This function evaluates the logarithmic integral.
Function Return Value
ALI — Function value. (Output)
Required Arguments
X — Argument for
which the logarithmic integral is desired. (Input)
It must be
greater than zero and not equal to one.
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: ALI (X)
Specific: The specific interface names are S_ALI and D_ALI.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: ALI (X)
Double: The double precision function name is DALI.
Description
The logarithmic integral, li(x), is defined to be
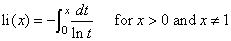
The argument x must be greater than zero and not equal to one. To avoid an undue loss of accuracy, x must be different from one at least by the square root of the machine precision.
The function li(x) approximates the function π(x), the number of primes less than or equal to x. Assuming the Riemann hypothesis (all non-real zeros of ζ(z) are on the line ℜz = 1/2), then
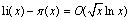
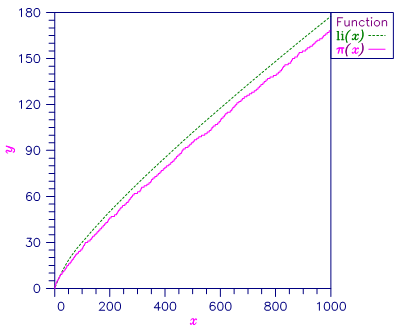
Figure 3- 2 Plot of li(x) and π(x)
Comments
Informational error
Type Code
3 2 Result of ALI(X) is accurate to less than one-half precision because X is too close to 1.0.
Example
In this example, li(2.3) is computed and printed.
USE ALI_INT
USE UMACH_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
! Declare variables
INTEGER NOUT
REAL VALUE, X
! Compute
X = 2.3
VALUE = ALI(X)
! Print the results
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) X, VALUE
99999 FORMAT (' ALI(', F6.3, ') = ', F6.3)
END
Output
ALI( 2.300) = 1.439
|
PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |