Class Sfun
- See Also:
-
Field Summary
FieldsModifier and TypeFieldDescriptionstatic final doubleThe largest relative spacing for doubles.static final doubleThe smallest relative spacing for doubles. -
Method Summary
Modifier and TypeMethodDescriptionstatic doublebeta(double a, double b) Returns the value of the beta function.static doublebetaIncomplete(double x, double p, double q) Returns the incomplete beta function ratio.static doublecot(double x) Returns the cotangent of adouble.static doubleerf(double x) Returns the error function of adouble.static doubleerfc(double x) Returns the complementary error function of adouble.static doubleerfce(double x) Returns the exponentially scaled complementary error function.static doubleerfcInverse(double x) Returns the inverse of the complementary error function.static doubleerfInverse(double x) Returns the inverse of the error function.static doublefact(int n) Returns the factorial of an integer.static doublegamma(double x) Returns the Gamma function of adouble.static doublegammaIncomplete(double a, double x) Evaluates the incomplete gamma function.static doublelog10(double x) Returns the common (base 10) logarithm of adouble.static doublelogBeta(double a, double b) Returns the logarithm of the beta function.static doublelogGamma(double x) Returns the logarithm of the absolute value of the Gamma function.static doublelogGammaCorrection(double x) Deprecated.static doublepoch(double a, double x) Returns a generalization of Pochhammer's symbol.static doublepsi(double x) Returns the derivative of the log gamma function, also called the digamma function.static doublepsi1(double x) Returns the \(\psi _1 \) function, also known as the trigamma function.static doubler9lgmc(double x) Deprecated.static doublesign(double x, double y) Returns the value of x with the sign of y.
-
Field Details
-
EPSILON_SMALL
public static final double EPSILON_SMALLThe smallest relative spacing for doubles.- See Also:
-
EPSILON_LARGE
public static final double EPSILON_LARGEThe largest relative spacing for doubles.- See Also:
-
-
Method Details
-
cot
public static double cot(double x) Returns the cotangent of adouble.- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the cotangent of x. If x is NaN, the result is NaN.
-
log10
public static double log10(double x) Returns the common (base 10) logarithm of adouble.- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the common logarithm ofx.
-
sign
public static double sign(double x, double y) Returns the value of x with the sign of y.- Parameters:
x- adoublevaluey- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the absolute value ofxand the sign ofy.
-
fact
public static double fact(int n) Returns the factorial of an integer.- Parameters:
n- anintvalue- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the factorial of n, n!. If n is negative, the result is NaN.
-
gamma
public static double gamma(double x) Returns the Gamma function of adouble.The gamma function, \(\Gamma (x)\), is defined to be
$$\Gamma \left( x \right) = \int_0^\infty {t^{x - 1} } e^{ - t} dt \,\,\,\, for \, x \gt 0$$
For \(x \lt 0\), the above definition is extended by analytic continuation.
The gamma function is not defined for integers less than or equal to zero. Also, the argument x must be greater than -170.56 so that \(\Gamma (x)\) does not underflow, and x must be less than 171.64 so that \(\Gamma (x)\) does not overflow. The underflow limit occurs first for arguments that are close to large negative half integers. Even though other arguments away from these half integers may yield machine-representable values of \(\Gamma (x)\), such arguments are considered illegal. Users who need such values should use the log gamma. Finally, the argument should not be so close to a negative integer that the result is less accurate than half precision.
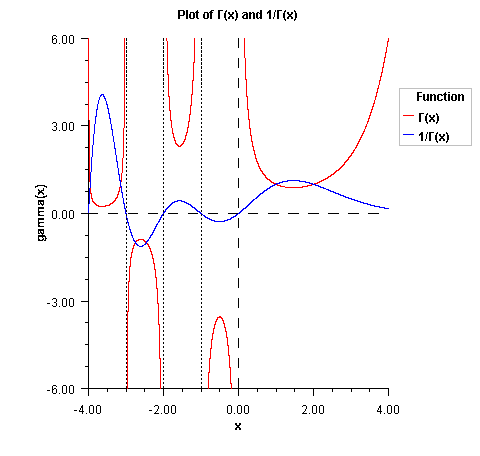
- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the Gamma function ofx. Ifxis a negative integer, the result is NaN. - See Also:
-
psi1
public static double psi1(double x) Returns the \(\psi _1 \) function, also known as the trigamma function.The trigamma function, \(\psi _1 (x)\), is defined to be
$$\psi _1\left(x\right)=\frac{d^2}{dx^2}\ln \Gamma(x)$$
The trigamma function is not defined for integers less than or equal to zero.
- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue, the point at which the trigamma function is to be evaluated.- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the trigamma function of x. If x is a negative integer or zero, the result is NaN. - See Also:
-
logGamma
public static double logGamma(double x) Returns the logarithm of the absolute value of the Gamma function.Method
logGammacomputes \(\ln\left|{\Gamma(x)} \right|\). Seegamma(double)for the definition of \(\Gamma(x)\).The gamma function is not defined for integers less than or equal to zero. Also, \(\left| x \right|\) must not be so large that the result overflows. Neither should x be so close to a negative integer that the accuracy is worse than half precision.
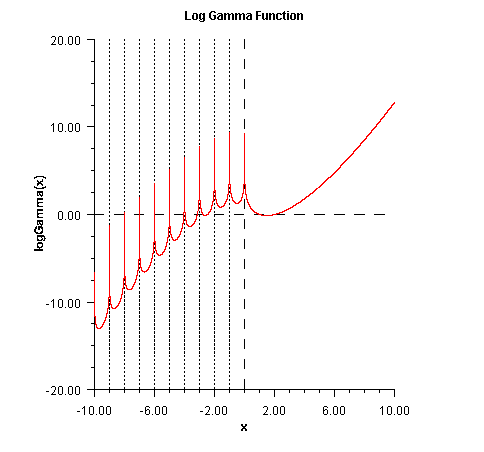
- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
double, the natural logarithm of the Gamma function ofx. If x is a negative integer, the result is NaN. - See Also:
-
r9lgmc
public static double r9lgmc(double x) Deprecated.Returns the log gamma correction term for argument values greater than or equal to 10.0.- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the log gamma correction term.
-
logGammaCorrection
public static double logGammaCorrection(double x) Deprecated.Returns the logarithm of the gamma correction term for argument values greater than or equal to 10.0.- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
doublecontaining the logarithm of the correction term.
-
beta
public static double beta(double a, double b) Returns the value of the beta function. The beta function is defined to be$$\beta(a,b)={{\Gamma(a)\Gamma(b)}\over {\Gamma(a+b)}}=\int_0^1{t^{a-1}}(1-t)^{b-1}dt$$
Seegamma(double)for the definition of \(\Gamma\left(x \right)\).The method
betarequires that both arguments be positive.- Parameters:
a- adoublevalueb- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the Beta function - See Also:
-
logBeta
public static double logBeta(double a, double b) Returns the logarithm of the beta function.Method
logBetacomputes \({\rm ln}\,\beta\left( {a,b}\right)={\rm ln}\,\beta\left({b,a}\right)\). Seebeta(double, double)for the definition of \(\beta\left({a,b}\right) \).logBetais defined for a \(\gt\) 0 and b \(\gt\) 0. It returns accurate results even when a or b is very small. It can overflow for very large arguments; this error condition is not detected except by the computer hardware.- Parameters:
a- adoublevalueb- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the natural logarithm of the beta function. - See Also:
-
betaIncomplete
public static double betaIncomplete(double x, double p, double q) Returns the incomplete beta function ratio. The incomplete beta function is defined to be$$I_x(p,\,\,q)={{\beta_x(p,\, \,q)}\over{\beta(p,\,\,q)}}={1\over{\beta(p,\,\,q)}}\int_0^x{t^{p-1}}(1-t )^{q-1}dt\,\,{\rm{for}}\,\,0\le x\le 1,\,p>0,\,q>0$$
Seebeta(double, double)for the definition of \(\beta\left({p,\,q} \right)\).The parameters p and q must both be greater than zero. The argument x must lie in the range 0 to 1. The incomplete beta function can underflow for sufficiently small x and large p; however, this underflow is not reported as an error. Instead, the value zero is returned as the function value.
The method
betaIncompleteis based on the work of Bosten and Battiste (1974).- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue specifying the upper limit of integration. It must be in the interval [0,1] inclusive.p- adoublevalue specifying the first Beta parameter. It must be positive.q- adoublevalue specifying the second Beta parameter. It must be positive.- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the incomplete Beta function ratio - See Also:
-
poch
public static double poch(double a, double x) Returns a generalization of Pochhammer's symbol.Method
pochevaluates Pochhammer's symbol \((a)_n = (a)(a - 1)\ldots (a - n + 1)\) for n a nonnegative integer. Pochhammer's generalized symbol is defined to be$$\left(a\right)_x=\frac{{\Gamma\left({a+x} \right)}}{{\Gamma\left(a\right)}}$$
See
gamma(double)for the definition of \(\Gamma (x)\).Note that a straightforward evaluation of Pochhammer's generalized symbol with either gamma or log gamma functions can be especially unreliable when a is large or x is small.
Substantial loss can occur if a + x or a are close to a negative integer unless \(\left|x\right|\) is sufficiently small. To insure that the result does not overflow or underflow, one can keep the arguments a and a + x well within the range dictated by the gamma function method gamma or one can keep \(\left|x\right|\) small whenever a is large.
pochalso works for a variety of arguments outside these rough limits, but any more general limits that are also useful are difficult to specify.- Parameters:
a- adoublevalue specifying the first argumentx- adoublevalue specifying the second, differential argument- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the generalized Pochhammer symbol, \( \frac{{\Gamma\left({a+x} \right)}}{{\Gamma\left(a\right)}}\) - See Also:
-
erf
public static double erf(double x) Returns the error function of adouble.The error function method,
erf(x), is defined to be$${\rm{erf}}\left(x\right)={2\over{\sqrt\pi}} \int_0^x{e^{-t^2}}dt$$
All values of x are legal.
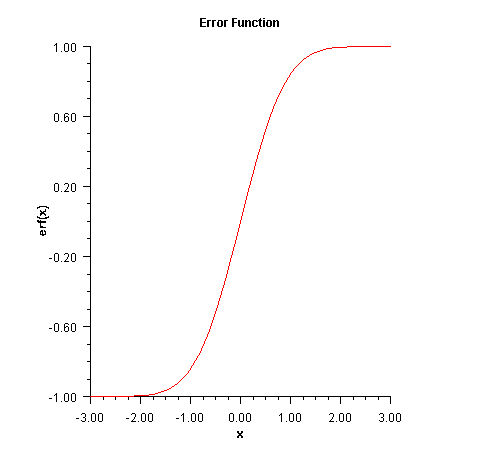
- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the error function of x - See Also:
-
erfc
public static double erfc(double x) Returns the complementary error function of adouble.The complementary error function method,
erfc(x), is defined to be$${\rm{erfc}}\left(x\right)={2\over{\sqrt\pi}} \int_x^\infty{e^{-t^2}}dt$$
The argument x must not be so large that the result underflows. Approximately, x should be less than
$${\left[-\ln\left({\sqrt{\pi}}s\right)\right]} ^{1/2}$$
where s =
Double.MIN_VALUEis the smallest representable positive floating-point number.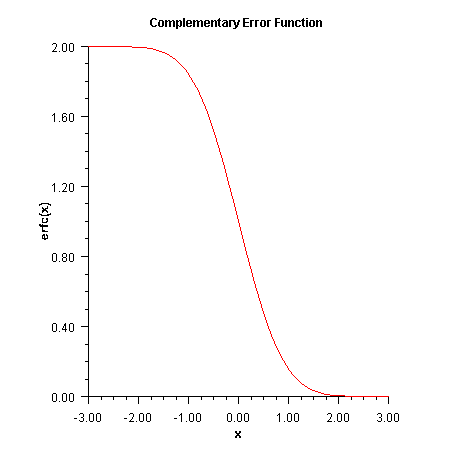
- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the complementary error function of x - See Also:
-
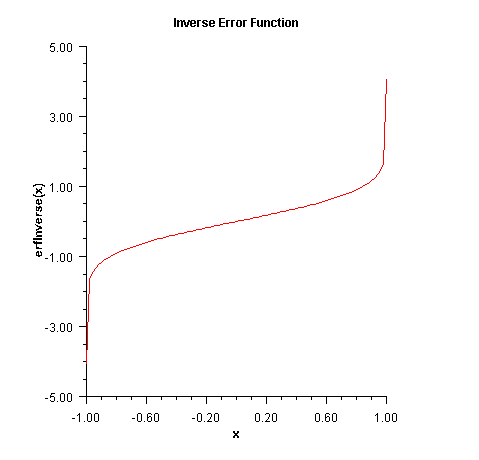
erfInverse
public static double erfInverse(double x) Returns the inverse of the error function.The
erfInversemethod computes the inverse of the error function erf x, defined inerf(double).The method
erfInverse(x)is defined for \(x_{\it max}\lt\left|x\right|\lt 1\), then the answer will be less accurate than half precision. Very approximately,$$x_{\max}\approx 1-\sqrt{\varepsilon /\left({ 4\pi}\right)}$$
where \(\varepsilon\) is the machine precision (approximately 1.11e-16).
- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the inverse of the error function ofx. - See Also:
-
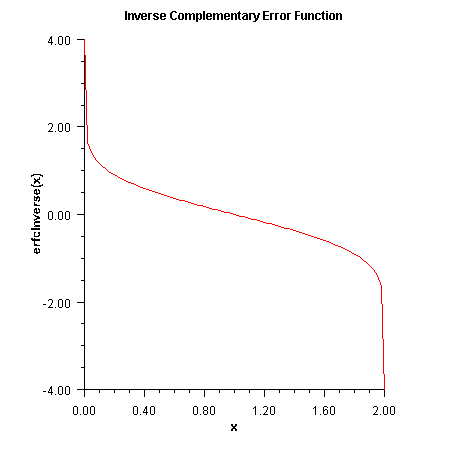
erfcInverse
public static double erfcInverse(double x) Returns the inverse of the complementary error function.The
erfcinversemethod computes the inverse of the complementary error function erfc x, defined inerfc.erfcinverse(x)is defined for \(0\lt x\lt 2 \). If \(x_{\max}\lt x\lt 2\), then the answer will be less accurate than half precision. Very approximately,$$x_{\it max}\approx 2-\sqrt{\varepsilon /(4\ pi)}$$
where \(\varepsilon\) = machine precision (approximately 1.11e-16).
- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue, \(0\le x\le 2\).- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the inverse of the error function ofx. - See Also:
-
erfce
public static double erfce(double x) Returns the exponentially scaled complementary error function.The exponentially scaled complementary error function is defined as
$$e^{x^{2}}\mathrm{erfc}(x)$$where erfc(x) is the complementary error function. See
erfc(double)for its definition.To prevent the answer from underflowing, x must be greater than
$$x_{\mathrm{min}}\simeq-\sqrt{\ln(b/2)} = -26.618735713751487$$where b =
Double.MAX_VALUEis the largest representable double precision number.- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue for which the function value is desired.- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the exponentially scaled complementary error function ofx.
-
gammaIncomplete
public static double gammaIncomplete(double a, double x) Evaluates the incomplete gamma function.The lower limit of integration of the incomplete gamma function, \(\gamma(a,x)\), is defined to be
$$\gamma(a,x)=\int_{0}^{x}t^{a-1}e^{-t}dt\;\;\;\; \mbox{for }x\ge0\mbox{ and }a>0$$Although \(\gamma(a,x)\) is well defined for \(x>-\infty\), this algorithm does not calculate \(\gamma(a,x)\) for negative x. For large a and sufficiently large x, \(\gamma(a,x)\) may overflow. \(\gamma(a,x)\) is bounded by \( \Gamma(a)\), and users may find this bound a useful guide in determining legal values for a.
Note that the upper limit of integration of the incomplete gamma, \(\Gamma(a,x)\), is defined to be
$$\Gamma(a,x)=\int_{x}^{\infty}t^{a-1}e^{-t}dt $$Therefore, by definition, the two incomplete gamma function forms satisfy the relationship
$$\Gamma(a,x)+\gamma(a,x)=\Gamma(a)$$- Parameters:
a- adoublevalue representing the integrand exponent parameter of the incomplete gamma function. It must be positive.x- adoublevalue specifying the point at which the incomplete gamma function is to be evaluated. It must be nonnegative.- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the incomplete gamma function.
-
psi
public static double psi(double x) Returns the derivative of the log gamma function, also called the digamma function.The psi function is defined to be $$\psi(x)= \frac{d}{dx}\ln\Gamma(x)=\frac{\Gamma'(x)}{\Gamma(x)}$$ See
gamma(double)for the definition of \(\Gamma(x)\).The argument x must not be exactly zero or a negative integer, or \(\psi(x)\) is undefined. Also, x must not be too close to a negative integer such that the accuracy of the result is less than half precision.
- Parameters:
x- adoublevalue, the point at which the digamma function is to be evaluated.- Returns:
- a
doublevalue specifying the logarithmic derivative of the gamma function of x. If x is a zero or a negative integer, the result is NaN. If x is too close to a negative integer the accuracy of the result will be less than half precision. - See Also:
-