Computes a two-dimensional tensor-product spline approximant using least squares, returning the tensor-product B-spline coefficients.
Required Arguments
XDATA — Array of
length NXDATA
containing the data points in the X-direction.
(Input)
XDATA must be
nondecreasing.
YDATA — Array of
length NYDATA
containing the data points in the Y-direction.
(Input)
YDATA must be
nondecreasing.
FDATA — Array of
size NXDATA by
NYDATA
containing the values on the X − Y grid to be
interpolated. (Input)
FDATA(I, J) contains the value
at (XDATA(I), YDATA(I)).
KXORD — Order of the spline in the X-direction. (Input)
KYORD — Order of the spline in the Y-direction. (Input)
XKNOT — Array of
length KXORD +
NXCOEF
containing the knots in the X-direction.
(Input)
XKNOT must be
nondecreasing.
YKNOT — Array of
length KYORD +
NYCOEF
containing the knots in the Y-direction.
(Input)
YKNOT must be
nondecreasing.
BSCOEF — Array of
length NXCOEF
* NYCOEF that contains
the tensor product B-spline coefficients. (Output)
BSCOEF is treated
internally as an array of size NXCOEF by NYCOEF.
Optional Arguments
NXDATA — Number
of data points in the X-direction.
(Input)
Default: NXDATA = size (XDATA,1).
NYDATA — Number
of data points in the Y-direction.
(Input)
Default: NYDATA = size (YDATA,1).
LDF — Leading
dimension of FDATA exactly as
specified in the dimension statement of calling program.
(Input)
Default: LDF = size (FDATA,1).
NXCOEF — Number
of B-spline coefficients in the X-direction.
(Input)
Default: NXCOEF = size (XKNOT,1) – KXORD.
NYCOEF — Number
of B-spline coefficients in the Y-direction.
(Input)
Default: NYCOEF = size (YKNOT,1) – KYORD.
XWEIGH — Array of
length NXDATA
containing the positive weights of XDATA.
(Input)
Default: XWEIGH = 1.0.
YWEIGH — Array of
length NYDATA
containing the positive weights of YDATA.
(Input)
Default: YWEIGH = 1.0.
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic:
CALL
BSLS2 (XDATA, YDATA, FDATA, KXORD, KYORD, XKNOT, YKNOT,
BSCOEF [,…])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_BSLS2 and D_BSLS2.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: CALL BSLS2 (NXDATA, XDATA, NYDATA, YDATA, FDATA, LDF, KXORD, KYORD, XKNOT, YKNOT, NXCOEF, NYCOEF, XWEIGH, YWEIGH, BSCOEF)
Double: The double precision name is DBSLS2.
Description
The routine BSLS2
computes the coefficients of a tensor-product spline least-squares approximation
to weighted tensor-product data. The input for this subroutine consists of data
vectors to specify the tensor-product grid for the data, two vectors with the
weights, the values of the surface on the grid, and the specification for the
tensor-product spline. The grid is specified by the two vectors x = XDATA
and y = YDATA
of length n = NXDATA
and m = NYDATA,
respectively. A two-dimensional array f = FDATA
contains the data values that are to be fit. The two vectors
wx = XWEIGH
and wy = YWEIGH
contain the weights for the weighted least-squares problem. The information for
the approximating tensor-product spline must also be provided. This information
is contained in kx = KXORD,
tx = XKNOT,
and N = NXCOEF
for the spline in the first variable, and in ky = KYORD
, ty = YKNOT
and M = NYCOEF
for the spline in the second variable. The coefficients of the resulting
tensor-product spline are returned in c = BSCOEF,
which is an N *
M array. The procedure computes coefficients by solving the normal
equations in tensor-product form as discussed
in de Boor (1978, Chapter 17). The interested reader might also want to study the paper by E. Grosse (1980).
The final result produces coefficients c minimizing
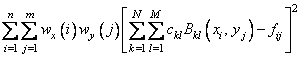
where the function Bkl is the tensor-product of two B-splines of order kx and ky. Specifically, we have
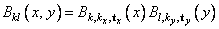
The spline
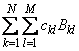
can be evaluated using BS2VL and its partial derivatives can be evaluated using BS2DR.
Comments
1. Workspace may be explicitly provided, if desired, by use of B2LS2/DB2LS2. The reference is:
CALL B2LS2 (NXDATA, XDATA, NYDATA, YDATA, FDATA, LDF, KXORD, KYORD, XKNOT, YKNOT, NXCOEF, NYCOEF, XWEIGH, YWEIGH, BSCOEF, WK)
The additional argument is:
WK — Work array of length (NXCOEF + 1) * NYDATA + KXORD * NXCOEF + KYORD * NYCOEF + 3 * MAX(KXORD, KYORD).
2. Informational errors
Type Code
3 14 There may be less than one digit of accuracy in the least squares fit. Try using higher precision if possible.
4 5 Multiplicity of the knots cannot exceed the order of the spline.
4 6 The knots must be nondecreasing.
4 7 All weights must be greater than zero.
4 9 The data point abscissae must be nondecreasing.
4 10 The smallest element of the data point array must be greater than or equal to the K_ORDth knot.
4 11 The largest element of the data point array must be less than or equal to the (N_COEF + 1)st knot.
Example
The data for this example arise from the function ex sin(x + y) + ɛ on the rectangle [0, 3] × [0, 5]. Here, ɛ is a uniform random variable with range [−1, 1]. We sample this function on a 100 × 50 grid and then try to recover it by using cubic splines in the x variable and quadratic splines in the y variable. We print out the values of the function ex sin(x + y) on a 3 × 5 grid and compare these values with the values of the tensor-product spline that was computed using the IMSL routine BSLS2.
USE IMSL_LIBRARIES
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER KXORD, KYORD, LDF, NXCOEF, NXDATA, NXVEC, NYCOEF,&
NYDATA, NYVEC
PARAMETER (KXORD=4, KYORD=3, NXCOEF=15, NXDATA=100, NXVEC=4,&
NYCOEF=7, NYDATA=50, NYVEC=6, LDF=NXDATA)
!
INTEGER I, J, NOUT
REAL BSCOEF(NXCOEF,NYCOEF), EXP, F, FDATA(NXDATA,NYDATA),&
FLOAT, RNOISE, SIN, VALUE(NXVEC,NYVEC), X,&
XDATA(NXDATA), XKNOT(NXCOEF+KXORD), XVEC(NXVEC),&
XWEIGH(NXDATA), Y, YDATA(NYDATA),&
YKNOT(NYCOEF+KYORD), YVEC(NYVEC), YWEIGH(NYDATA)
INTRINSIC EXP, FLOAT, SIN
! Define function
F(X,Y) = EXP(X)*SIN(X+Y)
! Set random number seed
CALL RNSET (1234579)
! Set up X knot sequence.
DO 10 I=1, NXCOEF - KXORD + 2
XKNOT(I+KXORD-1) = 3.0*(FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(NXCOEF-KXORD+1))
10 CONTINUE
XKNOT(NXCOEF+1) = XKNOT(NXCOEF+1) + 0.001
! Stack knots.
DO 20 I=1, KXORD - 1
XKNOT(I) = XKNOT(KXORD)
XKNOT(I+NXCOEF+1) = XKNOT(NXCOEF+1)
20 CONTINUE
! Set up Y knot sequence.
DO 30 I=1, NYCOEF - KYORD + 2
YKNOT(I+KYORD-1) = 5.0*(FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(NYCOEF-KYORD+1))
30 CONTINUE
YKNOT(NYCOEF+1) = YKNOT(NYCOEF+1) + 0.001
! Stack knots.
DO 40 I=1, KYORD - 1
YKNOT(I) = YKNOT(KYORD)
YKNOT(I+NYCOEF+1) = YKNOT(NYCOEF+1)
40 CONTINUE
! Set up X-grid.
DO 50 I=1, NXDATA
XDATA(I) = 3.0*(FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(NXDATA-1))
50 CONTINUE
! Set up Y-grid.
DO 60 I=1, NYDATA
YDATA(I) = 5.0*(FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(NYDATA-1))
60 CONTINUE
! Evaluate function on grid and
! introduce random noise in [1,-1].
DO 70 I=1, NYDATA
DO 70 J=1, NXDATA
RNOISE = RNUNF()
RNOISE = 2.0*RNOISE - 1.0
FDATA(J,I) = F(XDATA(J),YDATA(I)) + RNOISE
70 CONTINUE
! Use default weights equal to 1.
!
! Compute least squares approximation.
CALL BSLS2 (XDATA, YDATA, FDATA, KXORD, KYORD, &
XKNOT, YKNOT, BSCOEF)
! Get output unit number
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
! Write heading
WRITE (NOUT,99999)
! Print interpolated values
! on [0,3] x [0,5].
DO 80 I=1, NXVEC
XVEC(I) = FLOAT(I-1)
80 CONTINUE
DO 90 I=1, NYVEC
YVEC(I) = FLOAT(I-1)
90 CONTINUE
! Evaluate spline
CALL BS2GD (0, 0, XVEC, YVEC, KXORD, KYORD, XKNOT,&
YKNOT, BSCOEF, VALUE)
DO 110 I=1, NXVEC
DO 100 J=1, NYVEC
WRITE (NOUT,'(5F15.4)') XVEC(I), YVEC(J),&
F(XVEC(I),YVEC(J)), VALUE(I,J),&
(F(XVEC(I),YVEC(J))-VALUE(I,J))
100 CONTINUE
110 CONTINUE
99999 FORMAT (13X, 'X', 14X, 'Y', 10X, 'F(X,Y)', 9X, 'S(X,Y)', 10X,&
'Error')
END
Output
X
Y
F(X,Y)
S(X,Y)
Error
0.0000
0.0000
0.0000
0.2782
-0.2782
0.0000
1.0000
0.8415
0.7762
0.0653
0.0000
2.0000
0.9093
0.8203
0.0890
0.0000
3.0000
0.1411
0.1391
0.0020
0.0000
4.0000
-0.7568
-0.5705
-0.1863
0.0000
5.0000
-0.9589
-1.0290
0.0701
1.0000
0.0000
2.2874
2.2678
0.0196
1.0000
1.0000
2.4717
2.4490
0.0227
1.0000
2.0000
0.3836
0.4947
-0.1111
1.0000
3.0000
-2.0572
-2.0378
-0.0195
1.0000
4.0000
-2.6066
-2.6218
0.0151
1.0000
5.0000
-0.7595
-0.7274
-0.0321
2.0000
0.0000
6.7188
6.6923
0.0265
2.0000
1.0000
1.0427
0.8492
0.1935
2.0000
2.0000
-5.5921
-5.5885
-0.0035
2.0000
3.0000
-7.0855
-7.0955
0.0099
2.0000
4.0000
-2.0646
-2.1588
0.0942
2.0000
5.0000
4.8545
4.7339
0.1206
3.0000
0.0000
2.8345 2.5971
0.2373
3.0000
1.0000
-15.2008
-15.1079
-0.0929
3.0000
2.0000
-19.2605
-19.1698
-0.0907
3.0000
3.0000
-5.6122
-5.5820
-0.0302
3.0000
4.0000
13.1959
12.6659
0.5300
3.0000
5.0000
19.8718
20.5170 -0.6452
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |