.p>.CMCH3.DOC!SCATTERED_2D_INTERP;scattered_2d_interp
Computes a smooth bivariate interpolant to scattered data that is locally a quintic polynomial in two variables.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_scattered_2d_interp (int ndata, float xydata[], float fdata[], int nx_out, int ny_out, float x_out[], float y_out[], ¼, 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_scattered_2d_interp.
Required Arguments
int ndata
(Input)
Number of data points.
float xydata[]
(Input)
Array with ndata*2 components
containing the data points for the interpolation problem. The i-th data
point (xi, yi) is stored consecutively in the 2i
and 2i + 1 positions of xydata.
float fdata[]
(Input)
Array of size ndata containing the
values to be interpolated.
int nx_out
(Input)
Number of data points in the x direction for the output
grid.
int ny_out
(Input)
Number of data points in the y direction for the output
grid.
float x_out[]
(Input)
Array of length nx_out specifying the
x values for the output grid. It must be strictly increasing.
float y_out[]
(Input)
Array of length ny_out specifying the
y values for the output grid. It must be strictly increasing.
Return Value
A pointer to the nx_out ´ ny_out grid of values of the interpolant. If no answer can be computed, then NULL is returned. To release this space, use free.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_scattered_2d_interp (int
ndata,
float
xydata[],
float
fdata[],
int
nx_out,
int
ny_out,
float
x_out[],
float y_out[],
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
surface[],
IMSL_SUR_COL_DIM, int
surface_col_dim,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float surface[]
(Output)
This option allows the user to provide his own space for the result.
In this case, the answer will be returned in surface.
IMSL_SUR_COL_DIM, int
surface_col_dim (Input)
This option requires the user to
provide the column dimension of the two-dimensional array surface.
Default:
surface_col_dim = ny_out
Description
The function imsl_f_scattered_2d_interp computes a C1 interpolant to scattered data in the plane. Given the data points
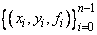
in R3 where n = ndata, imsl_f_scattered_2d_interp returns the values of the interpolant s on the user-specified grid. The computation of s is as follows: First the Delaunay triangulation of the points

is computed. On each triangle T in this triangulation, s has the form

Thus, s is a bivariate quintic polynomial on each triangle of the triangulation. In addition, we have

and s is continuously differentiable across the boundaries of neighboring triangles. These conditions do not exhaust the freedom implied by the above representation. This additional freedom is exploited in an attempt to produce an interpolant that is faithful to the global shape properties implied by the data. For more information on this procedure, refer to the article by Akima (1978). The output grid is specified by the two integer variables nx_out and ny_out that represent the number of grid points in the first (second) variable and by two real vectors that represent the first (second) coordinates of the grid.
Examples
Example 1
In this example, the interpolant
to the linear function (3 + 7x + 2y) is
computed from 20 data points equally spaced on the circle of radius 3. Then the
values are printed on a
3 ´ 3 grid.
#include <imsl.h>
#include
<stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define
NDATA 20
#define
OUTDATA
3
/*
Define function */
#define
F(x,y)
(float)(3.+7.*x+2.*y)
#define
SURF(I,J) surf[(J)
+(I)*OUTDATA]
main()
{
int
i, j;
float
fdata[NDATA], xydata[2*NDATA], *surf;
float
x, y, z,
x_out[OUTDATA], y_out[OUTDATA], pi;
pi =
imsl_f_constant("pi",
0);
/* Set up output grid */
for (i = 0; i <
OUTDATA; i++) {
x_out[i] =
y_out[i] = (float) i / ((float) (OUTDATA - 1));
}
for (i = 0; i < 2*NDATA; i += 2)
{
xydata[i] =
3.*cos(pi*i/NDATA);
xydata[i+1] =
3.*sin(pi*i/NDATA);
fdata[i/2] = F(xydata[i], xydata[i+1]);
}
/* Compute scattered data interpolant */
surf =
imsl_f_scattered_2d_interp (NDATA, xydata, fdata,
OUTDATA,
OUTDATA, x_out, y_out,
0);
/* Print results */
printf("
x
y F(x, y)
Interpolant Error\n");
for (i = 0;
i < OUTDATA; i++) {
for
(j = 0; j < OUTDATA; j++)
{
x =
x_out[i];
y =
y_out[j];
z =
SURF(i,j);
printf(" %6.3f %6.3f %10.3f %10.3f
%10.4f\n",
x, y, F(x,y),
z, fabs(F(x,y)-z));
}
}
}
Output
x
y F(x, y)
Interpolant Error
0.000
0.000
3.000
3.000 0.0000
0.000
0.500
4.000
4.000 0.0000
0.000
1.000 5.000
5.000
0.0000
0.500 0.000
6.500
6.500 0.0000
0.500
0.500
7.500
7.500 0.0000
0.500
1.000
8.500
8.500 0.0000
1.000
0.000 10.000
10.000 0.0000
1.000
0.500 11.000
11.000
0.0000
1.000 1.000
12.000
12.000 0.0000
Example 2
Recall that in the first example, the interpolant to the linear function 3 + 7x + 2y is computed from 20 data points equally spaced on the circle of radius 3. We then print the values on a 3 ´ 3 grid. This example used the optional arguments to indicate that the answer is stored noncontiguously in a two-dimensional array surf with column dimension equal to 11.
#include <imsl.h>
#include
<stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define
NDATA 20
#define
OUTDATA 3
#define
COLDIM
11
/* Define function */
#define
F(x,y)
(float)(3.+7.*x+2.*y)
main()
{
int
i, j;
float
fdata[NDATA], xydata[2*NDATA];
float
surf[OUTDATA][COLDIM];
float
x, y, z, x_out[OUTDATA], y_out[OUTDATA], pi;
pi =
imsl_f_constant("pi",
0);
/* Set up output grid */
for (i = 0; i <
OUTDATA; i++) {
x_out[i] =
y_out[i] = (float) i / ((float) (OUTDATA - 1));
}
for (i = 0; i < 2*NDATA; i += 2)
{
xydata[i] =
3.*cos(pi*i/NDATA);
xydata[i+1] =
3.*sin(pi*i/NDATA);
fdata[i/2] = F(xydata[i], xydata[i+1]);
}
/* Compute scattered data interpolant */
imsl_f_scattered_2d_interp (NDATA, xydata, fdata,
OUTDATA,
OUTDATA, x_out,
y_out,
IMSL_RETURN_USER,
surf,
IMSL_SUR_COL_DIM,
COLDIM,
0);
/* Print results */
printf("
x
y F(x, y)
Interpolant Error\n");
for (i = 0;
i < OUTDATA; i++) {
for
(j = 0; j < OUTDATA; j++)
{
x =
x_out[i];
y =
y_out[j];
z =
surf[i][j];
printf(" %6.3f %6.3f %10.3f %10.3f
%10.4f\n",
x, y, F(x,y), z, fabs(F(x,y)-z));
}
}
}
Output
x
y F(x, y)
Interpolant Error
0.000
0.000
3.000
3.000 0.0000
0.000
0.500
4.000
4.000 0.0000
0.000
1.000
5.000
5.000 0.0000
0.500
0.000
6.500
6.500 0.0000
0.500
0.500
7.500
7.500 0.0000
0.500
1.000
8.500
8.500 0.0000
1.000
0.000 10.000
10.000 0.0000
1.000
0.500 11.000
11.000 0.0000
1.000
1.000 12.000
12.000 0.0000
Fatal Errors
IMSL_DUPLICATE_XYDATA_VALUES The two-dimensional data values must be distinct.
IMSL_XOUT_NOT_STRICTLY_INCRSING The vector x_out must be strictly increasing.
IMSL_YOUT_NOT_STRICTLY_INCRSING The vector y_out must be strictly increasing.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |