Generates pseudorandom numbers from a chi-squared distribution.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float *imsls_f_random_chi_squared (int n_random, float df, ..., 0)
The type double function is imsls_d_random_chi_squared.
Required Arguments
int n_random
(Input)
Number of random numbers to generate.
float df
(Input)
Degrees of freedom. Parameter df must be
positive.
Return Value
An array of length n_random containing the random chi-squared deviates.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
float
*imsls_f_random_chi_squared (int n_random,
float
df,
IMSLS_RETURN_USER,
float r[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, float r[]
(Output)
User-supplied array of length n_random containing
the random chi-squared deviates.
Description
Function imsls_f_random_chi_squared generates pseudorandom numbers from a chi-squared distribution with df degrees of freedom. If df is an even integer less than 17, the chi-squared deviate r is generated as
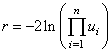
where n = df/2 and the ui are independent random deviates from a uniform (0, 1) distribution. If df is an odd integer less than 17, the chi-squared deviate is generated in the same way, except the square of a normal deviate is added to the expression above. If df is is greater than 16 or is not an integer, and if it is not too large to cause overflow in the gamma random number generator, the chi-squared deviate is generated as a special case of a gamma deviate, using function imsls_f_random_gamma. If overflow would occur in imsls_f_random_gamma, the chi-squared deviate is generated in the manner described above, using the logarithm of the product of uniforms, but scaling the quantities to prevent underflow and overflow.
Example
In this example, imsls_f_random_chi_squared generates five pseudorandom chi-squared deviates with five degrees of freedom.
#include <imsls.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n_random = 5;
float df = 5.0;
float *r;
imsls_random_seed_set(123457);
r = imsls_f_random_chi_squared(n_random, df, 0);
imsls_f_write_matrix("Chi-Squared random deviates: ",
1, n_random, r, IMSLS_NO_COL_LABELS, 0);
}
Output
Chi-Squared random deviates:
12.09 0.48 1.80 14.87 1.75
