Computes the Hermite cubic spline interpolant.
Required Arguments
XDATA — Array of
length NDATA
containing the data point abscissas. (Input)
The data point
abscissas must be distinct.
FDATA — Array of length NDATA containing the data point ordinates. (Input)
DFDATA — Array of length NDATA containing the values of the derivative. (Input)
BREAK — Array of length NDATA containing the breakpoints for the piecewise cubic representation. (Output)
CSCOEF — Matrix of size 4 by NDATA containing the local coefficients of the cubic pieces. (Output)
Optional Arguments
NDATA — Number of
data points. (Input)
Default: NDATA = size (XDATA,1).
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: CALL CSHER (XDATA, FDATA, DFDATA, BREAK, CSCOEF [,…])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_CSHER and D_CSHER.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: CALL CSHER (NDATA, XDATA, FDATA, BREAK, CSCOEF)
Double: The double precision name is DCSHER.
Description
The routine CSHER computes a C 1 cubic spline interpolant to the set of data points
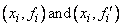
for i = 1, …, NDATA = N. The breakpoints of the spline are the abscissas.
If the data points arise from the values of a smooth (say C 4) function f, i.e.,
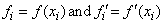
then the error will behave in a predictable fashion. Let ξ be the
breakpoint vector for the above spline interpolant. Then, the maximum absolute error satisfies
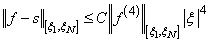
where
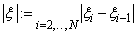
For more details, see de Boor (1978, page 51).
Comments
1. Workspace may be explicitly provided, if desired, by use of C2HER/DC2HER. The reference is:
CALL C2HER (NDATA, XDATA, FDATA, DFDATA, BREAK, CSCOEF, IWK)
The additional argument is:
IWK — Work array of length NDATA.
2. Informational error
Type Code
4 2 The XDATA values must be distinct.
3. The cubic spline can be evaluated using CSVAL; its derivative can be evaluated using CSDER.
4. Note that column NDATA of CSCOEF is used as workspace.
Example
In this example, a cubic spline interpolant to a function f is computed. The value of the function f and its derivative f ʹ are computed on the interpolation nodes and passed to CSHER. The values of this spline are then compared with the exact function values.
USE CSHER_INT
USE UMACH_INT
USE CSVAL_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER NDATA
PARAMETER (NDATA=11)
!
INTEGER I, NINTV, NOUT
REAL BREAK(NDATA), COS, CSCOEF(4,NDATA), DF,&
DFDATA(NDATA), F, FDATA(NDATA), FLOAT, SIN, X,&
XDATA(NDATA)
INTRINSIC COS, FLOAT, SIN
! Define function and derivative
F(X) = SIN(15.0*X)
DF(X) = 15.0*COS(15.0*X)
! Set up a grid
DO 10 I=1, NDATA
XDATA(I) = FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(NDATA-1)
FDATA(I) = F(XDATA(I))
DFDATA(I) = DF(XDATA(I))
10 CONTINUE
! Compute cubic spline interpolant
CALL CSHER (XDATA, FDATA, DFDATA, BREAK, CSCOEF)
! Get output unit number
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
! Write heading
WRITE (NOUT,99999)
99999 FORMAT (13X, 'X', 9X, 'Interpolant', 5X, 'Error')
NINTV = NDATA - 1
! Print the interpolant on a finer grid
DO 20 I=1, 2*NDATA - 1
X = FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(2*NDATA-2)
WRITE (NOUT,'(2F15.3, F15.6)') X, CSVAL(X,BREAK,CSCOEF)&
, F(X) - CSVAL(X,BREAK,&
CSCOEF)
20 CONTINUE
END
Output
X
Interpolant
Error
0.000
0.000
0.000000
0.050
0.673
0.008654
0.100
0.997 0.000000
0.150
0.768
0.009879
0.200
0.141
0.000000
0.250
-0.564
-0.007257
0.300
-0.978
0.000000
0.350
-0.848
-0.010906
0.400
-0.279
0.000000
0.450
0.444
0.005714
0.500
0.938
0.000000
0.550
0.911
0.011714
0.600
0.412
0.000000
0.650
-0.315
-0.004057
0.700
-0.880
0.000000
0.750
-0.956
-0.012288
0.800
-0.537
0.000000
0.850
0.180
0.002318
0.900
0.804
0.000000
0.950
0.981
0.012616
1.000
0.650 0.000000
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |