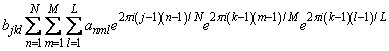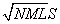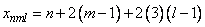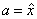Computes the inverse Fourier transform of a complex periodic three-dimensional array.
Required Arguments
A Three-dimensional complex matrix containing the data to be transformed. (Input)
B
Three-dimensional complex matrix containing the inverse Fourier coefficients of
A.
(Output)
The matrices A and B may be the same.
Optional Arguments
N1 Limit on the
first subscript of matrices A and B.
(Input)
Default: N1 = size (A,1).
N2 Limit on the
second subscript of matrices A and B.
(Input)
Default: N2 = size (A,2).
N3 Limit on the
third subscript of matrices A and B.
(Input)
Default: N3 = size (A,3).
LDA Leading
dimension of A exactly as specified
in the dimension statement of the calling program.
(Input)
Default: LDA = size (A,1).
MDA Middle
dimension of A exactly as specified
in the dimension statement of the calling program.
(Input)
Default: MDA = size (A,2).
LDB Leading
dimension of B exactly as specified
in the dimension statement of the calling program.
(Input)
Default: LDB = size (B,1).
MDB Middle
dimension of B exactly as specified
in the dimension statement of the calling program.
(Input)
Default: MDB = size (B,2).
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: CALL FFT3B (A, B [, ])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_FFT3B and D_FFT3B.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: CALL FFT3B (N1, N2, N3, A, LDA, MDA, B, LDB, MDB)
Double: The double precision name is DFFT3B.
Description
The routine FFT3B computes the inverse discrete complex Fourier transform of a complex three-dimensional array of size (N1 = N) Χ (N2 = M) Χ (N3 = L). The method used is a variant of the Cooley-Tukey algorithm, which is most efficient when N, M, and L are each products of small prime factors. If N, M, and L satisfy this condition, then the computational effort is proportional to N M L log N M L. This considerable savings has historically led people to refer to this algorithm as the fast Fourier transform or FFT.
Specifically, given an N ΄ M ΄ L array a, FFT3B returns in b
Furthermore, a vector of Euclidean norm S is mapped into a vector of norm
Finally, note that an unnormalized inverse is implemented in FFT3F. The routine FFT3B is based on the complex FFT in FFTPACK. The package FFTPACK was developed by Paul Swarztrauber at the National Center for Atmospheric Research.
Comments
1. Workspace may be explicitly provided, if desired, by use of F2T3B/DF2T3B. The reference is:
CALL F2T3B (N1, N2, N3, A, LDA, MDA, B, LDB, MDB, WFF1, WFF2, WFF3, CPY)
The additional arguments are as follows:
WFF1 Real array of length 4 * N1 + 15 initialized by FFTCI. The initialization depends on N1. (Input)
WFF2 Real array of length 4 * N2 + 15 initialized by FFTCI. The initialization depends on N2. (Input)
WFF3 Real array of length 4 * N3 + 15 initialized by FFTCI. The initialization depends on N3. (Input)
CPY Real array of size 2 * MAX(N1, N2, N3). (Workspace)
2. The routine FFT3B is most efficient when N1, N2, and N3 are the product of small primes.
3. If FFT3F/FFT3B is used repeatedly with the same values for N1, N2 and N3, then use FFTCI to fill WFF1(N = N1), WFF2(N = N2), and WFF3(N = N3). Follow this with repeated calls to F2T3F/F2T3B. This is more efficient than repeated calls to FFT3F/FFT3B.
Example
In this example, we compute the Fourier transform of the 2 ΄ 3 ΄ 4 array
for 1 ≤ n ≤ 2, 1 ≤ m ≤ 3, and 1 ≤ l ≤ 4 using the IMSL routine FFT3F. The result
is then inverted using FFT3B. Note that the result is an array b satisfying b = 2(3)(4)x = 24x. In general, FFT3B is an unnormalized inverse with expansion factor N M L.
INTEGER LDA, LDB, MDA, MDB, NDA, NDB
PARAMETER (LDA=2, LDB=2, MDA=3, MDB=3, NDA=4, NDB=4)
! SPECIFICATIONS FOR LOCAL VARIABLES
INTEGER I, J, K, L, M, N, N1, N2, N3, NOUT
COMPLEX A(LDA,MDA,NDA), B(LDB,MDB,NDB), X(LDB,MDB,NDB)
! SPECIFICATIONS FOR INTRINSICS
! SPECIFICATIONS FOR SUBROUTINES
X(N,M,L) = N + 2*(M-1) + 2*3*(L-1)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) (X(I,J,K),K=1,4)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) (A(I,J,K),K=1,4)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) (B(I,J,K),K=1,4)
99995 FORMAT (13X, 'The unnormalized inverse is')
99996 FORMAT (13X, 'The input for FFT3F is')
99997 FORMAT (/, 13X, 'The results from FFT3F are')
99998 FORMAT (/, ' Face no. ', I1)
99999 FORMAT (1X, 4('(',F6.2,',',F6.2,')',3X))
Output
The input for FFT3F is
Face no. 1
( 1.00,
0.00) ( 7.00, 0.00) ( 13.00,
0.00) ( 19.00, 0.00)
( 3.00, 0.00)
( 9.00, 0.00) ( 15.00, 0.00) (
21.00, 0.00)
( 5.00, 0.00) ( 11.00,
0.00) ( 17.00, 0.00) ( 23.00,
0.00)
Face no. 2
( 2.00, 0.00) (
8.00, 0.00) ( 14.00, 0.00) ( 20.00,
0.00)
( 4.00, 0.00) ( 10.00, 0.00)
( 16.00, 0.00) ( 22.00, 0.00)
( 6.00,
0.00) ( 12.00, 0.00) ( 18.00,
0.00) ( 24.00, 0.00)
The results from FFT3F
are
Face no. 1
(300.00, 0.00) (-72.00,
72.00) (-72.00, 0.00) (-72.00,-72.00)
(-24.00,
13.86) ( 0.00, 0.00) ( 0.00,
0.00) ( 0.00, 0.00)
(-24.00,-13.86)
( 0.00, 0.00) ( 0.00, 0.00)
( 0.00, 0.00)
Face no. 2
(-12.00, 0.00)
( 0.00, 0.00) ( 0.00, 0.00)
( 0.00, 0.00)
( 0.00, 0.00) (
0.00, 0.00) ( 0.00, 0.00) (
0.00, 0.00)
( 0.00, 0.00) ( 0.00,
0.00) ( 0.00, 0.00) ( 0.00,
0.00)
The unnormalized inverse is
Face no. 1
( 24.00,
0.00) (168.00, 0.00) (312.00,
0.00) (456.00, 0.00)
( 72.00, 0.00)
(216.00, 0.00) (360.00, 0.00) (504.00,
0.00)
(120.00, 0.00) (264.00, 0.00)
(408.00, 0.00) (552.00, 0.00)
Face no. 2
(
48.00, 0.00) (192.00, 0.00) (336.00,
0.00) (480.00, 0.00)
( 96.00, 0.00)
(240.00, 0.00) (384.00, 0.00) (528.00,
0.00)
(144.00, 0.00) (288.00, 0.00)
(432.00, 0.00) (576.00, 0.00)
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |