Given an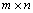 real matrix
real matrix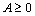 , and an integer
, and an integer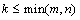 , compute a factorization
, compute a factorization 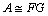 . The matrix factors
. The matrix factors 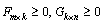 are computed to minimize the
Frobenius, or sum of squares, norm of the error matrix:
are computed to minimize the
Frobenius, or sum of squares, norm of the error matrix:  .
.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_nonneg_matrix_factorization (int m, int n, int k, float a[], float f[], float g[],…, 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_nonneg_matrix_factorization.
Required Arguments
int m
(Input)
The number of rows in the matrix.
int n
(Input)
The number of columns in the matrix.
int k
(Input)
The number of columns in the matrix F and rows in the matrix
G.
float a[]
(Input)
An array of length m × n containing the
A matrix.
float f[]
(Input/Output)
An array of length m × k containing the
F matrix. If IMSL_INITIAL_FACTORS
is used, the sweeps begin using the input values for 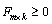 .
.
float g[]
(Output)
An array of length k × n containing the
G matrix.
Return Value
A scalar containing the Frobenius norm of the error matrix
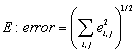 .
.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_nonneg_matrix_factorization (int m, int n, int k, float a[], float f[], float g[],
IMSL_WEIGHT, float w[],
IMSL_INITIAL_FACTORS, int factors,
IMSL_ITMAX, int itmax,
IMSL_RESIDUAL_ERROR, float err,
IMSL_RELATIVE_ERROR, float rerr,
IMSL_STOPPING_CRITERION, int *reason,
IMSL_NSTEPS_TAKEN, int *nsteps,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_WEIGHT,
float w[]
(Input)
An array of length m × n containing the
matrix W ≥ 0 of weights that will be applied to the entries of
A ≥ 0 during the solution sweeps. The factorization obtained
is FG ≅W ° A, where the weights
are applied element-wise.
Default: Weights are not applied, or equivalently,
the weights all have value 1.
IMSL_INITIAL_FACTORS,
int factors
(Input)
A flag that signifies if the matrix F is given an input
estimate. If factors = 0, start sweeps using
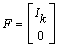 .
.
Otherwise, use initial values in f as the matrix
F to start the sweeps.
Default: factors = 0
IMSL_ITMAX,
int itmax
(Input)
The maximum number of sweeps allowed for alternately solving for
G ≥ 0, then F ≥ 0.
Default: itmax = 2 * (m + n + 1)
IMSL_RESIDUAL_ERROR,
float err
(Input)
A scalar that will stop the sweeps at the first one satisfying
error ≤ err.
Default: err = 0
IMSL_RELATIVE_ERROR,
float rerr
(Input)
A scalar that will stop the sweeps at the first one satisfying
erroriter-2 - erroriter-1 ≤ rerr × erroriter, iter > 2.
This test is made after three values of the error matrix norm have been
computed. The sequence {erroriter} is decreasing with increasing
values of the iteration counter, iter. If erroriter ≥ erroriter-1 occurs, the
sweeps stop.
Default: rerr = (imsl_f_machine(3))0.4.
IMSL_STOPPING_CRITERION,
int *reason
(Output)
This flag has the value 0,1,2 or 3 depending on which of the
following conditions stopped the sweeps:
|
reason |
Description |
|
0 |
Errors in user input occurred |
|
1 |
Reached maximum iterations |
|
2 |
Residual norm is small |
|
3 |
Relative error convergence |
IMSL_NSTEPS_TAKEN,
int *nsteps
(Output)
The last value of the iteration count, 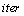 , that gives the number of sweeps.
, that gives the number of sweeps.
Description
Function imsl_f_nonneg_matrix_factorization
computes an approximation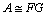 , or with weights,
W ° A ≅ FG;
the factors are constrained:
, or with weights,
W ° A ≅ FG;
the factors are constrained: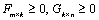 . The matrix factors
. The matrix factors 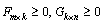 are computed to minimize the Frobenius
or sum of squares, norm of the error matrix:
are computed to minimize the Frobenius
or sum of squares, norm of the error matrix:  .
.
The algorithm is based on Alternating Least Squares, presented by P. Paatero and U. Tapper, “Positive Matrix Factorization, etc.” Environmetrics, (5), p. 111-126 (1994).
Each constrained least squares problem is solved using
imsl_f_nonneg_least_squares. This
process alternates between computing the batch of 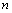 columns of
columns of 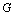 and then the batch of
and then the batch of 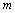 rows of
rows of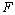 . This constitutes a “sweep.”
. This constitutes a “sweep.”
There is no restriction on the relative sizes of 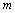 and
and 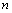 . The restrictions on the integer
. The restrictions on the integer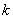 are
are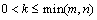 . When an initial matrix
. When an initial matrix 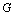 is to be used, instead of an
initial
is to be used, instead of an
initial 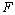 , repose the factorization in
transposed form
, repose the factorization in
transposed form 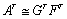 , or with weights, AT ° WT ≅ GTFT.
, or with weights, AT ° WT ≅ GTFT.
The matrix factors 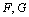 are not unique. In the function,
the output rows of
are not unique. In the function,
the output rows of 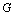 are scaled to have sum equal to the
value 1. The scaled columns of
are scaled to have sum equal to the
value 1. The scaled columns of 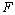 are sorted so the column sums
are non-increasing. This sort order is then applied to the rows of
are sorted so the column sums
are non-increasing. This sort order is then applied to the rows of 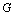 .
.
Example
Five customers, Beth, Dick, Fred, Joe and Kay make purchases at a convenience store.
|
|
Flour |
Balloons |
Beer |
Sugar |
Chips |
|
Beth |
|
3 |
8 |
|
1 |
|
Dick |
|
2 |
5 |
1 |
|
|
Fred |
5 |
|
1 |
10 |
|
|
Joe |
|
20 |
40 |
2 |
1 |
|
Kay |
10 |
|
1 |
10 |
1 |
This matrix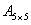 of customers versus items
purchased is approximated by a non-negative matrix factorization, using
of customers versus items
purchased is approximated by a non-negative matrix factorization, using 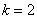 :
: 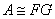 . The example is taken from one due to
H. Jin and M. Saunders, “Exploring Nonnegative Matrix Factorization,” A
Workshop on Algorithms for Massive Data Sets, Stanford University, June 25-28, (2008).
. The example is taken from one due to
H. Jin and M. Saunders, “Exploring Nonnegative Matrix Factorization,” A
Workshop on Algorithms for Massive Data Sets, Stanford University, June 25-28, (2008).
#include <imsl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define M 5
#define N 5
#define K 2
int main() {
float a[M][N]= {
{ 0, 3, 8, 0, 1},
{ 0, 2, 5, 1, 0},
{ 5, 0, 1, 10, 0},
{ 0, 20, 40, 2, 1},
{10, 0, 1, 10, 1}
};
float error, f[M*K], g[K*N];
int nsteps, reason;
/* Solve for factors, constraining values to be non-negative.
Get reason for stopping and number of sweeps. */
error = imsl_f_nonneg_matrix_factorization(M, N, K, &a[0][0], f, g,
IMSL_STOPPING_CRITERION, &reason,
IMSL_NSTEPS_TAKEN, &nsteps,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("Matrix Factor F", M, K, f, 0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("Matrix Factor G", K, N, g, 0);
printf("\nFrobenius Norm of E=A-F*G is %e\n", error);
printf("Reason for stopping sweeps: %d\n", reason);
printf("Number of sweeps taken: %d\n", nsteps);
}
Output
Matrix Factor F
1 2
1 11.96 0.00
2 7.51 0.94
3 0.33 16.61
4 62.90 0.13
5 0.00 21.35
Matrix Factor G
1 2 3 4 5
1 0.0000 0.3150 0.6373 0.0298 0.0178
2 0.4048 0.0000 0.0473 0.5190 0.0288
Frobenius Norm of E=A-F*G is 3.195350e+000
Reason for stopping sweeps: 3
Number of sweeps taken: 10

