Computes basic univariate statistics.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float *imsls_f_simple_statistics (int n_observations, int n_variables, float x[], ..., 0)
The type double function is imsls_d_simple_statistics.
Required Arguments
int
n_observations (Input)
Number of observations.
int
n_variables (Input)
Number of variables.
float x[]
(Input)
Array of size n_observations × n_variables containing
the data matrix.
Return Value
A pointer to an array containing some simple statistics for
each of the columns in x.
If IMSLS_MEDIAN
and IMSLS_MEDIAN_AND_SCALE
are not used as optional arguments, the size of the matrix is 14 × n_variables.
The columns of this matrix correspond to the columns of x,
and the rows contain the following statistics:
|
Row |
Statistic |
|
0 |
mean |
|
1 |
variance |
|
2 |
standard deviation |
|
3 |
coefficient of skewness |
|
4 |
coefficient of excess (kurtosis) |
|
5 |
minimum value |
|
6 |
maximum value |
|
7 |
range |
|
8 |
coefficient of variation (when defined) If the coefficient of variation is not defined, 0 is returned. |
|
9 |
number of observations (the counts) |
|
10 |
lower confidence limit for the mean (assuming normality) The default is a 95-percent confidence interval. |
|
11 |
upper confidence limit for the mean (assuming normality) |
|
12 |
lower confidence limit for the variance (assuming
normality) |
|
13 |
upper confidence limit for the variance (assuming normality) |
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
float
*imsls_f_simple_statistics (int n_observations, int n_variables, float x[],
IMSLS_CONFIDENCE_MEANS, float confidence_means,
IMSLS_CONFIDENCE_VARIANCES, float confidence_variances,
IMSLS_X_COL_DIM, int
x_col_dim,
IMSLS_STAT_COL_DIM, int
stat_col_dim,
IMSLS_MEDIAN, or
IMSLS_MEDIAN_AND_SCALE,
IMSLS_MISSING_LISTWISE, or
IMSLS_MISSING_ELEMENTWISE,
IMSLS_FREQUENCIES, float frequencies[],
IMSLS_WEIGHTS, float weights[],
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, float simple_statistics[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_CONFIDENCE_MEANS, float
confidence_means (Input)
Confidence level for a two-sided
interval estimate of the means (assuming normality) in percent. Argument confidence_means must
be between 0.0 and 100.0 and is often 90.0, 95.0, or 99.0. For a one-sided
confidence interval with confidence level c, set confidence_means = 100.0 − 2(100 − c). If IMSLS_CONFIDENCE_MEANS
is not specified, a 95-percent confidence interval is computed.
IMSLS_CONFIDENCE_VARIANCES, float
confidence_variances (Input)
The confidence level for a
two-sided interval estimate of the variances (assuming normality) in percent.
The confidence intervals are symmetric in probability (rather than in length).
For a one-sided confidence interval with confidence level c, set confidence_means
= 100.0 − 2(100 − c). If IMSLS_CONFIDENCE_VARIANCES
is not specified, a 95-percent confidence interval is computed.
IMSLS_X_COL_DIM, int x_col_dim
(Input)
Column dimension of array x.
Default: x_col_dim = n_variables
IMSLS_STAT_COL_DIM, int
stat_col_dim (Input)
Column dimension of the returned
value array, or if IMSLS_RETURN_USER is
specified, the column dimension of array simple_statistics.
Default:
stat_col_dim = n_variables
IMSLS_MEDIAN, or
IMSLS_MEDIAN_AND_SCALE
Exactly
one of these optional arguments can be specified in order to indicate the
additional simple robust statistics to be computed. If IMSLS_MEDIAN is
specified, the medians are computed and stored in one additional row (row number
14) in the returned matrix of simple statistics. If IMSLS_MEDIAN_AND_SCALE
is specified, the medians, the medians of the absolute deviations from the
medians, and a simple robust estimate of scale are computed, then stored in
three additional rows (rows 14, 15, and 16) in the returned matrix of simple
statistics.
IMSLS_MISSING_LISTWISE, or
IMSLS_MISSING_ELEMENTWISE
If
IMSLS_MISSING_ELEMENTWISE
is specified, all non missing data for any variable is used in computing the
statistics for that variable. If IMSLS_MISSING_LISTWISE
is specified and if an observation (row of x) contains a missing
value, the observation is excluded from computations for all variables. The
default is IMSLS_MISSING_LISTWISE.
In either case, if weights and/or frequencies are specified and the value of the
weight and/or frequency is missing, the observation is excluded from
computations for all variables.
IMSLS_FREQUENCIES, float frequencies[]
(Input)
Array of length n_observations
containing the frequency for each observation.
Default: Each observation has
a frequency of 1
IMSLS_WEIGHTS, float weights[]
(Input)
Array of length n_observations
containing the weight for each observation.
Default: Each observation has a
weight of 1
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, float
simple_statistics[] (Output)
User-supplied array
containing the matrix of statistics. If neither IMSLS_MEDIAN nor IMSLS_MEDIAN_AND_SCALE
is specified, the matrix is 14 × n_variables. If IMSLS_MEDIAN is
specified, the matrix is 15 × n_variables. If IMSLS_MEDIAN_AND_SCALE
is specified, the matrix is 17 × n_variables.
Description
For the data in each column of x, imsls_f_simple_statistics computes the sample mean, variance, minimum, maximum, and other basic statistics. This function also computes confidence intervals for the mean and variance (under the hypothesis that the sample is from a normal population).
Frequencies are interpreted as multiple occurrences of the other values in the observations. In other words, a row of x with a frequency variable having a value of 2 has the same effect as two rows with frequencies of 1. The total of the frequencies is used in computing all the statistics based on moments (mean, variance, skewness, and kurtosis). Weights are not viewed as replication factors. The sum of the weights is used only in computing the mean (the weighted mean is used in computing the central moments). Both weights and frequencies can be 0, but neither can be negative. In general, a 0 frequency means that the row is to be eliminated from the analysis; no further processing or error checking is done on the row. A weight of 0 results in the row being counted, and updates are made of the statistics.
The definitions of some of the statistics are given below in terms of a single variable x of which the i-th datum is xi.
Mean
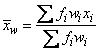
Variance
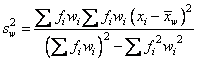
Skewness

Excess or Kurtosis

Minimum
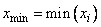
Maximum
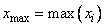
Range
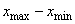
Coefficient of Variation
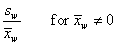
Median
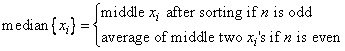
Median Absolute Deviation
MAD = median {|xi − median {xj}|}
Simple Robust Estimate of Scale
MAD/Φ−1(3/4)
where Φ−1(3/4) ≈ 0.6745 is the inverse of the standard normal distribution function evaluated at 3/4. This standardizes MAD in order to make the scale estimate consistent at the normal distribution for estimating the standard deviation (Huber 1981, pp. 107−108).
Example
"means", "variances", "std. dev", "skewness", "kurtosis",
"minima", "maxima", "ranges", "C.V.", "counts", "lower mean",
"upper mean", "lower var", "upper var"};
simple_statistics = imsls_f_simple_statistics(N_OBSERVATIONS,
imsls_f_write_matrix("* * * Statistics * * *\n", 14, N_VARIABLES,
IMSLS_WRITE_FORMAT, "%7.3f", 0);
Output
means 7.462 48.154 11.769 30.000 95.423
variances 34.603 242.141 41.026 280.167 226.314
std. dev 5.882 15.561 6.405 16.738 15.044
skewness 0.688 -0.047 0.611 0.330 -0.195
kurtosis 0.075 -1.323 -1.079 -1.014 -1.342
minima 1.000 26.000 4.000 6.000 72.500
maxima 21.000 71.000 23.000 60.000 115.900
ranges 20.000 45.000 19.000 54.000 43.400
C.V. 0.788 0.323 0.544 0.558 0.158
counts 13.000 13.000 13.000 13.000 13.000
lower mean 3.907 38.750 7.899 19.885 86.332
upper mean 11.016 57.557 15.640 40.115 104.514
lower var 17.793 124.512 21.096 144.065 116.373
upper var 94.289 659.817 111.792 763.434 616.688
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |