.p>.CMCH7.DOC!ZEROS_FCN;zeros_fcn
Finds the real zeros of a real function using Müller’s method.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_zeros_fcn (float fcn(), ¼, 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_zeros_fcn.
Required Arguments
float fcn
(float
x) (Input/Output)
User-supplied function to compute the
value of the function of which the zeros will be found, where x is the point at
which the function is evaluated.
Return Value
A pointer to the zeros x of the function. To release this space, use free. If no zeros can be found, then NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_zeros_fcn (float
fcn(),
IMSL_XGUESS, float
xguess[],
IMSL_NUM_ROOTS, int
nroot,
IMSL_ERR_ABS, float
err_abs,
IMSL_ERR_REL, float
err_rel,
IMSL_ETA, float
eta,
IMSL_EPS, float
eps,
IMSL_MAX_ITN, int
max_itn,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
x[],
IMSL_INFO, int
**info,
IMSL_INFO_USER, int
info[],
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA, float
fcn (
),
void *data,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_XGUESS, float xguess[]
(Input)
Array with nroot components
containing the initial guesses for the zeros.
Default: xguess = 0
IMSL_NUM_ROOTS, int nroot
(Input)
The number of zeros to be found by imsl_f_zeros_fcn.
Default:
nroot = 1
IMSL_ERR_ABS, float err_abs
(Input)
First stopping criterion. A zero xi is accepted if
|f(xi)| < err_abs.
Default:
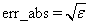
where e is the machine precision
IMSL_ERR_REL, float err_rel
(Input)
Second stopping criterion. A zero xi is accepted if
the relative change of two successive approximations to xi is less than
err_rel.
Default:
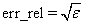
where ɛ is the machine precision
IMSL_ETA, float eta
(Input)
Spread criteria for multiple zeros. If the zero xi has been computed
and
|xi − xj| < eps, where xj is a previously
computed zero, then the computation is restarted with a guess equal to
xi + eta.
Default: eta = 0.01
IMSL_EPS, float eps
(Input)
See eta.
Default:
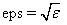
where ɛ is the machine precision
IMSL_MAX_ITN, int max_itn
(Input)
The maximum allowable number of iterations per zero.
Default:
max_itn = 100
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float x[]
(Output)
Array with nroot components
containing the computed zeros.
IMSL_INFO, int **info
(Output)
The address of a pointer info to an array of
length nroot
containing convergence information. On return, the necessary space is allocated
by imsl_f_zeros_fcn. The
value info[j − 1] is the number of
iterations used in finding the j-th zero when convergence is achieved. If
convergence is not obtained in max_itn iterations,
info[j − 1] would be greater
than max_itn.
IMSL_INFO_USER, int info[]
(Output)
A user-allocated array with nroot components. On
return, the value
info[j − 1] is the number of
iterations used in finding the j-th zero when convergence is achieved. If
convergence is not obtained in max_itn iterations,
info[j − 1] would be greater
than max_itn.
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA, float fcn
(float
x,
void
*data) , void *data (Input)
User
supplied function to compute the value of the function of which the zeros will
be found, which also accepts a pointer to data that is supplied by the
user. data
is a pointer to the data to be passed to the user-supplied function.
See the Introduction,
Passing Data to User-Supplied Functions at the beginning of this manual
for more details.
Description
The function imsl_f_zeros_fcn computes n real zeros of a real function f. Given a user-supplied function f(x) and an n-vector of initial guesses x1, x2, ¼, xn, the function uses Müller’s method to locate n real zeros of f. The function has two convergence criteria: the first requires that
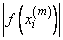
be less than err_abs; the second requires that the relative change of any two successive approximations to an xi be less than err_rel. Here,
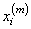
is the m-th approximation to xi. Let err_abs be denoted by ɛ1 and err_rel be denoted by ɛ2. The criteria may be stated mathematically as follows:
Criterion 1:
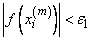
Criterion 2:
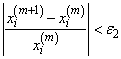
“Convergence” is the satisfaction of either criterion.
Examples
Example 1
This example finds a real zero of the third-degree polynomial
f(x) = x3 − 3x2 + 3x − 1
#include
<imsl.h>
float
fcn(float x);
main()
{
float
*x;
/* Solve fcn(x)=0 for x */
x =
imsl_f_zeros_fcn (fcn,
0);
/* Print x */
imsl_f_write_matrix ("x", 1, 1, x,
0);
}
float fcn(float x)
{
return x * x
* x - 3.0 * x * x + 3.0 * x - 1.0;
}
Output
x
1
Example 2
This example finds three real zeros of the third-degree polynomial
f(x) = x3 + 3x2 − 4x − 6
with the three initial guesses (4.6, 0.0, −193.3).
#include
<imsl.h>
float
fcn(float x);
main()
{
float xguess[ ] = {4.6, 0.0,
-193.3};
int nroot =
3;
float eps =
1.0e-5;
float err_abs
= 1.0e-5;
float
err_rel = 1.0e-5;
float eta = 1.0e-2;
int max_itn =
100;
float
*x;
/* Solve fcn(x)=0 for x */
x =
imsl_f_zeros_fcn
(fcn,
IMSL_XGUESS,
xguess,
IMSL_ERR_REL,
err_rel,
IMSL_ERR_ABS,
err_abs,
IMSL_ETA,
eta,
IMSL_EPS,
eps,
IMSL_NUM_ROOTS,
nroot,
IMSL_MAX_ITN,
max_itn,
0);
/* Print x */
imsl_f_write_matrix ("x", 1, 3, x,
0);
}
float fcn(float x)
{
return x * x
* x + 3.0 * x * x - 4.0 * x - 6.0;
}
Output
x
1
2
3
1.646
-1.000 -3.646
In the following plot, the initial guesses
x = 0.0 and x = 4.6 are marked with hollow
circles, and the solutions are marked with filled circles. The other initial
guess
x = −193.3 does not fit on this
plot.
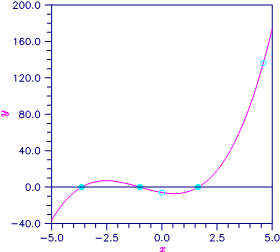
Figure 7- 1 Plot of x3 + 3x2 − 4x − 6
Warning Errors
IMSL_NO_CONVERGE_MAX_ITER Failure to converge within max_itn iterations for at least one of the nroot roots.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |