Converts nominal data into a series of binary encoded columns for input to a neural network. Optionally, it can also reverse the binary encoding, accepting a series of binary encoded columns and returning a single column of nominal classes.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
int*
imsls_unsupervised_nominal_filter (int
n_obs,
int
n_classes, int
x[], …,
0)
Required Arguments
int n_obs
(Input)
Number of observations.
int *
n_classes (Input/Output)
A
pointer to the number of classes in x[]. n_classes is output
for IMSLS_ENCODE
and input for IMSLS_DECODE.
int x[]
(Input)
A one or two-dimensional array depending upon whether encoding or
decoding is requested. If encoding is requested,
x is
an array of length n_obs containing the
categories for a nominal variable numbered from 1 to n_classes. If
decoding is requested, then x is an array of size n_obs by n_classes. In
this case, the columns contain only zeros and ones that are interpreted as
binary encoded representations for a single nominal variable.
Return Value
A pointer to an internally allocated array, z[]. The values in z are either the encoded or decoded values for x, depending upon whether IMSLS_ENCODE or IMSLS_DECODE is requested. If errors are encountered, NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
int*
imsls_f_unsupervised_nominal_filter (int
n_obs, int x[],
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, int z[],
IMSLS_ENCODE or
IMSLS_DECODE,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_ENCODE or
IMSLS_DECODE
(Input)
If IMSLS_ENCODE is
specified, binary encoding is requested. Classes must be numbered
sequentially from 1 to n_classes. IMSLS_DECODE is used
to request that x be decoded.
The values in each column should be zeros and ones. The values in the
ith column of x are associated with
the ith class of the nominal variable.
Default: IMSLS_ENCODE.
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, int z[]
(Output)
A user-supplied array of size n_obs by n_classes. If
IMSLS_DECODE is
specified, then z should be length
n_obs. The
value in z[i] is either the
encoded or decoded value for x[i], depending upon
whether
IMSLS_ENCODE or IMSLS_DECODE is
specified.
Description
The function imsls_unsupervised_nominal_filter is designed to either encode or decode nominal variables using a simple binary mapping.
Binary Encoding: IMSLS_ENCODE
In this case, x[] is an input array to which a binary filter is applied. Binary encoding takes each category in x[], and creates a column in z[], the output matrix, containing all zeros and ones. A value of zero indicates that this category is not present and a value of one indicates that it is present.
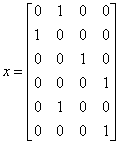
For example, if x[]={2, 1, 3, 4, 2, 4} then n_classes=4, and
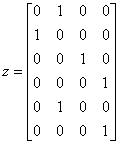
Notice that the number of columns in z is equal to the number of distinct classes in x. The number of rows in z is equal to the length of x.
Binary Decoding: IMSLS_DECODE
Binary decoding takes each column in x[], and returns the appropriate class in z[].
For example, if x[] is the same as described above:
then z[] would be returned as z[]={2, 1, 3, 4, 2, 4}. Notice this is the same as the original array because classes are numbered sequentially from 1 to n_classes. This ensures that the ith column of x[] is associated with the ith class in the output array.
int x[N_OBS] = {3, 3, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2};
z = imsls_unsupervised_nominal_filter(N_OBS, &n_classes, x, 0);
printf("n_classes = %d\n",n_classes);
imsls_i_write_matrix("X", N_OBS, 1, (int*)x, 0);
imsls_i_write_matrix("Z", N_OBS, n_classes, z, 0);
x2 = imsls_unsupervised_nominal_filter(N_OBS, &n_classes, z,
imsls_i_write_matrix("Unfiltering result", N_OBS, 1, x2, 0);
Output
7 n_classes = 3
8
9 X
10 1 3
11 2 3
12 3 1
13 4 2
14 5 2
15 6 1
16 7 2
17
18 Z
19 1 2 3
20 1 0 0 1
21 2 0 0 1
22 3 1 0 0
23 4 0 1 0
24 5 0 1 0
25 6 1 0 0
26 7 0 1 0
27
28 Unfiltering result
29 1 3
30 2 3
31 3 1
32 4 2
33 5 2
34 6 1
35 7 2
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |