erfc¶
Evaluates the real complementary error function erfc(x).
Synopsis¶
erfc (x)
Required Arguments¶
- float
x(Input) - Point at which the complementary error function is to be evaluated.
Return Value¶
The value of the complementary error function erfc(x).
Description¶
The complementary error function erfc(x) is defined to be
\[\mathrm{erfc}(x) = \frac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}} \int_x^{\infty} e^{-t^2} dt\]
The argument x must not be so large that the result underflows.
Approximately, x should be less than
\[\left[-\ln(\sqrt{\pi}s)\right]^{1/2}\]
where s is the smallest representable floating-point number.
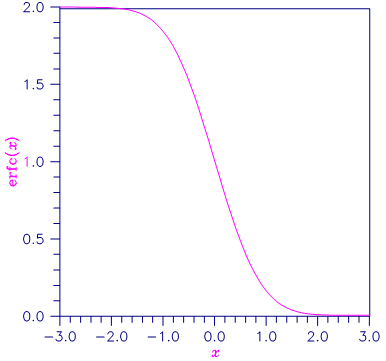
Figure 9.9 — Plot of erfc(x)
Example¶
Evaluate the error function at \(x=1/2\).
from __future__ import print_function
from numpy import *
from pyimsl.math.erfc import erfc
x = 0.5
ans = erfc(x)
print("erfc(%f) = %f" % (x, ans))
Output¶
erfc(0.500000) = 0.479500
Alert Errors¶
IMSL_LARGE_ARG_UNDERFLOW |
The argument x is so large that the result underflows. |