.p>.CMCH7.DOC!ZEROS_SYS_EQN;zeros_sys_eqn
Solves a system of n nonlinear equations f(x) = 0 using a modified Powell hybrid algorithm.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_zeros_sys_eqn (void fcn(), int n, ¼, 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_zeros_sys_eqn.
Required Arguments
void fcn (int n, float x[], float f[])
(Input/Output)
User-supplied function to evaluate the system of equations to
be solved, where n is the size of x and f, x is the point at
which the functions are evaluated, and f contains the
computed function values at the point x.
int n
(Input)
The number of equations to be solved and the number of unknowns.
Return Value
A pointer to the vector x that is a solution of the system of equations. To release this space, use free. If no solution can be computed, then NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_zeros_sys_eqn (void
fcn(),
int
n,
IMSL_XGUESS, float
xguess[],
IMSL_JACOBIAN, void
jacobian(),
IMSL_ERR_REL, float
err_rel,
IMSL_MAX_ITN, int
max_itn,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
x[],
IMSL_FNORM, float
*fnorm,
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA,
void
fcn ( ),
void *data,
IMSL_JACOBIAN_W_DATA, void
jacobian(),
void *data,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_XGUESS, float xguess[]
(Input)
Array with n components containing the initial estimate of the
root.
Default: xguess = 0
IMSL_JACOBIAN, void jacobian
(int
n,
float
x[],
float
fjac[]) (Input/Output)
User-supplied function to evaluate
the Jacobian, where n is the number of
components in x,
x is the point
at which the Jacobian is evaluated, and fjac is the computed
n ´ n Jacobian
matrix at the point x. Note that each
derivative
¶fi ∕ ¶xj should be returned in fjac[(i-1)*n+j-1].
IMSL_ERR_REL, float err_rel
(Input)
Stopping criterion. The root is accepted if the relative error
between two successive approximations to this root is less than err_rel.
Default:
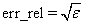
where ɛ is the machine precision
IMSL_MAX_ITN, int max_itn
(Input)
The maximum allowable number of iterations.
Default: max_itn = 200
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float x[]
(Output)
Array with n components
containing the best estimate of the root found by f_zeros_sys_eqn.
IMSL_FNORM, float *fnorm
(Output)
Scalar with the value
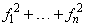
at the point x.
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA, void fcn (int n, float x[], float f[] , void *data) , void
*data
(Input)
User supplied function to evaluate the system of equations to be
solved, which also accepts a pointer to data that is supplied by the user.
data is a
pointer to the data to be passed to the user-supplied function. See the
Introduction, Passing Data
to User-Supplied Functions at the beginning of this manual for more
details.
IMSL_JACOBIAN_W_DATA, void jacobian
(int
m,
int
n,
float
x[],
float
fjac[], int fjac_col_dim, void *data),
void
*data (Input)
User supplied function to compute the Jacobian,
which also accepts a pointer to data that is supplied by the user. data is a pointer to
the data to be passed to the user-supplied function. See the Introduction, Passing Data to
User-Supplied Functions at the beginning of this manual for more
details.
Description
The function imsl_f_zeros_sys_eqn is based on the MINPACK subroutine HYBRDJ, which uses a modification of the hybrid algorithm due to M.J.D. Powell. This algorithm is a variation of Newton’s method, which takes precautions to avoid undesirable large steps or increasing residuals. For further description, see Moré et al. (1980).
Examples
Example 1
The following 2 ´ 2 system of nonlinear equations
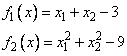
is solved.
#include <imsl.h>
#include
<stdio.h>
#define N
2
void
fcn(int, float[], float[]);
void
main()
{
float
*x;
x = imsl_f_zeros_sys_eqn(fcn, N,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("The solution to the system is",
1, N, x, 0);
}
void fcn(int n, float x[], float
f[])
{
f[0] = x[0] + x[1] - 3.0;
f[1] = x[0]*x[0] + x[1] * x[1] - 9.0;
}
Output
The solution to the system
is
1
2
0 3
Example 2
The following 3 ´ 3 system of nonlinear equations

is solved with the initial guess (4.0, 4.0, 4.0).
#include <imsl.h>
#include
<stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define
N
3
void
fcn(int, float[], float[]);
void main()
{
int maxitn =
100;
float *x, err_rel
= 0.0001, fnorm;
float
xguess[N] = {4.0, 4.0, 4.0};
x =
imsl_f_zeros_sys_eqn(fcn,
N,
IMSL_ERR_REL,
err_rel,
IMSL_MAX_ITN,
maxitn,
IMSL_XGUESS, xguess,
IMSL_FNORM, &fnorm,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("The solution to the system is", 1, N, x,
0);
printf("\nwith fnorm = %5.4f\n",
fnorm);
}
void fcn(int n, float x[], float
f[])
{
f[0] = x[0] + exp(x[0] - 1.0) + (x[1] + x[2]) *
(x[1] + x[2]) - 27.0;
f[1] = exp(x[1] - 2.0) / x[0] + x[2]
* x[2] - 10.0;
f[2] = x[2] + sin(x[1] - 2.0) + x[1] * x[1]
- 7.0;
}
Output
The solution to the system
is
1
2
3
1
2 3
with
fnorm = 0.0000
Warning Errors
IMSL_TOO_MANY_FCN_EVALS The number of function evaluations has exceeded max_itn. A new initial guess may be tried.
IMSL_NO_BETTER_POINT Argument err_rel is too small. No further improvement in the approximate solution is possible.
IMSL_NO_PROGRESS The iteration has not made good progress. A new initial guess may be tried.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |