Analyzes a completely nested random model with possibly unequal numbers in the subgroups.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float *imsls_f_anova_nested (int n_factors, int equal_option, int n_levels[], float y[], ..., 0)
The type double function is imsls_d_anova_nested.
Required Arguments
int n_factors
(Input)
Number of factors (number of subscripts) in the model, including
error.
int equal_option
(Input)
Equal numbers option.
equal_option Description
0 Unequal numbers in the subgroups
1 Equal numbers in the subgroups
int n_levels[]
(Input)
Array with the number of
levels.
If equal_option = 1, n_levels is of length n_factors and contains the number of levels for each of the factors. In this case, the following additional variables are referred to in the description of anova_nested:
Variable Description
LNL n_levels[0] + n_levels[0] * n_levels[1] + ... + n_levels[0] * n_levels[1] * ... * n_levels[n_factors – 2]
LNLNF n_levels[0] * n_levels[1] * ...* n_levels[n_factors – 2]
NOBS The number of observations. NOBS equals n_levels[0] * n_levels[1] * ... * n_levels[n_factors-1].
If equal_option = 0, n_levels contains the number of levels of each factor at each level of the factor in which it is nested. In this case, the following additional variables are referred to in the description of anova_nested:
Variable Description
LNL Length of n_levels.
LNLNF Length of the subvector of n_levels for the last factor.
NOBS Number of observations. NOBS equals the sum of the last LNLNF elements of n_levels.
For example, a random one-way model with two groups, five responses in the first
group and ten in the second group, would have LNL= 3, LNLNF= 2, NOBS = 15,
n_levels[0] = 2, n_levels[1] = 5, and
n_levels[2] =
10.
float y[]
(Input)
Array of length NOBS containing the
responses. The elements of Y are ordered
lexicographically, i.e., the last model subscript changes most rapidly, the next
to last model subscript changes the next most rapidly, and so forth, with the
first subscript changing the slowest.
Return Value
The p-value for the F-statistic, anova_table[9].
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
float * imsls_f_anova_nested (int n_factors, int equal_option, int n_levels[], float y[],
IMSLS_ANOVA_TABLE, float **anova_table,
IMSLS_ANOVA_TABLE_USER,
float
anova_table[]
IMSLS_CONFIDENCE, float
confidence, IMSLS_VARIANCE_COMPONENTS, float
**variance_components,
IMSLS_VARIANCE_COMPONENTS_USER, float
variance_components[],
IMSLS_EMS, float
**expect_mean_sq,
IMSLS_EMS_USER, float
expect_mean_sq[],
IMSLS_Y_MEANS, float
**y_means,
IMSLS_Y_MEANS_USER, float y_means[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_ANOVA_TABLE,
float **anova_table,
(Output)
Address of a pointer to an internally allocated array of size 15
containing the analysis of variance table. The analysis of variance
statistics are as follows:
Element Analysis of Variance Statistics
0 Degrees of freedom for the model
1 Degrees of freedom for error
2 Total (corrected) degrees of freedom
3 Sum of squares for the model
4 Sum of squares for error
5 Total (corrected) sum of squares
6 Model mean square
7 Error mean square
8 Overall F-statistic
9 p-value
10 R2 (in percent)
11 Adjusted R2 (in percent)
12 Estimate of the standard deviation
13 Overall mean of y
14 Coefficient of variation (in percent)
IMSLS_ANOVA_TABLE_USER,
float anova_table[]
(Output)
Storage for array anova_table is provided by the user.
See IMSLS_ANOVA_TABLE.
IMSLS_CONFIDENCE,
float confidence
(Input)
Confidence level for two-sided interval estimates on the variance
components, in percent. confidence
percent confidence intervals are computed, hence, confidence must be in
the interval
[0.0,
100.0). confidence often will be 90.0, 95.0,
or 99.0.
For one-sided intervals with confidence level ONECL, ONECL in the
interval [50.0, 100.0),
set
confidence = 100.0 - 2.0 * (100.0 - ONECL).
Default: confidence
= 95.0
IMSLS_VARIANCE_COMPONENTS, float **variance_components, (Output) Address to a pointer to an internally allocated array. variance_components is an n_factors by 9 matrix containing statistics relating to the particular variance components in the model. Rows of variance_components correspond to the n_factors factors. Columns of variance_components are as follows:
Column Description
1 Degrees of freedom
2 Sum of squares
3 Mean squares
4 F -statistic
5 p-value for F test
6 Variance component estimate
7 Percent of variance of variance explained by variance component
8 Lower endpoint for a confidence interval on the variance component
9 Upper endpoint for a confidence interval on the variance component
A test for the error variance equal to zero cannot be performed. variance_components(n_factors, 4) and variance_components(n_factors, 5) are set to NaN (not a number).
IMSLS_VARIANCE_COMPONENTS_USER, float variance_components[] (Output) Storage for array variance_components is provided by the user. See IMSLS_VARIANCE_COMPONENTS.
IMSLS_EMS,
float
**expect_mean_sq,
(Output)
Address
to a pointer to an internally allocated array of length
with expected mean
square
coefficients.
IMSLS_EMS_USER,
float expect_mean_sq[],
(Output)
Storage
for array expect_mean_sq is
provided by the user.
See IMSLS_EMS.
IMSLS_Y_MEANS,
float **y_means
(Output)
Address to a pointer to an internally allocated array containing the
subgroup means.
Equal options Length of y means
0 1 + n_levels[0] + n_levels[1] + … n_levels[(LNL - LNLNF)-1] (See the description of argument n_levels for definitions of LNL and LNLNF.)
1 1 + n_levels[0] + n_levels[0] * n_levels[1] + … + n_levels[0]* n_levels[1] * … * n_levels[n_factors – 2]
If the factors are labeled A, B, C, and error, the ordering of the means is grand mean, A means, AB means, and then ABC means.
IMSLS_Y_MEANS_USER,
float y_means[], Storage for
array y_means
is provided by the user. See IMSLS_Y_MEANS
Description
Routine imsls_f_anova_nested
analyzes a nested random model with equal or unequal numbers in the
subgroups. The analysis includes an analysis of variance table and computation
of subgroup means and variance component estimates. Anderson and Bancroft (1952,
pages 325−330)
discuss the methodology. The analysis of variance method is used for estimating
the variance components. This method solves a linear system in which the mean
squares are set to the expected mean squares. A problem that Hocking (1985,
pages
324−330)
discusses is that this method can yield negative variance component
estimates. Hocking suggests a diagnostic procedure for locating the cause
of a negative estimate. It may be necessary to reexamine the assumptions of the
model.
Example 1
An analysis of a three-factor nested random model with
equal numbers in the subgroups is performed using data discussed by Snedecor and
Cochran (1967, Table 10.16.1, pages 285−288).
The responses are calcium concentrations
(in percent, dry basis) as measured
in the leaves of turnip greens. Four plants are taken at random, then three
leaves are randomly selected from each plant.
Finally, from each selected
leaf two samples are taken to determine calcium concentration. The model is
yijk = m + ai + bij + eijk i = 1, 2, 3, 4; j = 1, 2, 3; k = 1, 2
where yijk is the calcium
concentration for the k-th sample of the j-th leaf of the
i-th plant, the ai’s are the plant
effects and are taken to be independently distributed
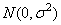
the bij’s are leaf effects each independently distributed
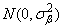
and the eijk’s are errors each independently distributed N(0, s2). The effects are all assumed to be independently distributed. The data are given in the following table:
|
Plant |
Leaf |
Samples | |
|
1 |
1 2 3 |
3.28 3.52 2.88 |
3.09 3.48 2.80 |
|
2 |
1 2 3 |
2.46 1.87 2.19 |
2.44 1.92 2.19 |
|
3 |
1 2 3 |
2.77 3.74 2.55 |
2.66 3.44 2.55 |
|
4 |
1 2 3 |
3.78 4.07 3.31 |
3.87 4.12 3.31 |
#include <imsls.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define Mfloat float
void main()
{
Mfloat pvalue, *aov, *varc, *ymeans, *ems;
Mfloat y[] = {3.28, 3.09, 3.52, 3.48, 2.88, 2.80, 2.46, 2.44, 1.87,
1.92, 2.19, 2.19, 2.77, 2.66, 3.74, 3.44, 2.55, 2.55, 3.78,
3.87, 4.07, 4.12, 3.31, 3.31};
int n_levels[] = {4, 3, 2};
char *aov_labels[] = {
"degrees of freedom for model",
"degrees of freedom for error",
"total (corrected) degrees of freedom",
"sum of squares for model",
"sum of squares for error",
"total (corrected) sum of squares",
"model mean square",
"error mean square",
"F-statistic",
"p-value",
"R-squared (in percent)",
"adjusted R-squared (in percent)",
"est. standard deviation of within error",
"overall mean of y",
"coefficient of variation (in percent)"};
char *ems_labels[] = {
"Effect A and Error",
"Effect A and Effect B",
"Effect A and Effect A",
"Effect B and Error",
"Effect B and Effect B",
"Error and Error"};
char *means_labels[] = {
"Grand mean",
" A means 1",
" A means 2",
" A means 3",
" A means 4",
"AB means 1 1",
"AB means 1 2",
"AB means 1 3",
"AB means 2 1",
"AB means 2 2",
"AB means 2 3",
"AB means 3 1",
"AB means 3 2",
"AB means 3 3",
"AB means 4 1",
"AB means 4 2",
"AB means 4 3"};
char *components_labels[] = {
"degrees of freedom for A",
"sum of squares for A",
"mean square of A",
"F-statistic for A",
"p-value for A",
"Estimate of A",
"Percent Variation Explained by A",
"95% Confidence Interval Lower Limit for A",
"95% Confidence Interval Upper Limit for A",
"degrees of freedom for B",
"sum of squares for B",
"mean square of B",
"F-statistic for B",
"p-value for B",
"Estimate of B",
"Percent Variation Explained by B",
"95% Confidence Interval Lower Limit for B",
"95% Confidence Interval Upper Limit for B",
"degrees of freedom for Error",
"sum of squares for Error",
"mean square of Error",
"F-statistic for Error",
"p-value for Error",
"Estimate of Error",
"Percent Explained by Error",
"95% Confidence Interval Lower Limit for Error",
"95% Confidence Interval Upper Limit for Error"};
pvalue = imsls_f_anova_nested(3, 1, n_levels, y,
IMSLS_ANOVA_TABLE, &aov,
IMSLS_Y_MEANS, &ymeans,
IMSLS_VARIANCE_COMPONENTS, &varc,
IMSLS_EMS, &ems,
0);
printf("pvalue = %f\n", pvalue);
imsls_f_write_matrix("* * * Analysis of Variance * * *", 15, 1, aov,
IMSLS_ROW_LABELS, aov_labels,
IMSLS_WRITE_FORMAT, "%10.5f",
0);
imsls_f_write_matrix("* * *
Expected Mean Square Coefficients * * *"
6, 1, ems,
IMSLS_ROW_LABELS, ems_labels,
IMSLS_WRITE_FORMAT, "%6.2f",
0);
imsls_f_write_matrix("* * * Means * * *", 17, 1, ymeans,
IMSLS_ROW_LABELS, means_labels,
IMSLS_WRITE_FORMAT, "%6.2f",
0);
imsls_f_write_matrix("* * Analysis of Variance / Variance Components * *",
27, 1, varc,
IMSLS_ROW_LABELS, components_labels,
IMSLS_WRITE_FORMAT, "%10.5f",
0);
}
Output
pvalue = 0.079854
* * * Analysis of Variance * * *
degrees of freedom for model 11.00000
degrees of freedom for error 12.00000
total (corrected) degrees of freedom 23.00000
sum of squares for model 10.19054
sum of squares for error 0.07985
total (corrected) sum of squares 10.27040
model mean square 0.92641
error mean square 0.00665
F-statistic 139.21599
p-value 0.00000
R-squared (in percent) 99.22248
adjusted R-squared (in percent) 98.50976
est. standard deviation of within error 0.08158
overall mean of y 3.01208
coefficient of variation (in percent) 2.70826
* * * Expected Mean Square Coefficients * * *
Effect A and Error 1.00
Effect A and Effect B 2.00
Effect A and Effect A 6.00
Effect B and Error 1.00
Effect B and Effect B 2.00
Error and Error 1.00
* * * Means * * *
Grand mean 3.01
A means 1 3.17
A means 2 2.18
A means 3 2.95
A means 4 3.74
AB means 1 1 3.18
AB means 1 2 3.50
AB means 1 3 2.84
AB means 2 1 2.45
AB means 2 2 1.89
AB means 2 3 2.19
AB means 3 1 2.72
AB means 3 2 3.59
AB means 3 3 2.55
AB means 4 1 3.82
AB means 4 2 4.10
AB means 4 3 3.31
* * Analysis of Variance / Variance Components * *
degrees of freedom for A 3.00000
sum of squares for A 7.56034
mean square of A 2.52011
F-statistic for A 7.66516
p-value for A 0.00973
Estimate of A 0.36522
Percent Variation Explained by A 68.53015
95% Confidence Interval Lower Limit for A 0.03955
95% Confidence Interval Upper Limit for A 5.78674
degrees of freedom for B 8.00000
sum of squares for B 2.63020
mean square of B 0.32878
F-statistic for B 49.40642
p-value for B 0.00000
Estimate of B 0.16106
Percent Variation Explained by B 30.22121
95% Confidence Interval Lower Limit for B 0.06967
95% Confidence Interval Upper Limit for B 0.60042
degrees of freedom for Error 12.00000
sum of squares for Error 0.07985
mean square of Error 0.00665
F-statistic for Error ***********
p-value for Error ***********
Estimate of Error 0.00665
Percent Explained by Error 1.24864
95% Confidence Interval Lower Limit for Error 0.00342
95% Confidence Interval Upper Limit for Error 0.01813
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |