.p>.CMCH3.DOC!SPLINE_2D_LEAST_SQUARES;spline_2d_least_squares
Computes a two-dimensional, tensor-product spline approximant using least squares.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
Imsl_f_spline *imsl_f_spline_2d_least_squares (int num_xdata, float xdata[], int num_ydata, float ydata[], float fdata[], int x_spline_space_dim, int y_spline_space_dim, ¼, 0)
The type Imsl_d_spline function is imsl_d_spline_2d_least_squares.
Required Arguments
int num_xdata
(Input)
Number of data points in the X direction.
float xdata[]
(Input)
Array with num_xdata components
containing the data points in the X direction.
int num_ydata
(Input)
Number of data points in the Y direction.
float ydata[]
(Input)
Array with num_ydata components
containing the data points in the Y direction.
float fdata[]
(Input)
Array of size num_xdata ´ num_ydata containing
the values to be approximated. fdata[i][j] is the (possibly
noisy) value at (xdata[i], ydata[j]).
int
x_spline_space_dim (Input)
The linear dimension of the
spline subspace for the x variable. It should be smaller than num_xdata and greater
than or equal to xorder (whose default
value is 4).
int
y_spline_space_dim (Input)
The linear dimension of the
spline subspace for the y variable. It should be smaller than num_ydata and greater
than or equal to yorder (whose default
value is 4).
Return Value
A pointer to the structure that represents the tensor-product spline interpolant. If an interpolant cannot be computed, then NULL is returned. To release this space, use free.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
Imsl_f_spline
*imsl_f_spline_2d_least_squares (int
num_xdata, float
xdata[],
int
num_ydata,
float
ydata[],
float fdata[], int
x_spline_space_dim, int
y_spline_space_dim,
IMSL_SSE, float
*sse,
IMSL_ORDER, int
xorder,
int
yorder,
IMSL_KNOTS, float
xknots[],
float
yknots[],
IMSL_FDATA_COL_DIM, int
fdata_col_dim,
IMSL_WEIGHTS, float
xweights[],
float
yweights[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_SSE, float *sse
(Output)
This option places the weighted error sum of squares in the place
pointed to by sse.
IMSL_ORDER, int xorder, int yorder
(Input)
This option is used to communicate the order of the spline
subspace.
Default: xorder, yorder = 4
(i.e., tensor-product cubic splines)
IMSL_KNOTS, float xknots[], float yknots[]
(Input)
This option requires the user to provide the knots.
Default: The
default knots are equally spaced in the x and y dimensions.
IMSL_FDATA_COL_DIM, int
fdata_col_dim (Input)
The column dimension of fdata.
Default:
fdata_col_dim = num_ydata
IMSL_WEIGHTS, float xweights[], float
yweights[] (Input)
This option requires the user to
provide the weights for the least-squares fit.
Default: all weights are
equal to 1.
Description
The imsl_f_spline_2d_least_squares procedure computes a tensor-product spline least-squares approximation to weighted tensor-product data. The input for this function consists of data vectors to specify the tensor-product grid for the data, two vectors with the weights (optional, the default is 1), the values of the surface on the grid, and the specification for the tensor-product spline (optional, a default is chosen). The grid is specified by the two vectors x = xdata and y = ydata of length n = num_xdata and m = num_ydata, respectively. A two-dimensional array f = fdata contains the data values which are to be fit. The two vectors wx = xweights and wy = yweights contain the weights for the weighted least-squares problem. The information for the approximating tensor-product spline can be provided using the keywords IMSL_ORDER and IMSL_KNOTS. This information is contained in kx = xorder, tx = xknots, and N = xspline_space_dim for the spline in the first variable, and in ky = yorder, ty = yknots and M = y_spline_space_dim for the spline in the second variable.
This function computes coefficients for the tensor-product spline by solving the normal equations in tensor-product form as discussed in de Boor (1978, Chapter 17). The interested reader might also want to study the paper by Grosse (1980).
As the computation proceeds, we obtain coefficients c minimizing
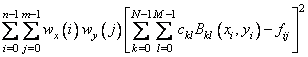
where the function Bkl is the tensor-product of two B-splines of order kx and ky. Specifically, we have
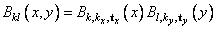
The spline
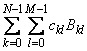
and its partial derivatives can be evaluated using imsl_f_spline_2d_value.
The return value for this
function is a pointer to the structure Imsl_f_spline. The
calling
program must receive this in a pointer of type Imsl_f_spline. This
structure contains all the information to determine the spline that is computed
by this
procedure. For example, the following code sequence evaluates this
spline
(stored in the structure sp at (x,
y) and returns the value in v.
v = imsl_f_spline_2d_value (x, y, sp, 0)
Examples
Example 1
The data for this example comes
from the function ex sin (x + y) on
the rectangle
[0, 3] ´ [0, 5]. This
function is sampled on a 50 ´ 25 grid. Next try to recover it by
using tensor-product cubic splines. The values of the function ex sin
(x + y) are printed on a 2 ´ 2 grid and compared with the values of
the tensor-product spline least-squares fit.
#include <imsl.h>
#include
<stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define
NXDATA 50
#define
NYDATA 25
#define
OUTDATA
2
/* Define function */
#define
F(x,y)
(float)(exp(x)*sin(x+y))
main()
{
int
i, j, num_xdata, num_ydata;
float
fdata[NXDATA][NYDATA];
float
xdata[NXDATA], ydata[NYDATA], x, y, z;
Imsl_f_spline
*sp;
/* Set up grid */
for (i = 0; i <
NXDATA; i++) {
xdata[i] =
3.*(float) i / ((float)(NXDATA-1));
}
for (i = 0; i < NYDATA; i++)
{
ydata[i] = 5.*(float) i /
((float)(NYDATA-1));
}
/* Compute function values on grid */
for (i =
0; i < NXDATA; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <
NYDATA; j++)
{
fdata[i][j] = F(xdata[i],
ydata[j]);
}
}
num_xdata = NXDATA;
num_ydata =
NYDATA;
/* Compute tensor-product interpolant */
sp =
imsl_f_spline_2d_least_squares(num_xdata, xdata,
num_ydata,
ydata,
fdata, 5, 7,
0);
/* Print results */
printf("
x
y F(x, y) Fitted
Values Error\n");
for (i = 0; i
< OUTDATA; i++) {
x =
(float)i / (float)(OUTDATA);
for
(j = 0; j < OUTDATA; j++)
{
y =
(float)j /
(float)(OUTDATA);
z = imsl_f_spline_2d_value(x, y, sp,
0);
printf(" %6.3f %6.3f %10.3f %10.3f
%10.4f\n",
x, y, F(x, y), z, fabs(F(x,y)-z));
}
}
}
Output
x
y F(x, y) Fitted
Values Error
0.000
0.000
0.000
-0.020 0.0204
0.000
0.500
0.479
0.500 0.0208
0.500
0.000
0.790
0.816 0.0253
0.500
0.500
1.387
1.384 0.0031
Example 2
The same data is used as in the previous example. Optional argument IMSL_SSE is used to return the error sum of squares.
#include <imsl.h>
#include
<stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define
NXDATA 0 50
#define
NYDATA 25
#define
OUTDATA
2
/* Define function */
#define
F(x,y)
(float)(exp(x)*sin(x+y))
main()
{
int
i, j, num_xdata, num_ydata;
float
fdata[NXDATA][NYDATA];
float
xdata[NXDATA], ydata[NYDATA], x, y, z;
Imsl_f_spline
*sp;
/* Set up grid */
for (i = 0; i <
NXDATA; i++) {
xdata[i] =
3.*(float) i / ((float) (NXDATA - 1));
}
for (i = 0; i < NYDATA; i++)
{
ydata[i] = 5.*(float) i /
((float) (NYDATA - 1));
}
/* Compute function values on grid */
for (i =
0; i < NXDATA; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <
NYDATA; j++)
{
fdata[i][j] = F(xdata[i],
ydata[j]);
}
}
num_xdata = NXDATA;
num_ydata =
NYDATA;
/* Compute tensor-product interpolant */
sp =
imsl_f_spline_2d_least_squares(num_xdata, xdata,
num_ydata,
ydata,
fdata, 5, 7,
IMSL_SSE,
&x,
0);
/* Print results */
printf("The error sum of squares is
%10.3f\n\n", x);
printf("
x
y F(x, y) Fitted
Values Error\n");
for (i = 0; i
< OUTDATA; i++) {
x =
(float) i / (float) (OUTDATA);
for
(j = 0; j < OUTDATA; j++)
{
y =
(float) j / (float)
(OUTDATA);
z = imsl_f_spline_2d_value(x, y, sp,
0);
printf(" %6.3f %6.3f %10.3f %10.3f
%10.4f\n",
x, y, F(x,y), z, fabs(F(x,y)-z));
}
}
}
Output
The error sum of squares is
3.753
x
y F(x, y) Fitted
Values Error
0.000
0.000
0.000
-0.020 0.0204
0.000
0.500
0.479
0.500 0.0208
0.500
0.000
0.790
0.816 0.0253
0.500
0.500
1.387
1.384 0.0031
Warning Errors
IMSL_ILL_COND_LSQ_PROB The least-squares matrix is ill-conditioned. The solution might not be accurate.
IMSL_SPLINE_LOW_ACCURACY There may be less than one digit of accuracy in the least-squares fit. Try using a higher precision if possible.
Fatal Errors
IMSL_KNOT_MULTIPLICITY Multiplicity of the knots cannot exceed the order of the spline.
IMSL_KNOT_NOT_INCREASING The knots must be nondecreasing.
IMSL_SPLINE_LRGST_ELEMNT
The data arrays xdata and ydata must satisfy
datai ≤ tspline_space_dim,
for i = 1,
¼,
num_data.
IMSL_SPLINE_SMLST_ELEMNT The data arrays xdata and ydata must satisfy datai ³ torder-1, for i = 1, ¼, num_data.
IMSL_NEGATIVE_WEIGHTS All weights must be greater than or equal to zero.
IMSL_DATA_DECREASING The xdata values must be nondecreasing.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |