FDF
This function evaluates the F cumulative distribution function.
Function Return Value
FDF — Function value, the probability that an F random variable takes a value less than or equal to the input F. (Output)
Required Arguments
F — Argument for which the F cumulative distribution function is to be evaluated. (Input)
DFN — Numerator degrees of freedom. (Input)
DFN must be positive.
DFN must be positive.
DFD — Denominator degrees of freedom. (Input)
DFD must be positive.
DFD must be positive.
Optional Arguments
COMPLEMENT — Logical. If .TRUE., the complement of the F cumulative distribution function is evaluated. If .FALSE., the F cumulative distribution function is evaluated. (Input)
See the Description section for further details on the use of COMPLEMENT.
Default: COMPLEMENT = .FALSE..
See the Description section for further details on the use of COMPLEMENT.
Default: COMPLEMENT = .FALSE..
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: FDF (F, DFN, DFD [, …])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_FDF and D_FDF.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: FDF (F, DFN, DFD)
Double: The double precision name is DFDF.
Description
Function FDF evaluates the distribution function of a Snedecor’s F random variable with DFN numerator degrees of freedom and DFD denominator degrees of freedom. The function is evaluated by making a transformation to a beta random variable and then using the routine BETDF. If X is an F variate with ν1 and ν2 degrees of freedom and Y = ν1X/(ν2 + ν1X), then Y is a beta variate with parameters p = ν1/2 and q = ν2/2. The function FDF also uses a relationship between F random variables that can be expressed as follows.
FDF(X, DFN, DFD) = 1.0 ‑ FDF(1.0/X, DFD, DFN)
If COMPLEMENT = .TRUE., the value of FDF at the point x is 1 ‑ p, where 1 ‑ p is the probability that the random variable takes a value greater than x. In those situations where the desired end result is 1 ‑ p, the user can achieve greater accuracy in the right tail region by using the result returned by FDF with the optional argument COMPLEMENT set to .TRUE. rather than by using 1 ‑ p where p is the result returned by FDF with COMPLEMENT set to .FALSE..
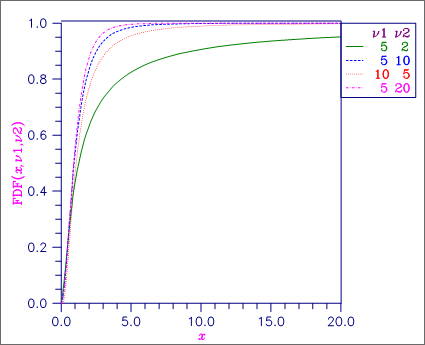
Figure 27, F Distribution Function
Comments
Informational error
Type | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | 3 | Since the input argument F is not positive, the distribution function is zero at F. |
Example
In this example, we find the probability that an F random variable with one numerator and one denominator degree of freedom is greater than 648.
USE UMACH_INT
USE FDF_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER NOUT
REAL DFD, DFN, F, P
!
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
F = 648.0
DFN = 1.0
DFD = 1.0
P = FDF(F,DFN,DFD, COMPLEMENT=.TRUE.)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) P
99999 FORMAT (' The probability that an F(1,1) variate is greater ', &
'than 648 is ', F6.4)
END
Output
The probability that an F(1, 1) variate is greater than 648 is 0.0250