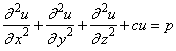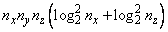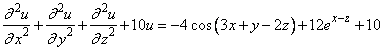Solves Poisson's or Helmholtz's equation on a three-dimensional box using a fast Poisson solver based on the HODIE finite-difference scheme on a uniform mesh.
Required Arguments
PRHS — User-supplied FUNCTION to evaluate the right side of the partial differential equation. The form is PRHS(X, Y, Z), where
X – The
x-coordinate value. (Input)
Y – The
y-coordinate value. (Input)
Z – The
z-coordinate value. (Input)
PRHS – Value of the
right side at (X, Y, Z).
(Output)
PRHS must be declared EXTERNAL in the calling program.
BRHS — User-supplied FUNCTION to evaluate the right side of the boundary conditions. The form is BRHS(ISIDE, X, Y, Z), where
ISIDE – Side
number. (Input)
See IBCTY for the definition of the side
numbers.
X – The x-coordinate
value. (Input)
Y – The y-coordinate
value. (Input)
Z – The z-coordinate
value. (Input)
BRHS – Value of the
right side of the boundary condition at (X, Y, Z).
(Output)
BRHS must be declared EXTERNAL in the calling program.
COEFU — Value of the coefficient of U in the differential equation. (Input)
NX — Number of
grid lines in the x-direction. (Input)
NX must be at least 4.
See Comment 2 for further restrictions on NX.
NY — Number of
grid lines in the y-direction. (Input)
NY must be at least 4.
See Comment 2 for further restrictions on NY.
NZ — Number of
grid lines in the y-direction. (Input)
NZ must be at least 4.
See Comment 2 for further restrictions on NZ.
AX — Value of X along the left side of the domain. (Input)
BX — Value of X along the right side of the domain. (Input)
AY — Value of Y along the bottom of the domain. (Input)
BY — Value of Y along the top of the domain. (Input)
AZ — Value of Z along the front of the domain. (Input)
BZ — Value of Z along the back of the domain. (Input)
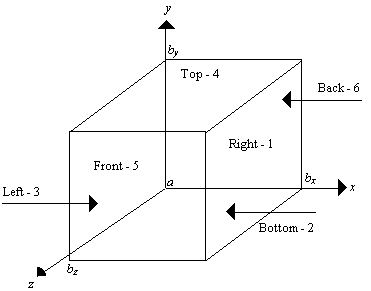
IBCTY — Array of
size 6 indicating the type of boundary condition on each face of the domain or
that the solution is periodic. (Input)
The sides are
numbers 1 to 6 as follows:
Side Location
1 - Right (X = BX)
2 - Bottom (Y = AY)
3 - Left (X = AX)
4 - Top (Y = BY)
5 - Front (Z = BZ)
6 - Back (Z = AZ)
There are three boundary condition types.
IBCTY Boundary Condition
1 Value of U is given. (Dirichlet)
2 Value of dU/dX is given (sides 1 and/or 3). (Neumann) Value of dU/dY is given (sides 2 and/or 4). Value of dU/dZ is given (sides 5 and/or 6).
3 Periodic.
U — Array of size NX by NY by NZ containing the solution at the grid points. (Output)
Optional Arguments
IORDER — Order of accuracy of the
finite-difference approximation. (Input)
It can be either 2 or
4. Usually, IORDER = 4 is
used.
Default: IORDER = 4.
LDU — Leading
dimension of U exactly as specified
in the dimension statement of the calling program.
(Input)
Default: LDU = size (U,1).
MDU — Middle
dimension of U exactly as specified
in the dimension statement of the calling program.
(Input)
Default: MDU = size (U,2).
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: CALL FPS3H (PRHS, BRHS, COEFU, NX, NY, NZ, AX, BX, AY, BY, AZ, BZ, IBCTY, U [,…])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_FPS3H and D_FPS3H.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: CALL FPS3H (PRHS, BRHS, COEFU, NX, NY, NZ, AX, BX, AY, BY, AZ, BZ, IBCTY, IORDER, U, LDU, MDU)
Double: The double precision name is DFPS3H.
Description
Let c = COEFU, ax = AX, bx = BX, nx = NX, ay = AY, by = BY, ny = NY, az = AZ, bz = BZ, and nz = NZ.
FPS3H is based on the code HFFT3D by Boisvert (1984). It solves the equation
on the domain (ax, bx) (ay, by) (az, bz) (a box) with a user-specified combination of Dirichlet (solution prescribed), Neumann (first derivative prescribed), or periodic boundary conditions. The six sides are numbered as shown in the following diagram.
When c = 0 and only Neumann or periodic boundary conditions are prescribed, then any constant may be added to the solution to obtain another solution to the problem. In this case, the solution of minimum -norm is returned.
The solution is computed using either a second-or fourth-order accurate finite-difference approximation of the continuous equation. The resulting system of linear algebraic equations is solved using fast Fourier transform techniques. The algorithm relies upon the fact that nx 1 and nz 1 are highly composite (the product of small primes). For details of the algorithm, see Boisvert (1984). If nx 1 and nz 1 are highly composite, then the execution time of FPS3H is proportional to
If evaluations of p(x, y, z)
are inexpensive, then the difference in running time between
IORDER
= 2 and IORDER
= 4 is small.
Comments
1. Workspace may be explicitly provided, if desired, by use of F2S3H/DF2S3H. The reference is:
CALL F2S3H (PRHS, BRHS, COEFU, NX, NY, NZ, AX, BX, AY, BY, AZ, BZ, IBCTY, IORDER, U, LDU, MDU, UWORK, WORK)
The additional arguments are as follows:
UWORK — Work array of size NX + 2 by NY + 2 by NZ + 2. If the actual dimensions of U are large enough, then U and UWORK can be the same array.
WORK — Work
array of length (NX + 1)(NY + 1)(NZ + 1)(IORDER 2)/2 + 2(NX * NY + NX * NZ + NY
* NZ) + 2(NX + NY + 1) +
MAX(2 * NX * NY, 2 * NX + NY + 4 * NZ + (NX + NZ)/2
+ 29)
2.
The grid spacing is the distance between the (uniformly spaced) grid lines. It
is given by the formulas
HX = (BX AX)/(NX 1),
HY = (BY AY)/(NY 1),
and
HZ = (BZ AZ)/(NZ 1).
The grid spacings in the X, Y and Z directions must be
the same, i.e., NX, NY and NZ must be such that
HX = HY = HZ. Also, as noted
above, NX, NY and NZ must all be at
least 4. To increase the speed of the Fast Fourier transform, NX 1 and NZ 1 should
be the product of small primes. Good choices for NX and NZ are 17, 33 and
65.
3. If COEFU is nearly equal to an eigenvalue of the Laplacian with homogeneous boundary conditions, then the computed solution might have large errors.
Example
This example solves the equation
with the boundary conditions u/z
= 2
sin(3x + y 2z) exp(x z) on the front side and
u =
cos(3x + y 2z) + exp(x z) + 1 on the other five
sides. The domain is the box [0, 1/4] × [0, 1/2] × [0, 1/2]. The output of FPS3H
is a 9 17 17 table of U values. The quadratic interpolation
routine QD3VL
is used to print a table of values.
! SPECIFICATIONS FOR PARAMETERS
INTEGER LDU, MDU, NX, NXTABL, NY, NYTABL, NZ, NZTABL
PARAMETER (NX=5, NXTABL=4, NY=9, NYTABL=3, NZ=9, &
INTEGER I, IBCTY(6), IORDER, J, K, NOUT
REAL AX, AY, AZ, BRHS, BX, BY, BZ, COEFU, FLOAT, PRHS, &
U(LDU,MDU,NZ), UTABL, X, ERROR, TRUE, &
XDATA(NX), Y, YDATA(NY), Z, ZDATA(NZ)
! Set boundary condition types
CALL FPS3H (PRHS, BRHS, COEFU, NX, NY, NZ, AX, BX, AY, BY, AZ, &
! Set up for quadratic interpolation
XDATA(I) = AX + (BX-AX)*FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(NX-1)
YDATA(J) = AY + (BY-AY)*FLOAT(J-1)/FLOAT(NY-1)
ZDATA(K) = AZ + (BZ-AZ)*FLOAT(K-1)/FLOAT(NZ-1)
WRITE (NOUT,'(8X,5(A,11X))') 'X', 'Y', 'Z', 'U', 'Error'
X = AX + (BX-AX)*FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(NXTABL-1)
Y = AY + (BY-AY)*FLOAT(J-1)/FLOAT(NYTABL-1)
Z = AZ + (BZ-AZ)*FLOAT(K-1)/FLOAT(NZTABL-1)
UTABL = QD3VL(X,Y,Z,XDATA,YDATA,ZDATA,U, CHECK=.false.)
TRUE = COS(3.0*X+Y-2.0*Z) + EXP(X-Z) + 1.0
WRITE (NOUT,'(5F12.4)') X, Y, Z, UTABL, ERROR
PRHS = -4.0*COS(3.0*X+Y-2.0*Z) + 12*EXP(X-Z) + 10.0
REAL FUNCTION BRHS (ISIDE, X, Y, Z)
BRHS = -2.0*SIN(3.0*X+Y-2.0*Z) - EXP(X-Z)
BRHS = COS(3.0*X+Y-2.0*Z) + EXP(X-Z) + 1.0
Output
X
Y
Z
U
Error
0.0000
0.0000 0.0000
3.0000
0.0000
0.0417
0.0000 0.0000
3.0348
0.0000
0.0833
0.0000 0.0000
3.0558
0.0001
0.1250
0.0000 0.0000
3.0637
0.0001
0.0000
0.1250 0.0000
2.9922
0.0000
0.0417
0.1250 0.0000
3.0115
0.0000
0.0833
0.1250 0.0000
3.0175
0.0000
0.1250
0.1250 0.0000
3.0107
0.0000
0.0000
0.2500 0.0000
2.9690
0.0001
0.0417
0.2500 0.0000
2.9731
0.0000
0.0833
0.2500 0.0000 2.9645
0.0000
0.1250
0.2500 0.0000
2.9440
-0.0001
0.0000
0.0000 0.1250
2.8514
0.0000
0.0417
0.0000 0.1250
2.9123
0.0000
0.0833
0.0000 0.1250
2.9592
0.0000
0.1250 0.0000
0.1250
2.9922
0.0000
0.0000
0.1250 0.1250
2.8747
0.0000
0.0417
0.1250 0.1250
2.9211
0.0010
0.0833
0.1250 0.1250
2.9524
0.0010
0.1250
0.1250 0.1250
2.9689
0.0000
0.0000
0.2500 0.1250
2.8825
0.0000
0.0417
0.2500 0.1250
2.9123
0.0000
0.0833
0.2500 0.1250
2.9281
0.0000
0.1250
0.2500 0.1250
2.9305
0.0000
0.0000
0.0000 0.2500
2.6314
-0.0249
0.0417
0.0000 0.2500
2.7420
-0.0004
0.0833
0.0000 0.2500
2.8112
-0.0042
0.1250
0.0000 0.2500
2.8609
-0.0138
0.0000
0.1250 0.2500
2.7093
0.0000
0.0417
0.1250 0.2500
2.8153
0.0344
0.0833
0.1250 0.2500
2.8628
0.0237
0.1250
0.1250 0.2500
2.8825
0.0000
0.0000
0.2500 0.2500
2.7351
-0.0127
0.0417
0.2500 0.2500
2.8030
-0.0011
0.0833
0.2500 0.2500
2.8424
-0.0040
0.1250
0.2500 0.2500
2.8735 -0.0012
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |