Generates pseudorandom numbers from a negative binomial distribution.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
int *imsls_f_random_neg_binomial (int n_random, float rk, float p, ..., 0)
The type double function is imsls_d_random_neg_binomial.
Required Arguments
int n_random
(Input)
Number of random numbers to generate.
float rk
(Input)
Negative binomial parameter. Parameter rk must be positive.
If rk is an
integer, the generated deviates can be thought of as the number of failures in a
sequence of Bernoulli trials before rk successes
occur.
float p
(Input)
Probability of failure on each trial. Parameter p must be greater than
machine epsilon (see imsls_f_machine, Chapter 15, “Utilities”) and
less than 1.0.
Return Value
An integer array of length n_random containing the random negative binomial deviates.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
int
*imsls_f_random_neg_binomial (int n_random,
float
rk,
float p,
IMSLS_RETURN_USER,
int ir[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, int ir[]
(Output)
User-supplied integer array of length n_random containing
the random negative binomial deviates.
Description
Function imsls_f_random_neg_binomial generates pseudorandom numbers from a negative binomial distribution with parameters rk and p. Parameters rk and p must be positive and p must be less than 1. The probability function (with r = rk and p = p) is
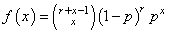
for x = 0, 1, 2, ...
If r is an integer, the distribution is often called the Pascal distribution and can be thought of as modeling the length of a sequence of Bernoulli trials until r successes are obtained, where p is the probability of getting a failure on any trial. In this form, the random variable takes values r, r + 1, r + 2, … and can be obtained from the negative binomial random variable defined above by adding r to the negative binomial variable. This latter form is also equivalent to the sum of r geometric random variables defined as taking values 1, 2, 3, ...
If rp/(1 − p) is less than 100 and (1 − p)r is greater than the machine epsilon, imsls_f_random_neg_binomial uses the inverse CDF technique; otherwise, for each negative binomial deviate, imsls_f_random_neg_binomial generates a gamma (r, p/(1 − p)) deviate Y and then generates a Poisson deviate with parameter Y.
Example
In this example, imsls_f_random_neg_binomial generates five pseudorandom negative binomial deviates from a negative binomial (Pascal) distribution with parameters r equal to 4 and p equal to 0.3.
#include <imsls.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n_random = 5;
float rk = 4.0;
float p = 0.3;
int *ir;
imsls_random_seed_set(123457);
ir = imsls_f_random_neg_binomial(n_random, rk, p, 0);
imsls_i_write_matrix(
"Negative Binomial (4.0, 0.3) random deviates: ",
1, n_random, ir, IMSLS_NO_COL_LABELS, 0);
}
Output
Negative Binomial (4.0, 0.3) random deviates:
5 1 3 2 3
