.p>.CMCH8.DOC!QUADRATIC_PROG;quadratic_prog
Solves a quadratic programming problem subject to linear equality or inequality constraints.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_quadratic_prog (int m, int n, int meq, float a[], float b[], float g[], float h[], ¼, 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_quadratic_prog.
Required Arguments
int m
(Input)
The number of linear constraints.
int n
(Input)
The number of variables.
int meq
(Input)
The number of linear equality constraints.
float a[]
(Input)
Array of size m ´ n containing the equality
constraints in the first meq rows, followed by
the inequality constraints.
float b[]
(Input)
Array with m components
containing right-hand sides of the linear constraints.
float g[]
(Input)
Array with n components
containing the coefficients of the linear term of the objective function.
float h[]
(Input)
Array of size n ´ n containing the Hessian matrix
of the objective function. It must be symmetric positive definite. If h is not positive
definite, the algorithm attempts to solve the QP problem with h replaced by h + diag* I such
that h + diag* I is
positive definite.
Return Value
A pointer to the solution x of the QP problem. To release this space, use free. If no solution can be computed, then NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_quadratic_prog (int
m, int n, int meq, float
a[],
float b[], float
g[],
float
h[],
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int
a_col_dim,
IMSL_H_COL_DIM, int
h_col_dim,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
x[],
IMSL_DUAL, float
**y,
IMSL_DUAL_USER, float
y[],
IMSL_ADD_TO_DIAG_H, float
*diag,
IMSL_OBJ, float
*obj,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int a_col_dim
(Input)
Leading dimension of A exactly as specified in the dimension
statement of the calling program.
Default: a_col_dim = n
IMSL_H_COL_DIM, int h_col_dim
(Input)
Leading dimension of h exactly as specified
in the dimension statement of the calling program.
Default: n_col_dim = n
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float x[]
(Output)
Array with n components
containing the solution.
IMSL_DUAL, float **y
(Output)
The address of a pointer y to an array with
m components
containing the Lagrange multiplier estimates. On return, the necessary space is
allocated by imsl_f_quadratic_prog.
Typically, float *y is declared, and
&y is used
as an argument.
IMSL_DUAL_USER, float y[]
(Output)
A user-allocated array with m components. On
return, y
contains the Lagrange multiplier estimates.
IMSL_ADD_TO_DIAG_H, float *diag
(Output)
Scalar equal to the multiple of the identity matrix added to h to give a positive
definite matrix.
IMSL_OBJ, float *obj
(Output)
The optimal object function found.
Description
The function imsl_f_quadratic_prog is based on M.J.D. Powell’s implementation of the Goldfarb and Idnani dual quadratic programming (QP) algorithm for convex QP problems subject to general linear equality/inequality constraints (Goldfarb and Idnani 1983); i.e., problems of the form
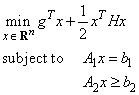
given the vectors b1, b2, and g, and the matrices H, A1, and A2. H is required to be positive definite. In this case, a unique x solves the problem or the constraints are inconsistent. If H is not positive definite, a positive definite perturbation of H is used in place of H. For more details, see Powell (1983, 1985).
If a perturbation of H, H + aI, is used in the QP problem, then H + aI also should be used in the definition of the Lagrange multipliers.
Examples
Example 1
The quadratic programming problem
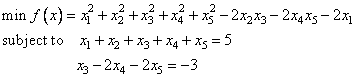
is solved.
#include
<imsl.h>
main()
{
int m = 2;
int n = 5;
int meq =
2;
float
*x;
float h[ ] =
{2.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0,
0.0, 2.0,-2.0, 0.0,
0.0,
0.0,-2.0, 2.0, 0.0,
0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
2.0,-2.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0,-2.0, 2.0};
float a[ ] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0,-2.0,-2.0};
float b[ ] = {5.0,
-3.0};
float g[ ]
= {-2.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0};
/* Solve the QP problem */
x = imsl_f_quadratic_prog
(m, n, meq, a, b, g, h,
0);
/* Print x */
imsl_f_write_matrix ("x", 1, 5, x,
0);
}
Output
x
1
2
3
4
5
1
1
1
1 1
Example 2
Another quadratic programming problem
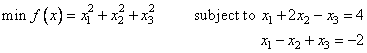
is solved.
#include <imsl.h>
float h[
] = {2.0, 0.0,
0.0,
0.0, 2.0,
0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 2.0};
float a[ ] = {1.0, 2.0,
-1.0,
1.0, -1.0, 1.0};
float b[ ] = {4.0,
-2.0};
float g[ ] = {0.0, 0.0,
0.0};
main()
{
int m =
2;
int n =
3;
int meq =
2;
float
obj;
float
d[2];
float
*x;
/* Solve the QP problem */
x =
imsl_f_quadratic_prog (m, n, meq, a, b, g, h,
IMSL_OBJ, &obj,
IMSL_DUAL_USER, d,
0);
/* Print x */
imsl_f_write_matrix ("x", 1, 3, x,
0);
/* Print d */
imsl_f_write_matrix ("d", 1, 2,
d, 0);
printf("\n obj = %g \n", obj);
}
Output
x
1
2
3
0.286
1.429
-0.857
d
1
2
1.143
-0.571
obj = 2.85714
Warning Errors
IMSL_NO_MORE_PROGRESS Due to the effect of computer rounding error, a change in the variables fail to improve the objective function value; usually the solution is close to optimum.
Fatal Errors
IMSL_SYSTEM_INCONSISTENT The system of equations is inconsistent. There is no solution.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |