts a pointer to data that is supplied by the user. data is
a pointer to the data to be passed to the user-supplied function. See the
Introduction, Passing Data
to User-Supplied Functions at the beginning of this manual for more
details.
Description
The function imsl_f_fcn_derivative
produces an estimate to the first, second, or third derivative of a
function. The estimate originates from first computing a spline interpolant to
the input function using value within the interval
(x
- 4.0*stepsize,
x +
4.0*stepsize),
then differentiating the spline at x.
Examples
Example 1
This example obtains the approximate first derivative of
the function
f(x) = -2sin(3x/2) at the point x =
2.
#include <imsl.h>
#include <math.h>
void main()
{
float fcn(float);
float x;
float deriv;
x = 2.0;
deriv = imsl_f_fcn_derivative(fcn, x,
0);
printf ("f’(x) = %7.4f\n", deriv);
}
float fcn(float x)
{
return -2.0*sin(1.5*x);
}
Output
f’(x) = 2.9701
Example 2
This example obtains the approximate first, second, and third derivative of the function f(x) = -2sin(3x/2) at the point x = 2.
#include "imsl.h"
#include <math.h>
void main()
{
double fcn(double);
double x;
double tolerance;
double deriv;
x = 2.0;
deriv =
imsl_d_fcn_derivative(fcn, x,
0);
printf ("f'(x) = %7.3f, error = %5.2e\n", deriv,
fabs(deriv+3.0*cos(1.5*x)));
deriv =
imsl_d_fcn_derivative(fcn, x,
IMSL_ORDER, 2,
0);
printf ("f''(x) = %7.4f, error = %5.2e\n", deriv,
fabs(deriv-4.5*sin(1.5*x)));
deriv =
imsl_d_fcn_derivative(fcn, x,
IMSL_ORDER, 3,
0);
printf ("f'''(x) = %7.4f, error = %5.2e\n", deriv,
fabs(deriv-6.75*cos(1.5*x)));
}
double fcn(double x)
{
return -2.0*sin(1.5*x);
}
Output
f’(x) = 2.970, error = 1.11e-07
f’’(x) = 0.6350, error = 8.52e-09
f’’’(x) = -6.6824, error = 1.12e-08
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |