.p>.CMCH3.DOC!SPLINE_KNOTS;spline_knots
Computes the knots for a spline interpolant
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_spline_knots (int ndata, float xdata[], ¼, 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_spline_knots.
Required Arguments
int ndata
(Input)
Number of data points.
float xdata[]
(Input)
Array with ndata components
containing the abscissas of the interpolation problem.
Return Value
A pointer to the knots. If the knots cannot be computed, then NULL is returned. To release this space, use free.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_spline_knots (int
ndata,
float
xdata[],
IMSL_ORDER, int
order,
IMSL_OPT,
IMSL_OPT_ITMAX, int
itmax,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
knots[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_ORDER, int order
(Input)
The order of the spline subspace for which the knots are desired.
This option is used to communicate the order of the spline subspace.
Default:
order = 4,
i.e., cubic splines
IMSL_OPT
This
option produces knots that satisfy an optimality criterion.
IMSL_OPT_ITMAX, int itmax
(Input)
This option allows the user to set the maximum number of iterations
of Newton’s method.
Default: itmax = 10
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float knots[]
(Output)
This option requires the user to provide the space for the return
knots. For example, the user could declare float knots[100]; and pass
in knots.
The return value is then also set to knots.
Description
Given the data points x = xdata, the order of the spline k = order, and the number n = ndata of elements in xdata, the default action of imsl_f_spline_knots returns a pointer to a knot sequence that is appropriate for interpolation of data on x by splines of order k (the default order is k = 4). The knot sequence is contained in its first n + k positions. If k is even, and we assume that the entries in the input vector x are increasing, then the resulting knot sequence t is returned as
tj = x0 for i = 0, …, k - 1
tj = xj-k/2-1 for i = k, …, n - 1
tj = xn-1 for i = n, …, n + k - 1
There is some discussion concerning this selection of knots in de Boor (1978, p. 211). If k is odd, then t is returned as
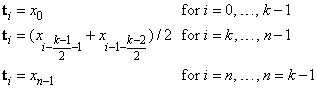
It is not necessary to sort the values in xdata.
If the option IMSL_OPT is selected, then the knot sequence returned minimizes the constant c in the error estimate
||f - s|| £ c|| f (k)||
In the above formula, f is any function in Ck, and s is the spline interpolant to f at the abscissas x with knot sequence t.
The algorithm is based on a routine described in de Boor (1978, p. 204), which in turn is based on a theorem of Micchelli et al. (1976).
Examples
Example 1
In this example, knots for a cubic spline are generated and printed. Notice that the knots are stacked at the endpoints and that the second and next to last data points are not knots.
#include <imsl.h>
#include
<stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define NDATA
6
main()
{
int i;
float *knots,
xdata[NDATA];
for(i = 0; i < NDATA;
i++)
xdata[i] =
i;
knots = imsl_f_spline_knots(NDATA, xdata,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("The knots for the cubic spline
are:\n",
1, NDATA+4, knots,
IMSL_COL_NUMBER_ZERO,
0);
}
Output
The knots for the cubic spline are:
0
1
2
3
4
5
0
0
0
0
2
3
6
7
8
9
5
5
5 5
Example 2
This is a continuation of the examples for imsl_f_spline_interp. Recall that in these examples, a cubic spline interpolant to a function f is computed first. The values of this spline are then compared with the exact function values. The second example uses a quadratic (k = 3) and a quintic (k = 6) spline interpolant to the data. Now, instead of using the default knots, select the “optimal” knots as described above. Notice that the error is actually worse in this case.
#include <imsl.h>
#include
<stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define NDATA
11
/* Define function */
#define F(x)
(float)(sin(15.0*x))
main()
{
int
i, order;
float
fdata[NDATA], xdata[NDATA], *knots, x, y;
Imsl_f_spline
*sp;
/* Set up a grid */
for (i = 0; i < NDATA;
i++) {
xdata[i] = (float)i
/((float)(NDATA-1));
fdata[i] =
F(xdata[i]);
}
for(order = 3;
order < 7; order += 3) {
knots = imsl_f_spline_knots(NDATA, xdata, IMSL_ORDER,
order,
IMSL_OPT,
0);
/* Compute spline interpolant */
sp = imsl_f_spline_interp (NDATA, xdata,fdata,
IMSL_ORDER,
order,
IMSL_KNOTS,
knots,
0);
/* Print results */
printf("\nThe
order of the spline is %d\n",
order);
printf("
x
F(x) Interpolant
Error\n");
for (i = NDATA/2;
i < 3*NDATA/2; i++)
{
x =
(float) i
/(float)(2*NDATA-2);
y = imsl_f_spline_value(x, sp,
0);
printf(" %6.3f %10.3f %10.3f %10.4f\n", x,
F(x),
y,
fabs(F(x)-y));
}
}
}
Output
The order of the spline is 3
x
F(x) Interpolant
Error
0.250
-0.572
-0.543 0.0290
0.300 -0.978
-0.978 0.0000
0.350 -0.859
-0.819 0.0401
0.400 -0.279
-0.279 0.0000
0.450
0.450
0.429 0.0210
0.500
0.938
0.938 0.0000
0.550
0.923
0.879 0.0433
0.600
0.412
0.412 0.0000
0.650 -0.320
-0.305 0.0150
0.700 -0.880
-0.880 0.0000
0.750 -0.968
-0.920 0.0478
The order of the spline
is 6
x
F(x) Interpolant
Error
0.250
-0.572
-0.578 0.0061
0.300 -0.978
-0.978 0.0000
0.350 -0.859
-0.854 0.0054
0.400 -0.279
-0.279 0.0000
0.450 0.450
0.448 0.0019
0.500
0.938
0.938 0.0000
0.550
0.923
0.920 0.0022
0.600
0.412
0.412 0.0000
0.650 -0.320
-0.317 0.0020
0.700 -0.880
-0.880 0.0000
0.750 -0.968
-0.966 0.0023
Warning Errors
IMSL_NO_CONV_NEWTON Newton’s method iteration did not converge.
Fatal Errors
IMSL_DUPLICATE_XDATA_VALUES The xdata values must be distinct.
IMSL_ILL_COND_LIN_SYS Interpolation matrix is singular. The xdata values may be too close together.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |