Class CsTCB
- All Implemented Interfaces:
Serializable,Cloneable
Let \(x=\)xData, \(y=\)yData,
and \(n = \) the length of xData and yData.
Class CsTCB computes the Kochanek-Bartels spline, a piecewise
cubic Hermite spline interpolant to the set of data points \({\{x_i, y_i\}}\)
for \(i = 0, \ldots, n-1\). The breakpoints of the spline are the abscissas.
As with all of the univariate interpolation functions, the abscissas need not be sorted.
The \(\{x_i\}\) values are the knots, so the \(i\)-th interval is \([x_i, x_{i+1}]\). (To simplify the explanation, it is assumed that the data points are given in increasing order.) The cubic Hermite in the \(i\)-th segment has a starting value of \(y_i\) and an ending value of \(y_{i+1}\). Its incoming tangent is
$$ DS_i = \frac{1}{2}(1-t_i)(1-c_i)(1+b_i)\frac{y_i-y_{i-1}}{x_{i+1}-x_i}+\frac{1}{2}(1-t_i)(1+c_i)(1-b_i)\frac{y_{i+1}-y_i}{x_{i+1}-x_i} $$
where \(t_i\) is the \(i\)-th tension value, \(c_i\) is the \(i\)-th continuity value, and \(b_i\) is the \(i\)-th bias value. Its outgoing tangent is$$ DD_i = \frac{1}{2}(1-t_i)(1+c_i)(1+b_i)\frac{y_i-y_{i-1}}{x_{i+1}-x_i}+\frac{1}{2}(1-t_i)(1-c_i)(1-b_i)\frac{y_{i+1}-y_i}{x_{i+1}-x_i} $$
The value of the tangent at the endpoint,left, is given as:
$$ \frac{y_0-y_{-1}}{x_1-x_0} $$
The value of the tangent at the endpoint, right, is given as:
$$ \frac{y_n-y_{n-1}}{x_n-x_{n-1}}$$
By default the values of the tangents at the leftmost and rightmost endpoints are zero. These values
can be reset via the setLeftEndTangent and setRightEndTangent methods.
The spline has a continuous first derivative (\(C^{-1}\)) if at each data point the left and right tangents are equal. This is true if the continuity parameters, \(c_i\), are all zero. For any values of the parameters the spline is continuous (\(C^{0}\)).
If \(t_i = c_i = b_i = 0 \) for all \(i\), then the curve is the Catmull-Rom spline.
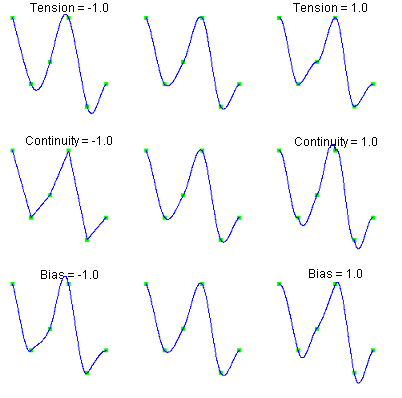
The following chart shows the same data points interpolated with different parameter values. All of the tension, continuity, and bias parameters are zero except for the labeled parameter, which has the indicated value at all data points.
Tension controls how sharply the spline bends at the data points. The tension values can be set via the
setTension method. If tension values are near +1, the curve tightens. If the
tension values are near -1, the curve slackens.
The continuity parameter controls the continuity of the first derivative. The continuity values
can be set via the setContinuity method. If the continuity value is zero, the
spline's first derivative is continuous, so the spline is \(C^{-1}\).
The bias parameter controls the weighting of the left and right tangents. If zero, the tangents are
equally weighted. If the bias parameter is near +1, the left tangent dominates. If the bias parameter is
near -1, the right tangent dominates. The bias values can be set via the setBias method.
- See Also:
-
Field Summary
Fields inherited from class com.imsl.math.Spline
breakPoint, coef, EPSILON_LARGE -
Constructor Summary
ConstructorsConstructorDescriptionCsTCB(double[] xData, double[] yData) Constructs the tension-continuity-bias (TCB) cubic spline interpolant to the given data points. -
Method Summary
Modifier and TypeMethodDescriptionvoidcompute()Computes the tension-continuity-bias (TCB) cubic spline interpolant.doubleReturns the value of the tangent at the leftmost endpoint.doubleReturns the value of the tangent at the rightmost endpoint.voidsetBias(double[] bias) Sets the bias values at the data points.voidsetContinuity(double[] continuity) Sets the continuity values at the data points.voidsetLeftEndTangent(double left) Sets the value of the tangent at the left endpoint.voidsetRightEndTangent(double right) Sets the value of the tangent at the right endpoint.voidsetTension(double[] tension) Sets the tension values at the data points.Methods inherited from class com.imsl.math.Spline
copyAndSortData, copyAndSortData, derivative, derivative, derivative, getBreakpoints, integral, value, value
-
Constructor Details
-
CsTCB
public CsTCB(double[] xData, double[] yData) Constructs the tension-continuity-bias (TCB) cubic spline interpolant to the given data points.- Parameters:
xData- adoublearray containing the x-coordinates of the data. Values must be distinct.xDataandyDatamust be of the same length.yData- adoublearray containing the y-coordinates of the data.xDataandyDatamust be of the same length.
-
-
Method Details
-
compute
public void compute()Computes the tension-continuity-bias (TCB) cubic spline interpolant. -
setBias
public void setBias(double[] bias) Sets the bias values at the data points.- Parameters:
bias- Adoublearray of lengthxData.lengthwhich contains bias values in the interval [-1,1]. For each point, if the bias value is zero, the left and right side tangents are equally weighted. If the value is near +1, the left-side tangent dominates. If the value is near -1, the right side tangent dominates. By default, all values ofbiasare zero.
-
setContinuity
public void setContinuity(double[] continuity) Sets the continuity values at the data points.- Parameters:
continuity- Adoublearray of lengthxData.lengthwhich contains continuity values in the interval [-1,1]. For each point, if the continuity value is zero, the curve is \(C^1\) at that point. Otherwise, the curve has a corner at that point, but is still continuous (\(C^0\)). By default, all values ofcontinuityare zero.
-
setTension
public void setTension(double[] tension) Sets the tension values at the data points.- Parameters:
tension- Adoublearray of lengthxData.lengthwhich contains tension values in the interval [-1,1]. For each point, if the tension value is near +1, the curve is tightened at that point. If it is near -1, the curve is slack. By default, all values oftensionare zero.
-
setLeftEndTangent
public void setLeftEndTangent(double left) Sets the value of the tangent at the left endpoint.- Parameters:
left- Adoublevalue of the tangent at the leftmost endpoint. The default value is zero.
-
setRightEndTangent
public void setRightEndTangent(double right) Sets the value of the tangent at the right endpoint.- Parameters:
right- Adoublevalue of the tangent at the rightmost endpoint. The default value is zero.
-
getLeftEndTangent
public double getLeftEndTangent()Returns the value of the tangent at the leftmost endpoint.- Returns:
- A
doublevalue of the tangent at the leftmost endpoint.
-
getRightEndTangent
public double getRightEndTangent()Returns the value of the tangent at the rightmost endpoint.- Returns:
- A
doublevalue of the tangent at the rightmost endpoint.
-