.p>.CMCH8.DOC!NONLIN_LEAST_SQUARES;nonlin_least_squares
Solve a nonlinear least-squares problem using a modified Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares (void fcn(), int m, int n, ¼, 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_nonlin_least_squares.
Required Arguments
void fcn (int m, int n, float x[], float f[])
(Input/Output)
User-supplied function to evaluate the function that defines
the least-squares problem where x is a vector of
length n at
which point the function is evaluated, and f is a vector of
length m
containing the function values at point x.
int m
(Input)
Number of functions.
int n
(Input)
Number of variables where n ≤ m.
Return Value
A pointer to the solution x of the nonlinear least-squares problem. To release this space, use free. If no solution can be computed, then NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares (void
fcn(),
int
m, int n,
IMSL_XGUESS, float
xguess[],
IMSL_JACOBIAN, void
jacobian(),
IMSL_XSCALE, float
xscale[],
IMSL_FSCALE, float
fscale[],
IMSL_GRAD_TOL, float
grad_tol,
IMSL_STEP_TOL, float
step_tol,
IMSL_REL_FCN_TOL, float
rfcn_tol,
IMSL_ABS_FCN_TOL, float
afcn_tol,
IMSL_MAX_STEP, float
max_step,
IMSL_INIT_TRUST_REGION, float
trust_region,
IMSL_GOOD_DIGIT, int
ndigit,
IMSL_MAX_ITN, int
max_itn,
IMSL_MAX_FCN, int
max_fcn,
IMSL_MAX_JACOBIAN, int
max_jacobian,
IMSL_INTERN_SCALE,
IMSL_TOLERANCE, float
tolerance,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
x[],
IMSL_FVEC, float
**fvec,
IMSL_FVEC_USER, float
fvec[],
IMSL_FJAC, float
**fjac,
IMSL_FJAC_USER, float
fjac[],
IMSL_FJAC_COL_DIM, int
fjac_col_dim,
IMSL_RANK, int
*rank,
IMSL_JTJ_INVERSE, float
**jtj_inv,
IMSL_JTJ_INVERSE_USER, float
jtj_inv[],
IMSL_JTJ_INV_COL_DIM, int
jtj_inv_col_dim,
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA,
void
fcn(),
void *data,
IMSL_JACOBIAN_W_DATA,
void
jacobian(),
void *data,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_XGUESS, float xguess[]
(Input)
Array with n components
containing an initial guess.
Default: xguess = 0
IMSL_JACOBIAN, void jacobian
(int
m,
int
n,
float
x[],
float
fjac[],
int
fjac_col_dim)(Input)
User-supplied function to compute the Jacobian
where x is a
vector of length n at which point the
Jacobian is evaluated, fjac is the computed
m ´ n Jacobian
at the point x,
and fjac_col_dim
is the column dimension of fjac.
Note that
each derivative ¶fi/¶xj should be returned in fjac[(i1)*fjac_col_dim+j-1]
IMSL_XSCALE, float xscale[]
(Input)
Array with n components
containing the scaling vector for the variables. xscale is used mainly
in scaling the gradient and the distance between two points. See keywords IMSL_GRAD_TOL and
IMSL_STEP_TOL
for more detail.
Default: xscale[] = 1
IMSL_FSCALE, float fscale[]
(Input)
Array with m components
containing the diagonal scaling matrix for the functions. The i-th
component of fscale is a positive
scalar specifying the reciprocal magnitude of the i-th component function
of the problem.
Default: fscale[] = 1
IMSL_GRAD_TOL, float grad_tol
(Input)
Scaled gradient tolerance. The i-th component of the scaled
gradient at x is
calculated as
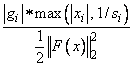
where g = Ñ F(x), s = xscale, and
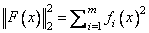
Default:
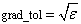
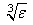 in
double where ɛ is the
machine precision
in
double where ɛ is the
machine precision
IMSL_STEP_TOL, float step_tol
(Input)
Scaled step tolerance. The i-th component of the scaled step
between two points x and y is computed as
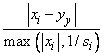
where s = xscale.
Default:
step_tol = ɛ2/3 where ɛ is the machine
precision.
IMSL_REL_FCN_TOL, float rfcn_tol
(Input)
Relative function tolerance.
Default: rfcn_tol = max (10-10, ɛ2/3),
max (10-20, ɛ2/3) in double,
where ɛ is the machine
precision
IMSL_ABS_FCN_TOL, float afcn_tol
(Input)
Absolute function tolerance.
Default: afcn_tol = max (10-20, ɛ2),
max (10-40, ɛ2) in double,
where ɛ is the machine
precision.
IMSL_MAX_STEP, float max_step
(Input)
Maximum allowable step size.
Default: max_step = 1000 max (ɛ1, ɛ2) where,
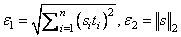
s = xscale, and t = xguess
IMSL_INIT_TRUST_REGION, float
trust_region (Input)
Size of initial trust region radius.
The default is based on the initial scaled Cauchy step.
IMSL_GOOD_DIGIT, int ndigit
(Input)
Number of good digits in the function.
Default: machine
dependent
IMSL_MAX_ITN, int max_itn
(Input)
Maximum number of iterations.
Default: max_itn = 100
IMSL_MAX_FCN, int max_fcn
(Input)
Maximum number of function evaluations.
Default: max_fcn = 400
IMSL_MAX_JACOBIAN, int
max_jacobian (Input)
Maximum number of Jacobian
evaluations.
Default: max_jacobian = 400
IMSL_INTERN_SCALE
Internal
variable scaling option. With this option, the values for xscale are set
internally.
IMSL_TOLERANCE, float tolerance
(Input)
The tolerance used in determining linear dependence for the
computation of the inverse of JTJ. For imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares,
if IMSL_JACOBIAN
is specified, then tolerance = 100 ´ imsl_d_machine(4) is
the default. Otherwise, the square root of imsl_f_machine(4) is
the default. For imsl_d_nonlin_least_
squares, if IMSL_JACOBIAN is
specified, then tolerance = 100 ´ imsl_machine(4) is the
default. Otherwise, the square root of imsl_d_machine(4) is
the default.
See imsl_f_machine
(Chapter 12, “Utilities”;).
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float x[]
(Output)
Array with n components
containing the computed solution.
IMSL_FVEC, float **fvec
(Output)
The address of a pointer to a real array of length m containing the
residuals at the approximate solution. On return, the necessary space is
allocated by imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares.
Typically, float *fvec is declared, and
&fvec is
used as an argument.
IMSL_FVEC_USER, float fvec[]
(Output)
A user-allocated array of size m containing the
residuals at the approximate solution.
IMSL_FJAC, float **fjac
(Output)
The address of a pointer to an array of size m ´ n containing the Jacobian at
the approximate solution. On return, the necessary space is allocated by imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares.
Typically, float *fjac is declared, and
&fjac is
used as an argument.
IMSL_FJAC_USER, float fjac[]
(Output)
A user-allocated array of size m ´ n containing the Jacobian at
the approximate solution.
IMSL_FJAC_COL_DIM, int
fjac_col_dim (Input)
The column dimension of fjac.
Default:
fjac_col_dim = n
IMSL_RANK, int *rank
(Output)
The rank of the Jacobian is returned in *rank.
IMSL_JTJ_INVERSE, float **jtj_inv
(Output)
The address of a pointer to an array of size n ´ n containing the inverse matrix
of JTJ where the J is the
final Jacobian. If JTJ is singular, the inverse is a
symmetric g2 inverse
of JTJ. (See imsl_f_lin_sol_nonnegdef in Chapter 1,
“Linear Systems” for a discussion of
generalized inverses and definition of the
g2 inverse.) On return, the
necessary space is allocated by imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares.
IMSL_JTJ_INVERSE_USER, float jtj_inv[]
(Output)
A user-allocated array of size n ´ n containing the inverse matrix
of JTJ where the J is the
Jacobian at the solution.
IMSL_JTJ_INV_COL_DIM, int
jtj_inv_col_dim (Input)
The column dimension of jtj_inv.
Default:
jtj_inv_col_dim = n
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA, void fcn (int m, int n, float x[], float f[], void *data),
void
*data (Input)
User supplied function to evaluate the function
that defines the least-squares problem, which also accepts a pointer to data
that is supplied by the user. data is a pointer to
the data to be passed to the user-supplied function. See the Introduction, Passing Data to
User-Supplied Functions at the beginning of this manual for more
details.
IMSL_JACOBIAN_W_DATA, void jacobian
(int
m,
int
n,
float
x[],
float
fjac[], int fjac_col_dim, void *data),
void
*data (Input)
User supplied function to compute the Jacobian,
which also accepts a pointer to data that is supplied by the user. data is a pointer to
the data to be passed to the user-supplied function. See the Introduction, Passing Data to
User-Supplied Functions at the beginning of this manual for more
details.
Description
The function imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares is based on the MINPACK routine LMDER by Moré et al. (1980). It uses a modified Levenberg-Marquardt method to solve nonlinear least-squares problems. The problem is stated as follows:
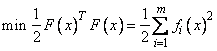
where m ³ n, F : Rn ® Rm, and fi(x) is the i-th component function of F(x). From a current point, the algorithm uses the trust region approach,
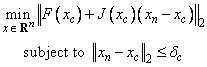
to get a new point xn, which is computed as
xn = xc − (J(xc)T J(xc) + μcI)-1 J(xc)T F(xc)
where μc = 0 if δc ³ ||(J(xc)T J(xc))-1
J(xc)T F(xc)||2 and μc > 0,
otherwise. The value
μc is defined by the
function. The vector and matrix F(xc) and
J(xc) are the function
values and the Jacobian evaluated at the current point xc, respectively. This
function is repeated until the stopping criteria are satisfied.
The first stopping criterion for imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares occurs when the norm of the function is less than the absolute function tolerance fcn_tol. The second stopping criterion occurs when the norm of the scaled gradient is less than the given gradient tolerance grad_tol. The third stopping criterion for imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares occurs when the scaled distance between the last two steps is less than the step tolerance step_tol. For more details, see Levenberg (1944), Marquardt (1963), or Dennis and Schnabel (1983, Chapter 10).
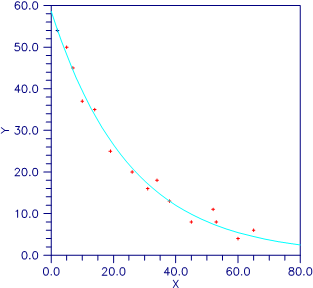
Figure 8-1 Plot of the Nonlinear Fit
Examples
Example 1
In this example, the nonlinear data-fitting problem found in Dennis and Schnabel (1983, p. 225),
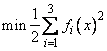
where
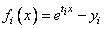
is solved with the data t = (1, 2, 3) and y = (2, 4, 3).
#include <stdio.h>
#include
<imsl.h>
#include
<math.h>
void
fcn(int, int, float[], float[]);
void
main()
{
int m=3,
n=1;
float *result,
fx[3];
result =
imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares(fcn, m, n,
0);
fcn(m, n, result,
fx);
/* Print results
*/
imsl_f_write_matrix("The
solution is", 1, 1, result, 0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("The function values are", 1, 3, fx,
0);
}
/* End of main */
void fcn(int m, int n, float x[], float
f[])
{
int
i;
float y[3] = {2.0, 4.0,
3.0};
float t[3] = {1.0, 2.0,
3.0};
for (i=0; i<m;
i++)
f[i] =
exp(x[0]*t[i]) -
y[i];
}
/* End of function */
Output
The solution
is
0.4401
The function
values are
1
2
3
-0.447
-1.589 0.744
Example 2
In this example, imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares is first invoked to fit the following nonlinear regression model discussed by Neter et al. (1983, pp. 475−478):

where the ei’s are independently distributed each normal with mean zero and variance σ2. The estimate of σ2 is then computed as
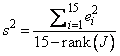
where ei is the i-th
residual and J is the Jacobian. The estimated asymptotic
variance-covariance matrix of 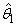 and
and 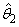 is computed as
is computed as
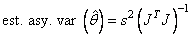 2
2
Finally, the diagonal elements of this matrix are used together with imsl_f_t_inverse_cdf (see Chapter 9, Special Functions) to compute 95% confidence intervals on θ1 and θ2.
#include
<math.h>
#include
<imsl.h>
void
exampl(int, int, float[], float[]);
void
main()
{
int i,
j, m=15, n=2, rank;
float a, *result,
e[15], jtj_inv[4], s2, dfe;
char
*fmt="%12.5e";
static
float xguess[2] = {60.0, -0.03};
static float
grad_tol = 1.0e-3;
result
= imsl_f_nonlin_least_squares(exampl, m, n,
IMSL_XGUESS,
xguess,
IMSL_GRAD_TOL,
grad_tol,
IMSL_FVEC_USER,
e,
IMSL_RANK, &rank,
IMSL_JTJ_INVERSE_USER,
jtj_inv,
0);
dfe = (float) (m - rank);
s2
= 0.0;
for (i=0; i<m;
i++)
s2 +=
e[i] * e[i];
s2 = s2 /
dfe;
j = n *
n;
for (i=0; i<j; i++)
jtj_inv[i] = s2 *
jtj_inv[i];
/*
Print results */
imsl_f_write_matrix
(
"Estimated Asymptotic Variance-Covariance
Matrix",
2, 2, jtj_inv, IMSL_WRITE_FORMAT, fmt,
0);
printf("
\n 95%% Confidence
Intervals \n
");
printf("
Estimate Lower Limit Upper Limit \n
");
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
j = i *
(n+1);
a =
imsl_f_t_inverse_cdf (0.975, dfe) *
sqrt(jtj_inv[j]);
printf(" %10.3f %12.3f %12.3f \n", result[i],
result[i] - a, result[i] + a);
}
}
/* End of main */
void exampl(int m, int n, float x[], float
f[])
{
int
i;
float y[15] = { 54.0,
50.0, 45.0, 37.0, 35.0, 25.0, 20.0, 16.0,
18.0, 13.0, 8.0, 11.0, 8.0, 4.0, 6.0
};
float xdata[15] = { 2.0, 5.0,
7.0, 10.0, 14.0, 19.0, 26.0,
31.0,
34.0, 38.0, 45.0, 52.0, 53.0, 60.0, 65.0 };
for (i=0; i<m; i++)
f[i] = y[i] -
x[0]*exp(x[1]*xdata[i]);
}
/* End of function */
Output
Estimated Asymptotic Variance-Covariance
Matrix
1
2
1
2.17524e+00
-1.80141e-03
2
-1.80141e-03
2.97216e-06
95% Confidence Intervals
Estimate Lower Limit Upper Limit
58.608
55.422 61.795
-0.040
-0.043 -0.036
Informational Errors
IMSL_STEP_TOLERANCE Scaled step tolerance satisfied. The current point may be an approximate local solution, but it is also possible that the algorithm is making very slow progress and is not near a solution, or that step_tol is too big.
Warning Errors
IMSL_LITTLE_FCN_CHANGE Both the actual and predicted relative reductions in the function are less than or equal to the relative function tolerance.
IMSL_TOO_MANY_ITN Maximum number of iterations exceeded.
IMSL_TOO_MANY_FCN_EVAL Maximum number of function evaluations exceeded.
IMSL_TOO_MANY_JACOBIAN_EVAL Maximum number of Jacobian evaluations exceeded.
IMSL_UNBOUNDED Five consecutive steps have been taken with the maximum step length.
Fatal Errors
IMSL_FALSE_CONVERGE The iterates appear to be converging to a noncritical point.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |