.p>.CMCH2.DOC!GENEIG;geneig
Computes the generalized eigenexpansion of a system Ax = λBx, with A and B real.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
void imsl_f_geneig (int n, float *a, float *b, f_complex *alpha, float *beta, ..., 0)
The double analogue is imsl_d_geneig.
Required Arguments
int n
(Input)
Number of rows and columns in A and B.
float *a
(Input)
Array of size n × n containing the
coefficient matrix A.
float *b
(Input)
Array of size n × n containing the
coefficient matrix B.
f_complex *alpha
(Output)
Vector of size n containing scalars αi. If βi ≠ 0, λi = αi/βi for
i = 0, …, n − 1 are the eigenvalues of the
system.
float *beta
(Output)
Vector of size n.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
void
imsl_f_geneig (int
n, float *a, float *b,
IMSL_VECTORS, f_complex
**evec,
IMSL_VECTORS_USER, f_complex
evecu[],
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int
a_col_dim,
IMSL_B_COL_DIM, int
b_col_dim,
IMSL_EVECU_COL_DIM, int
evecu_col_dim,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_VECTORS,
f_complex
**evec (Output)
The address of a pointer to an array of
size n × n
containing eigenvectors of the problem. Each vector is normalized to have
Euclidean length equal to the value one. On return, the necessary space is
allocated by the function. Typically, f_complex *evec is declared, and
&evec is
used as an argument.
IMSL_VECTORS_USER, f_complex evecu[]
(Output)
Compute eigenvectors of the matrix. An array of size n × n containing the
matrix of generalized eigenvectors is returned in the space evecu. Each vector is
normalized to have Euclidean length equal to the value one.
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int a_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of A.
Default: a_col_dim =
n
IMSL_B_COL_DIM, int b_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of B.
Default: b_col_dim =
n.
IMSL_EVECU_COL_DIM, int
evecu_col_dim (Input)
The column dimension of evecu.
Default: evecu_col_dim =
n
Description
The function imsl_f_geneig uses the QZ algorithm to compute the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the generalized eigensystem Ax = λBx, where A and B are real matrices of order n. The eigenvalues for this problem can be infinite, so α and β are returned instead of λ. If β is nonzero, λ = α/β.
The first step of the QZ algorithm is to simultaneously reduce A to upper-Hessenberg form and B to upper-triangular form. Then, orthogonal transformations are used to reduce A to quasi-upper-triangular form while keeping B upper triangular. The generalized eigenvalues and eigenvectors for the reduced problem are then computed.
The function imsl_f_geneig is based on the QZ algorithm due to Moler and Stewart (1973), as implemented by the EISPACK routines QZHES, QZIT and QZVAL; see Garbow et al. (1977).
Examples
Example 1
In this example, the eigenvalue, λ, of system Ax = λBx is computed, where
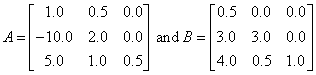
#include <imsl.h>
main()
{
int n = 3;
f_complex alpha[3];
float beta[3];
int i;
f_complex eval[3];
float a[] = {1.0, 0.5, 0.0,
-10.0, 2.0, 0.0,
5.0, 1.0, 0.5};
float b[] = {0.5, 0.0, 0.0,
3.0, 3.0, 0.0,
4.0, 0.5, 1.0};
/* Compute eigenvalues */
imsl_f_geneig
(n, a, b, alpha, beta, 0);
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
if (beta[i] != 0.0)
eval[i] = imsl_c_div(alpha[i],
imsl_cf_convert(beta[i], 0.0));
else
printf ("Infinite eigenvalue\n");
/* Print eigenvalues */
imsl_c_write_matrix ("Eigenvalues", 1, n, eval, 0);
}
Output
Eigenvalues
1 2 3
( 0.833, 1.993) ( 0.833, -1.993) ( 0.500, 0.000)
Example 2
This example finds the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the same eigensystem given in the last example.
imsl_f_geneig (n, a, b, alpha, beta,
eval[i] = imsl_c_div(alpha[i],
imsl_cf_convert(beta[i], 0.0));
printf ("Infinite eigenvalue\n");
imsl_c_write_matrix ("Eigenvalues", 1, n, eval, 0);
imsl_c_write_matrix ("Eigenvectors", n, n, evec, 0);
Output
( 0.833, 1.993) ( 0.833, -1.993) ( 0.500, -0.000)
1 ( -0.197, 0.150) ( -0.197, -0.150) ( -0.000, 0.000)
2 ( -0.069, -0.568) ( -0.069, 0.568) ( -0.000, 0.000)
3 ( 0.782, 0.000) ( 0.782, 0.000) ( 1.000, 0.000)
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |