Compute the non-negative least squares (NNLS) solution of
an m × n real linear least squares system, 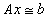 ,
,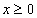 .
.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_nonneg_least_squares (int m, int n, float a[], float b[],…, 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_nonneg_least_squares.
Required Arguments
int m
(Input)
The number of rows in the matrix.
int n
(Input)
The number of columns in the matrix.
float a[]
(Input)
An array of length m × n containing the
matrix.
float b[]
(Input)
An array of length m containing the
right-hand side vector.
Return Value
An array of length n containing the approximate solution vector, x ≥ 0.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_nonneg_least_squares (int m, int n, float a[], float b[],
IMSL_ITMAX, int itmax,
IMSL_DROP_MAX_POS_DUAL, int maxdual,
IMSL_DROP_TOLERANCE, float tol,
IMSL_SUPPLY_WORK_ARRAYS, int lwork, float work[], int liwork, int iwork[],
IMSL_OPTIMIZED, int *iflag,
IMSL_DUAL_SOLUTION, float **dual,
IMSL_DUAL_SOLUTION_USER, float udual[],
IMSL_RESIDUAL_NORM, float *rnorm,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float x[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_ITMAX,
int itmax
(Input)
The number of times a constraint is added or dropped should not
exceed this maximum value. An approximate solution x ≥ 0 is
returned when the maximum number is reached.
Default: itmax = 3 × n.
IMSL_DROP_MAX_POS_DUAL,
int maxdual
(Input)
Indicates how a variable is moved from its constraint to a positive
value, or dropped, when its current dual value is positive. By dropping the
variable corresponding to the first computed positive dual value, instead of the
maximum, better runtime efficiency usually results by avoiding work in the early
stages of the algorithm.
If maxdual = 0,
the first encountered positive dual is used. Otherwise, the maximum positive
dual, is used. The results for x ≥ 0 will usually vary
slightly depending on the choice.
Default: maxdual = 0
IMSL_DROP_TOLERANCE,
float tol
(Input)
This is a rank-determination tolerance. A candidate column
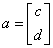
has values eliminated below the first entry of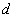 . The resulting value must satisfy the
relative condition
. The resulting value must satisfy the
relative condition
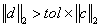 .
.
Otherwise the constraint remains satisfied because the column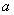 is linearly dependent on
previously dropped columns.
is linearly dependent on
previously dropped columns.
Default: tol = sqrt(imsl_f_machine(3));
IMSL_SUPPLY_WORK_ARRAYS
, int lwork, float work[], int liwork, int iwork[]
(Input/Output)
The use of this optional argument will increase efficiency and
avoid memory fragmentation run-time failures for large problems by allowing the
user to provide the sizes and locations of the working arrays work and iwork. With maxt as the maximum
number of threads that will be active, it is required that:
lwork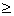 maxt*(m*(n+2) + n),
and liwork
maxt*(m*(n+2) + n),
and liwork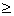 maxt*n.
maxt*n.
Without the use of OpenMP and parallel threading, maxt=1.
IMSL_OPTIMIZED,
int *flag
(Output)
A
0-1 flag noting whether or not the optimum residual norm was obtained. A value
of 1 indicates the optimum residual norm was obtained. A value of 0 occurs if
the maximum number of iterations was reached.
|
flag |
Description |
|
0 |
the maximum number of iterations was reached. |
|
1 |
the optimum residual norm was obtained. |
IMSL_DUAL_SOLUTION,
float **dual
(Output)
An
array of length n containing the dual
vector, 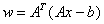 . This may not be optimal (all
components may not satisfy
. This may not be optimal (all
components may not satisfy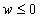 ), if the maximum number of
iterations occurs first.
), if the maximum number of
iterations occurs first.
IMSL_DUAL_SOLUTION_USER,
float dual[]
(Output)
Storage for dual provided
by the user. See
IMSL_DUAL_SOLUTION.
IMSL_RESIDUAL_NORM,
float *rnorm
(Output)
The value of the residual vector norm, 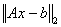 .
.
IMSL_RETURN_USER,
float x[]
(Output)
A user-allocated array of length n containing the
approximate solution vector, 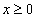 .
.
Description
Function imsl_f_nonneg_least_squares
computes the constrained least squares solution of 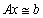 , by minimizing
, by minimizing 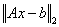 subject to
subject to 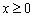 . It uses the algorithm NNLS
found in Charles L. Lawson and Richard J. Hanson, Solving Least Squares
Problems, SIAM Publications, Chap. 23, (1995). The functionality for multiple
threads and the constraint dropping strategy are new features. The original NNLS
algorithm was silent about multiple threads; all dual components were computed
when only one was used. Using the first encountered eligible variable to make
non-active usually improves performance. An optimum solution is obtained in
either approach. There is no restriction on the relative sizes of m
and n.
. It uses the algorithm NNLS
found in Charles L. Lawson and Richard J. Hanson, Solving Least Squares
Problems, SIAM Publications, Chap. 23, (1995). The functionality for multiple
threads and the constraint dropping strategy are new features. The original NNLS
algorithm was silent about multiple threads; all dual components were computed
when only one was used. Using the first encountered eligible variable to make
non-active usually improves performance. An optimum solution is obtained in
either approach. There is no restriction on the relative sizes of m
and n.
Examples
Example 1
A model function of exponentials is

The exponential function argument parameters
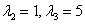
are fixed. The coefficients
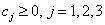 ,
,
are estimated by sampling data values,
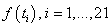
using non-negative least squares. The values used for the data are
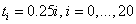 ,
,
with
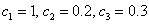 .
.
#include <imsl.h>
#include <math.h>
#define M 21
#define N 3
int main() {
int i;
float a[M][N], b[M], *c;
for (i = 0; i < M; i++) {
/* Generate exponential values. This model is
y(t) = c_0 + c_1*exp(-t) + c_2*exp(-5*t) */
a[i][0] = 1.0;
a[i][1] = exp(-(i*0.25));
a[i][2] = exp(-(i*0.25)*5.0);
/* Compute sample values */
b[i] = a[i][0] + 0.2*a[i][1] + 0.3*a[i][2];
}
/* Solve for coefficients, constraining values
to be non-negative. */
c = imsl_f_nonneg_least_squares(M, N, &a[0][0], b, 0);
/* With noise level = 0, solution should be (1, 0.2, 0.3) */
imsl_f_write_matrix("Coefficients", 1, N, c, 0);
}
Output
Coefficients
1 2 3
1.0 0.2 0.3
Example 2
The model function of exponentials is
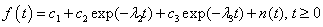 .
.
The values λ2,
λ3 are the same as in Example 1. The
function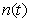 represents normally distributed random
noise with a standard deviation
represents normally distributed random
noise with a standard deviation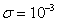 . A simulation is done with
ns = 10001samples for n (t). The resulting
problem is solved using OpenMP. To check that the OpenMP results are correct, a
loop computes the solutions without OpenMP followed by the same loop using
OpenMP. The residual norms agree, showing that the routine returns the same
values using OpenMP as without using OpenMP.
. A simulation is done with
ns = 10001samples for n (t). The resulting
problem is solved using OpenMP. To check that the OpenMP results are correct, a
loop computes the solutions without OpenMP followed by the same loop using
OpenMP. The residual norms agree, showing that the routine returns the same
values using OpenMP as without using OpenMP.
#include <imsl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <omp.h>
#define M 21
#define N 3
#define NS 10001
int main() {
#define BS(i_,j_) bs[(i_)*M + (j_)]
#define X(i_,j_) x[(i_)*N + (j_)]
int thread_safe=1, seed=123457, i, *iwork, j, lwork, liwork, maxt;
float b[M], *work, sigma=1.0e-3, a[M][N], rseq[NS], rpar[NS],
*bs, *x;
/* Allocate work memory for all threads that are
used in the loops below. */
maxt = omp_get_max_threads();
lwork = maxt*(M*(N+2)+N);
liwork = maxt*N;
work = (float *) malloc(lwork * sizeof(float));
iwork = (int *) malloc(liwork * sizeof(int));
x = (float *) malloc(NS*N * sizeof(float));
bs = (float *) malloc(NS*M * sizeof(float));
for (i = 0; i < M; i++) {
/* Generate matrix values.
This model is y(t) =
c_0 + c_1*exp(-t) + c_2*exp(-5*t) + n(t) */
a[i][0] = 1.0;
a[i][1] = exp(-(i*0.25));
a[i][2] = exp(-(i*0.25)*5.0);
}
/* Solve for coefficients, constraining values to be non-negative.
First use a sequential for loop. Then a parallel for loop.
Record the residual norms and compare them. */
imsl_random_seed_set(seed);
/* First the sequential loop.
Working memory is not included as an argument. */
for (j = 0; j < NS; j++) {
imsl_f_random_normal(M, IMSL_RETURN_USER, b, 0);
/* Add normal pdf noise at the level sigma. */
for (i=0; i<M; i++) {
b[i] = sigma*b[i] + a[i][0] + 0.2*a[i][1] + 0.3*a[i][2];
BS(j,i) = b[i];
}
imsl_f_nonneg_least_squares(M, N, &a[0][0], &BS(j,0),
IMSL_RETURN_USER, &X(j,0),
IMSL_RESIDUAL_NORM, &rseq[j],
0);
}
/* Then the parallel for loop using OpenMP.
Working memory is an optional argument. This is not required
but helps prevent memory fragmentation. */
/* Reset x for output for the OpenMP loop. */
for (i = 0; i < NS*N; i++)
x[i] = 0.0;
#pragma omp parallel for private(j)
for (j = 0; j < NS; j++) {
imsl_f_nonneg_least_squares(M, N, &a[0][0], &BS(j,0),
IMSL_RETURN_USER, &X(j,0),
IMSL_RESIDUAL_NORM, &rpar[j],
IMSL_SUPPLY_WORK_ARRAYS, lwork, work, liwork, iwork,
0);
}
/* Check that residual norms agree exactly for both loops. They
should because the same problems are solved - one set
sequentially and the next set in parallel. */
for (j = 0; j < NS; j++) {
/* Since the two loops solve the same set of problems, the
residual norms must agree exactly. */
if (rpar[j] != rseq[j]) {
thread_safe = 0;
break;
}
}
if(thread_safe)
printf("imsl_f_nonneg_least_squares is thread-safe.\n");
else
printf("imsl_f_nonneg_least_squares is not thread-safe.\n");
system("pause");
}
Output
imsl_f_nonneg_least_squares is thread-safe.
Warning Errors
|
IMSL_MAX_NNLS_ITER_REACHED |
The maximum number of iterations was reached. The best answer will be returned. “itmax” = # was used. A larger value may help the algorithm complete. |
