Generates pseudorandom numbers from a Poisson distribution.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
int *imsls_random_poisson (int n_random, float theta, ..., 0)
Required Arguments
int n_random
(Input)
Number of random numbers to generate.
float theta
(Input)
Mean of the Poisson distribution. Argument theta must be
positive.
Return Value
An array of length n_random containing the random Poisson deviates.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
int
*imsls_random_poisson (int
n_random, float
theta,
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, int
r[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, int r[]
(Output)
User-supplied array of length n_random containing
the random Poisson deviates.
Description
Function imsls_random_poisson generates pseudorandom numbers from a Poisson distribution with positive mean theta. The probability function (with θ = theta) is
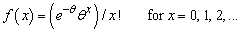
If theta is less than 15, imsls_random_poisson uses an inverse CDF method; otherwise, the PTPE method of Schmeiser and Kachitvichyanukul (1981) (see also Schmeiser 1983) is used. The PTPE method uses a composition of four regions, a triangle, a parallelogram, and two negative exponentials. In each region except the triangle, acceptance/rejection is used. The execution time of the method is essentially insensitive to the mean of the Poisson.
Function imsls_random_seed_set can be used to initialize the seed of the random number generator; function imsls_random_option can be used to select the form of the generator.
Example
In this example, imsls_random_poisson is used to generate five pseudorandom deviates from a Poisson distribution with mean equal to 0.5.
#include <imsls.h>
#define N_RANDOM 5
int main()
{
int *r;
int seed = 123457;
float theta = 0.5;
imsls_random_seed_set (seed);
r = imsls_random_poisson (N_RANDOM, theta, 0);
imsls_i_write_matrix ("Poisson(0.5) random deviates", 1, N_RANDOM, r, 0);
}
Output
Poisson(0.5) random deviates
1 2 3 4 5
2 0 1 0 1

