| MinConNLP Class |
Namespace: Imsl.Math
Assembly: ImslCS (in ImslCS.dll) Version: 6.5.2.0
The MinConNLP type exposes the following members.
| Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Equals | Determines whether the specified object is equal to the current object. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| Finalize | Allows an object to try to free resources and perform other cleanup operations before it is reclaimed by garbage collection. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| GetConstraintResiduals |
Returns the constraint residuals.
| |
| GetHashCode | Serves as a hash function for a particular type. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| GetLagrangeMultiplierEst |
Returns the Lagrange multiplier estimates of the constraints.
| |
| GetSolution |
Returns the last computed solution.
| |
| GetType | Gets the Type of the current instance. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| MemberwiseClone | Creates a shallow copy of the current Object. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| SetGuess |
Sets the initial guess of the minimum point of the input function.
| |
| SetXlowerBound |
Sets the lower bounds on the variables.
| |
| SetXscale |
The internal scaling of the variables.
| |
| SetXupperBound |
Sets the upper bounds on the variables.
| |
| Solve |
Solve a general nonlinear programming problem using the successive
quadratic programming algorithm with a finite-difference gradient or
with a user-supplied gradient.
| |
| ToString | Returns a string that represents the current object. (Inherited from Object.) |
| Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| BindingThreshold |
The binding threshold for constraints.
| |
| BoundViolationBound |
The amount by which bounds may be violated during numerical
differentiation.
| |
| DifferentiationType |
The type of numerical differentiation to be used.
| |
| FunctionPrecision |
The relative precision of the function evaluation routine.
| |
| GradientPrecision |
The relative precision in gradients.
| |
| MaximumIterations |
The maximum number of iterations allowed.
| |
| MultiplierError |
The error allowed in the multipliers.
| |
| NumberOfProcessors |
Perform the parallel calculations with the maximum possible number of
processors set to NumberOfProcessors.
| |
| Parallel |
Enable or disable performing MinConNLP.IFunction.F in parallel.
| |
| PenaltyBound |
The universal bound for describing how much the unscaled
penalty-term may deviate from zero.
| |
| ScalingBound |
The scaling bound for the internal automatic scaling of the
objective function.
| |
| ViolationBound |
Defines allowable constraint violations of the
final accepted result.
|
MinConNLP is based on the FORTRAN subroutine, DONLP2, by Peter Spellucci and licensed from TU Darmstadt. MinConNLP uses a sequential equality constrained quadratic programming method with an active set technique, and an alternative usage of a fully regularized mixed constrained subproblem in case of nonregular constraints (i.e. linear dependent gradients in the "working sets"). It uses a slightly modified version of the Pantoja-Mayne update for the Hessian of the Lagrangian, variable dual scaling and an improved Armjijo-type stepsize algorithm. Bounds on the variables are treated in a gradient-projection like fashion. Details may be found in the following two papers:
P. Spellucci: An SQP method for general nonlinear programs using only equality constrained subproblems. Math. Prog. 82, (1998), 413-448.
P. Spellucci: A new technique for inconsistent problems in the SQP method. Math. Meth. of Oper. Res. 47, (1998), 355-500. (published by Physica Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany).
The problem is stated as follows:
- A good initial starting point is very problem specific and should be provided by the calling program whenever possible. See method SetGuess.
- Gradient approximation methods can have an effect on the success of MinConNLP. Selecting a higher order approximation method may be necessary for some problems. See property DifferentiationType.
-
If a two sided constraint
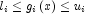 is transformed into two constraints,
is transformed into two constraints, 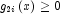 and
and 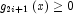 , then choose
, then choose 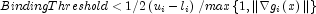 , or at least try to provide an estimate
for that value. This will increase the efficiency of the algorithm.
See property BindingThreshold.
, or at least try to provide an estimate
for that value. This will increase the efficiency of the algorithm.
See property BindingThreshold.
- The parameter ierr provided in the interface to the user supplied function F can be very useful in cases when evaluation is requested at a point that is not possible or reasonable. For example, if evaluation at the requested point would result in a floating point exception, then setting ierr to true and returning without performing the evaluation will avoid the exception. MinConNLP will then reduce the stepsize and try the step again. Note, if ierr is set to true for the initial guess, then an error is issued.