Computes a two-dimensional, tensor-product spline interpolant from two-dimensional, tensor-product data.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
Imsl_f_spline *imsl_f_spline_2d_interp (int num_xdata, float xdata[], int num_ydata, float ydata[], float fdata[], ¼, 0)
The type Imsl_d_spline function is imsl_d_spline_2d_interp.
Required Arguments
int num_xdata
(Input)
Number of data points in the X direction.
float xdata[]
(Input)
Array with num_xdata components
containing the data points in the X direction.
int num_ydata
(Input)
Number of data points in the Y direction.
float ydata[]
(Input)
Array with num_ydata components
containing the data points in the Y direction.
float fdata[]
(Input)
Array of size num_xdata ´ num_ydata containing
the values to be interpolated. fdata[i][j] is the value
at (xdata[i], ydata[j]).
Return Value
A pointer to the structure that represents the tensor-product spline interpolant. If an interpolant cannot be computed, then NULL is returned. To release this space, use free.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
Imsl_f_spline
*imsl_f_spline_2d_interp (int
num_xdata,
float xdata[], int
num_ydata,
float
ydata[],
float
fdata[],
IMSL_ORDER, int
xorder,
int
yorder,
IMSL_KNOTS, float
xknots[],
float
yknots[],
IMSL_FDATA_COL_DIM, int
fdata_col_dim,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_ORDER, int xorder, int yorder
(Input)
This option is used to communicate the order of the spline
subspace.
Default: xorder, yorder = 4,
(i.e., tensor-product cubic splines)
IMSL_KNOTS, float xknots[], float yknots[]
(Input)
This option requires the user to provide the knots. The default knots
are selected by the function imsl_f_spline_knots
using its defaults.
IMSL_FDATA_COL_DIM, int
fdata_col_dim (Input)
The column dimension of the matrix
fdata.
Default: fdata_col_dim =
num_ydata
Description
The function imsl_f_spline_2d_interp computes a tensor-product spline interpolant. The tensor-product spline interpolant to data {(xj, yj, fjj)}, where 0 ≤ i ≤ nx − 1 and 0 ≤ j ≤ ny − 1 has the form
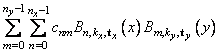
where kx and ky are the orders of the splines. These numbers are defaulted to be 4, but can be set to any positive integer using the keyword, IMSL_ORDER. Likewise, tx and ty are the corresponding knot sequences (xknots and yknots). These values are defaulted to the knots returned by imsl_f_spline_knots. The algorithm requires that
tx(kx - 1) £ xi £ tx(nx) 0 £ i £ nx - 1
ty(ky - 1) £ yj £ ty(ny - 1) 0 £ j £ ny - 1
Tensor-product spline interpolants in two dimensions can be computed quite efficiently by solving (repeatedly) two univariate interpolation problems.
The computation is motivated by the following observations. It is necessary to solve the system of equations
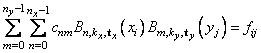
Setting
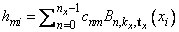
note that for each fixed i from 0 to nx − 1, we have ny linear equations in the same number of unknowns as can be seen below:
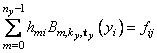
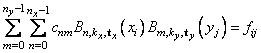
Setting
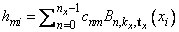
note that for each fixed i from 1 to nx − 1, we have ny − 1 linear equations in the same number of unknowns as can be seen below:
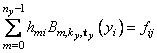
The same matrix appears in all of the equations above:
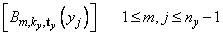
Thus, only factor this matrix once and then apply this factorization to the nx right-hand sides. Once this is done and hmi is computed, then solve for the coefficients cnm using the relation
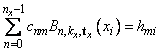
for m from 0 to ny − 1, which again involves one factorization and ny solutions to the different right-hand sides. The function imsl_f_spline_2d_interp is based on the routine SPLI2D by de Boor (1978, p. 347).
The return value for this function is a pointer to the structure imsl_f_spline. The calling program must receive this in a pointer imsl_f_spline *sp. This structure contains all the information to determine the spline (stored in B-spline format) that is computed by this procedure. For example, the following code sequence evaluates this spline at (x,y) and returns the value in z.
z = imsl_f_spline_2d_value (x, y, sp, 0);
Examples
Example 1
In this example, a tensor-product
spline interpolant to a function f is computed.
The values of the
interpolant and the error on a 4 ´ 4 grid are displayed.
#include <imsl.h>
#include
<stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define
NDATA 11
#define
OUTDATA
2
/* Define function */
#define F(x,
y)
(float)(x*x*x+y*y)
main()
{
int
i, j, num_xdata, num_ydata;
float
fdata[NDATA][NDATA], xdata[NDATA], ydata[NDATA];
float
x, y, z;
Imsl_f_spline
*sp;
/* Set up grid */
for (i = 0; i <
NDATA; i++) {
xdata[i] =
ydata[i] = (float)i / ((float)(NDATA-1));
}
for (i = 0; i < NDATA; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <
NDATA; j++)
{
fdata[i][j] = F(xdata[i],
ydata[j]);
}
}
num_xdata = num_ydata =
NDATA;
/* Compute tensor-product interpolant
*/
sp = imsl_f_spline_2d_interp(num_xdata, xdata,
num_ydata,
ydata, fdata,
0);
/* Print results */
printf("
x
y F(x,
y) Interpolant Error
\n");
for (i = 0; i < OUTDATA; i++)
{
x = (float) i / (float)
(OUTDATA);
for (j = 0; j
< OUTDATA; j++)
{
y =
(float) j / (float)
(OUTDATA);
z = imsl_f_spline_2d_value(x, y, sp,
0);
printf(" %6.3f %6.3f %10.3f %10.3f
%10.4f\n",
x, y, F(x,y), z, fabs(F(x,y)-z));
}
}
}
Output
x
y F(x, y)
Interpolant Error
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000 0.0000
0.000
0.500
0.250
0.250 0.0000
0.500
0.000
0.125
0.125 0.0000
0.500
0.500
0.375
0.375 0.0000
Example 2
Recall that in the first example, a tensor-product spline interpolant to a function f is computed. The values of the interpolant and the error on a 4 ´ 4 grid are displayed. Notice that the first interpolant with order = 3 does not reproduce the cubic data, while the second interpolant with order = 6 does reproduce the data.
#include <imsl.h>
#include
<stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define
NDATA 7
#define
OUTDATA
4
/* Define function */
#define
F(x,y)
(float)(x*x*x+y*y)
main()
{
int
i, j, num_xdata, num_ydata, order;
float
fdata[NDATA][NDATA], xdata[NDATA], ydata[NDATA];
float
x, y, z;
Imsl_f_spline
*sp;
/* Set up grid */
for (i = 0; i <
NDATA; i++) {
xdata[i] =
ydata[i] = (float) i / ((float) (NDATA - 1));
}
for (i = 0; i < NDATA; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < NDATA; j++)
{
fdata[i][j] = F(xdata[i],
ydata[j]);
}
}
num_xdata = num_ydata = NDATA;
for(order = 3; order < 7; order += 3)
{
/* Compute tensor-product interpolant
*/
sp =
imsl_f_spline_2d_interp(num_xdata, xdata,
num_ydata,
ydata, fdata,
IMSL_ORDER, order,
order,
0);
/* Print results */
printf("\nThe order
of the spline is %d \n", order);
printf(" x
y F(x, y)
Interpolant Error\n");
for (i = 0; i < OUTDATA; i++)
{
x =
(float) i / (float)
(OUTDATA);
for (j = 0; j < OUTDATA; j++)
{
y = (float) j / (float)
(OUTDATA);
z = imsl_f_spline_2d_value(x, y, sp,
0);
printf(" %6.3f %6.3f %10.3f %10.3f
%10.4f
\n",
x, y, F(x,y), z,
fabs(F(x,y)-z));
}
}
}
}
Output
The order of the spline is 3
x
y F(x, y)
Interpolant Error
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000 0.0000
0.000 0.250
0.062
0.063 0.0000
0.000 0.500
0.250
0.250 0.0000
0.000 0.750
0.562
0.562 0.0000
0.250 0.000
0.016 0.016
0.0002
0.250 0.250
0.078
0.078 0.0002
0.250 0.500
0.266
0.266 0.0002
0.250 0.750
0.578
0.578 0.0002
0.500 0.000
0.125
0.125 0.0000
0.500 0.250
0.188
0.188 0.0000
0.500 0.500
0.375
0.375 0.0000
0.500 0.750
0.688
0.687 0.0000
0.750 0.000
0.422
0.422 0.0002
0.750 0.250
0.484
0.484 0.0002
0.750 0.500
0.672
0.672 0.0002
0.750 0.750
0.984
0.984 0.0002
The order
of the spline is 6
x
y F(x, y)
Interpolant Error
0.000
0.000 0.000
0.000
0.0000
0.000
0.250
0.062
0.063 0.0000
0.000 0.500
0.250
0.250 0.0000
0.000 0.750
0.562
0.562 0.0000
0.250 0.000
0.016
0.016 0.0000
0.250 0.250
0.078
0.078 0.0000
0.250 0.500
0.266
0.266 0.0000
0.250 0.750
0.578
0.578 0.0000
0.500 0.000
0.125
0.125 0.0000
0.500 0.250
0.188
0.188 0.0000
0.500 0.500
0.375
0.375 0.0000
0.500 0.750
0.688
0.688 0.0000
0.750 0.000
0.422
0.422 0.0000
0.750 0.250
0.484 0.484
0.0000
0.750
0.500
0.672
0.672 0.0000
0.750 0.750
0.984
0.984 0.0000
Warning Errors
IMSL_ILL_COND_INTERP_PROB The interpolation matrix is ill-conditioned. The solution might not be accurate.
Fatal Errors
IMSL_XDATA_NOT_INCREASING The xdata values must be strictly increasing.
IMSL_YDATA_NOT_INCREASING The ydata values must be strictly increasing.
IMSL_KNOT_MULTIPLICITY Multiplicity of the knots cannot exceed the order of the spline.
IMSL_KNOT_NOT_INCREASING The knots must be nondecreasing.
IMSL_KNOT_DATA_INTERLACING The i-th smallest element of the data arrays xdata and ydata must satisfy ti ≤ datai < ti+order, where t is the knot sequence.
IMSL_DATA_TOO_LARGE The data arrays xdata and ydata must satisfy datai ≤ tnum_data, for i = 1, ¼, num_data.
IMSL_DATA_TOO_SMALL The data arrays xdata and ydata must satisfy datai ³ torder-1, for i = 1, ¼, num_data.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |