| FeynmanKacIForcingTermForce Method |
Computes approximations to the forcing term 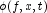 and its derivative
and its derivative 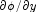 .
.
Namespace: Imsl.Math
Assembly: ImslCS (in ImslCS.dll) Version: 6.5.2.0
void Force( int interval, double[] y, double time, double width, double[] xlocal, double[] qw, double[,] u, double[] phi, double[,] dphi )
Parameters
- interval
- Type: SystemInt32
An int, the index related to the integration interval [xGrid[interval-1], xGrid[interval]]. - y
- Type: SystemDouble
An input double array of length 3*xGrid.Length containing the coefficients of the Hermite quintic spline representing the solution of the Feynman-Kac equation at time point time. For eachthe approximate solution is locally defined by![x \in [x_i,x_{i+1}], \, h_i=x_{i+1}-x_i, z_i=(x-x_i)/h_i,\,i=1,\ldots, \text{xGrid.Length}-1](eqn/eqn_1214.png) The values
The values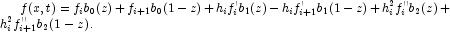
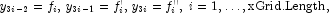 are stored as successive triplets in y.
are stored as successive triplets in y.
- time
- Type: SystemDouble
A double scalar, the time point. - width
- Type: SystemDouble
A double scalar, the width of the integration interval, width=xGrid[interval]-xGrid[interval-1]. - xlocal
- Type: SystemDouble
An input double array containing the Gauss-Legendre points translated and normalized to the interval [xGrid[interval-1], xGrid[interval]]. The array length is equal to the degree of the Gauss-Legendre polynomial. - qw
- Type: SystemDouble
An input double array containing the Gauss-Legendre weights. The array length is equal to the degree of the Gauss-Legendre polynomial. - u
- Type: SystemDouble
An input double matrix of dimension 12 by xlocal.Length containing the basis function values that define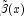 at the Gauss-Legendre
points xlocal. Setting
vector
at the Gauss-Legendre
points xlocal. Setting
vector![u_{k,i}:=\text{u[k,i]} \quad \mbox{and} \quad x_i:=\text{xlocal[i]} \,,](eqn/eqn_1218.png)
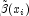 is defined as
is defined as
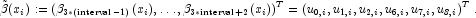
- phi
- Type: SystemDouble
An output double array of length 6 containing Gauss-Legendre approximations for the local contributionswhere t=time and![\phi_t := \int_{\text{xgrid[interval-1]}}^{\text{xgrid[interval]}}\phi(f,x,t)
\tilde{\beta}(x) dx,](eqn/eqn_1221.png)
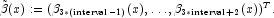 Denoting by degree the number of Gauss-Legendre points (xlocal.Length) and setting
Denoting by degree the number of Gauss-Legendre points (xlocal.Length) and setting
![x_j:=\text{xlocal[j]}](eqn/eqn_1223.png) , vector phi
contains elements
for i=0,...,5.
, vector phi
contains elements
for i=0,...,5.![\text{phi[i]} = \text{width}*\sum_{j=0}^{\text{degree-1}}\text{qw}[j]\,\tilde{\beta}_i(x_j)\,\phi(f,x_j,t)](eqn/eqn_1224.png)
- dphi
- Type: SystemDouble
An output double matrix of dimension 6 by 6 containing a Gauss-Legendre approximation for the Jacobian of the local contributions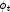 at time point t=time,
The approximation to this symmetric matrix is stored row-wise, i.e.
at time point t=time,
The approximation to this symmetric matrix is stored row-wise, i.e.![\frac{\partial \phi_t}{\partial y}=\int_{\text{xgrid[interval-1]}}^{\text{xgrid[interval]}}
\frac{\partial \phi (f,x,t)}{\partial f} \,\tilde{\beta}(x)\,\tilde{\beta}^T(x)dx\,.](eqn/eqn_1226.png) for i,j=0,...,5.
for i,j=0,...,5.![\text{dphi[i,j]} = \text{width} * \sum_{k=0}^{\text{degree-1}}\text{qw}[k]\,\tilde{\beta}_i(x_k)\,\tilde{\beta}_j(x_k)
\left. \frac{\partial{\phi}}{\partial f}\right|_{x=\text{xlocal}[k],\,t=\text{time}}](eqn/eqn_1227.png)