Approximates the gradient using central differences.
Required Arguments
FCN — User-supplied subroutine to evaluate the function to be minimized. The usage is CALL FCN (N, X, F), where
N – Length of X. (Input)
X – The point at which
the function is evaluated. (Input)
X should not be
changed by FCN.
F – The computed function value at the point X. (Output)
FCN must be declared EXTERNAL in the calling program.
XC — Vector of length N containing the point at which the gradient is to be estimated. (Input)
GC — Vector of length N containing the estimated gradient at XC. (Output)
Optional Arguments
N — Dimension of
the problem. (Input)
Default: N = size
(XC,1).
XSCALE — Vector
of length N
containing the diagonal scaling matrix for the variables. (Input)
In the absence of other information, set all entries to 1.0.
Default:
XSCALE =
1.0.
EPSFCN — Estimate
for the relative noise in the function. (Input)
EPSFCN must be less
than or equal to 0.1. In the absence of other information, set EPSFCN to
0.0.
Default: EPSFCN = 0.0.
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: CALL CDGRD (FCN, XC, GC [,…])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_CDGRD and D_CDGRD.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: CALL CDGRD (FCN, N, XC, XSCALE, EPSFCN, GC)
Double: The double precision name is DCDGRD.
Description
The routine CDGRD uses the following finite-difference formula to estimate the gradient of a function of n variables at x:
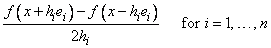
where hi = ɛ1/2 max{|xi|, 1/si} sign(xi), ɛ is the machine epsilon, si is the scaling factor of the i-th variable, and ei is the i-th unit vector. For more details, see Dennis and Schnabel (1983).
Since the finite-difference method has truncation error, cancellation error, and rounding error, users should be aware of possible poor performance. When possible, high precision arithmetic is recommended.
Comments
This is Description A5.6.4, Dennis and Schnabel, 1983, page 323.
Example
In this example, the gradient of f(x) = x1- x1x2 - 2 is estimated by the finite-difference method at the point (1.0, 1.0).
USE
CDGRD_INT
USE UMACH_INT
IMPLICIT
NONE
INTEGER I, N, NOUT
PARAMETER (N=2)
REAL EPSFCN, GC(N), XC(N)
EXTERNAL FCN
! Initialization.
DATA XC/2*1.0E0/
! Set function noise.
EPSFCN = 0.01
!
CALL CDGRD (FCN, XC, GC, EPSFCN=EPSFCN)
!
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) (GC(I),I=1,N)
99999 FORMAT (' The gradient is', 2F8.2, /)
!
END
!
SUBROUTINE FCN (N, X, F)
INTEGER N
REAL X(N), F
!
F = X(1) - X(1)*X(2) - 2.0E0
!
RETURN
END
Output
The gradient is 0.00 -1.00
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |