Creates a multilayered feedforward neural network.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
Imsls_f_NN_Network
*ffnet imsls_f_mlff_network_init
(int
n_inputs,
int n_outputs)
void imsls_f_mlff_network (Imsls_f_NN_Network *ff_net, ..., 0)
void imsls_f_mlff_network_free (Imsls_f_NN_Network *ff_net)
The type double functions are imsls_d_mlff_network_init, imsls_d_mlff_network, and imsls_d_mlff_network_free.
The function imsl_f_mlff_network_init is used to initialize the network, the function imsl_f_mlff_network is used to build up the network in preparation for training, and the function imsl_f_mlff_network_free is used to free the internally allocated structure ff_net. Descriptions of these functions are provided below.
Required Arguments for imsls_f_mlff_network_init
int n_inputs
(Input/Output)
Number of input attributes in the network.
int n_outputs
(Input)
Number of output attributes in the network.
Return Value for imsls_f_mlff_network_init
Pointer to structure of type Imsls_f_NN_Network containing the multilayered feed forward network.
Required Argument for imsls_f_mlff_network
Imsls_f_NN_Network *ff_net
(Input/Output)
Pointer to structure of type Imsls_f_NN_Network
containing the multilayered feed forward network.
Required Argument for imsls_f_mlff_network_free
Imsls_f_NN_Network *ff_net
(Input)
Pointer to structure of type Imsls_f_NN_Network containing
the multilayered feed forward network.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
void
imsls_f_mlff_network (Imsls_f_NN_Network
*ff_net,
IMSLS_CREATE_HIDDEN_LAYER, int
n_perceptrons,
IMSLS_ACTIVATION_FCN, int
layer_id,
int activation_fcn[],
IMSLS_BIAS, int
layer_id,
float bias[],
IMSLS_LINK_ALL,
IMSLS_LINK_LAYER, int to, int from,
IMSLS_LINK_NODE, int to, int
from,
IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK, int
to, int
from,
IMSLS_WEIGHTS, float
weights[],
IMSLS_N_LINKS, int
*n_links,
0)
Optional Arguments for imsls_f_mlff_network
IMSLS_CREATE_HIDDEN_LAYER, int
n_perceptrons (Input)
Creates a hidden layer with n_perceptrons.
To create one or more hidden layers imsls_f_mlff_network
must be called multiple times with optional argument IMSLS_CREATE_HIDDEN_LAYER.
Default:
No hidden layer is created.
IMSLS_ACTIVATION_FCN,
int layer_id, int
activation_fcn[]
(Input)
Specifies the activation function for each perceptron in a hidden
layer or the output layer, indicated by layer_id.
layer_id must be
between 1 and the number of layers. If a hidden layer has been created,
layer_id set to
1 will indicate the first hidden layer. If there are zero hidden layers,
layer_id set to
1 indicates the output layer. Argument activation_fcn is an
array of length n_perceptrons in layer_id, where n_perceptrons is the
number of perceptrons in layer_id. activation_fcn
contains the activation function for the ith perceptron. Valid
values for activation_fcn
are:
|
IMSLS_LINEAR |
Linear |
|
IMSLS_LOGISTIC |
Logistic |
|
IMSLS_TANH |
Hyperbolic-tangent |
|
IMSLS_SQUASH |
Squash |
Default: Output Layer activation_fcn[i] = IMSLS_LINEAR. All hidden layers activation_fcn[i] = IMSLS_LOGISTIC.
IMSLS_BIAS, int layer_id,
float bias[],
(Input)
Specifies the the bias values for each perceptron in a hidden layer
or the output layer, indicated by layer_id.
layer_id must be
between 1 and the number of layers. If a hidden layer has been created,
layer_id set to
1 indicates the first hidden layer. If there are zero hidden layers, layer_id set to 1
indicates the output layer. Argument bias is an array of
length n_perceptrons
in layer_id, where n_perceptrons is the
number of perceptrons in layer_id. bias contains the
initial bias values for the ith perceptron.
Default: bias[i] = 0.0
IMSLS_LINK_ALL, (Input)
Connects all nodes
in a layer to each node in the next layer, for all layers in the network. To
create a valid network, use IMSLS_LINK_ALL, IMSLS_LINK_LAYER, or
IMSLS_LINK_NODE.
IMSLS_LINK_LAYER,
int to,
int
from (Input)
Creates a link between all nodes in layer
from to all
nodes in layer to. Layers are
numbered starting at zero with the input layer, then the hidden layers in the
order they are created, and finally the output layer. To create a valid network,
use IMSLS_LINK_ALL, IMSLS_LINK_LAYER, or
IMSLS_LINK_NODE.
or
IMSLS_LINK_NODE,
int to,
int from
(Input)
Links node from to node to. Nodes are numbered starting at zero with
the input nodes, then the hidden layer perceptrons, and finally the output
perceptrons. To create a valid
network, use IMSLS_LINK_ALL, IMSLS_LINK_LAYER, or
IMSLS_LINK_NODE.
or
IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,
int
to, int
from (Input)
Removes the link between node from and node to. Nodes are
numbered starting at zero with the input nodes, then the hidden layer
perceptrons, and finally output perceptrons.
IMSLS_WEIGHTS,
float
weights[] (Input)
Array of length n_links containing the
initial weight for the ith link in the network. See keyword IMSLS_N_LINKS.
Default: weights[] = 1.0.
IMSLS_N_LINKS,
int
*n_links (Output)
Returns the number of links in the
network.
Description
A multilayerd feedforward network contains an input layer, an output layer and zero or more hidden layers. The input and output layers are created by the function imsls_f_mlff_network_init, where n_inputs specifies the number of inputs in the input layer and n_outputs specifies the number of perceptrons in the output layer. The hidden layers are created by one or more calls to imsls_f_mlff_network with the keyword IMSLS_CREATE_HIDDEN_LAYER, where n_perceptrons specifies the number of perceptrons in the hidden layer.
The network also contains links or connections between nodes. Links are created by using one of the three optional arguments in the imsls_f_mlff_network function, IMSLS_LINK_ALL, IMSLS_LINK_LAYER, IMSLS_LINK_NODE. The most useful is the IMSLS_LINK_ALL, which connects every node in each layer to every node in the next layer. A feed forward network is a network in which links are only allowed from one layer to a following layer.
Each link has a weight and gradient value. Each perceptron node has a bias value. When the network is trained, the weight and bias values are used as initial guesses. After the network is trained using imsls_f_mlff_network_trainer, the weight, gradient and bias values are updated in the Imsls_f_NN_Network structure.
Each perceptron has an activation function g, and a biasm. The value of the percepton is given by g(Z), where g is the activation function and z is the potential calculated using
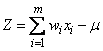
where xi are the values of nodes input to this perceptron with weights wi.
All information for the network is stored in the structure called Imsls_f_NN_Network. (If the type is double, then the structure name is Imsls_d_NN_Network.) This structure describes the network that is trained by imsls_f_mlff_network_trainer.
The following code gives a detailed description of this structure:
typedef struct
{
int n_layers;
Imsls_NN_Layer *layers;
int n_links;
int next_link;
Imsls_f_NN_Link *links;
int n_nodes;
Imsls_f_NN_Node *nodes;
} Imsls_f_NN_Network;
Where Imsls_NN_Layer is:
typedef struct
{
int n_nodes;
int *nodes;
} Imsls_NN_Layer;
Imsls_NN_Link is:
typedef struct
{
float weight;
int to_node;
int from_node;
} Imsls_f_NN_Link;
And, Imsls_NN_Node is:
typedef struct
{
int layer_id;
int n_inLinks;
int n_outLinks;
int *inLinks;
int *outLinks;
float delta;
float bias;
int ActivationFcn;
} Imsls_f_NN_Node;
In particular, if ff_net
is a pointer to the structure of type Imsls_f_NN_Network ,
then:
|
Structure member |
Description |
|
ff_net->n_layers |
Number of layers in network. Layers are numbered starting at 0 for the input layer. |
|
ff_net->n_nodes |
Total number of nodes in network, including the input attributes. |
|
ff_net->n_links |
Total number of links or connections between input attributes and perceptrons and between perceptrons from layer to layer. |
|
ff_net->layers[0] |
Input layer with n_inputs attributes. |
|
ff_net->layers[ff_net->n_layers-1] |
Output layer with n_outputs perceptrons. |
|
ff_net->layers[0].n_nodes |
n_inputs (number of input attributes). |
|
ff_net->layers[ffnet->n_layers-1].n_nodes |
n_outputs (number of output perceptrons). |
|
ff_net->layers[1].n_nodes |
Number of output perceptrons in first hidden layer. |
|
ff_net->n_links[i].weight |
|
|
ff_net->n_nodes[i].bias |
Initial bias value for the ith node. After the training has completed the bias value is updated. |
Table 3. Structure Members and Their Descriptions
Nodes are numbered starting at zero with the input nodes, then the hidden layer perceptrons and finally the output perceptrons.
Layers are numbered starting at zero with the input layer, then the hidden layers and finally the output layer. If there are zero hidden layers, the output layer is numbered one.
Use function imsls_f_mlff_network_free to free memory allocated by imsls_f_mlff_network_init.
Examples
Example 1
This code fragment creates a single-layer feedforward network. The network inputs are directly connected to the output perceptrons. The output perceptrons use the default linear activation function and default bias values of 0.0.
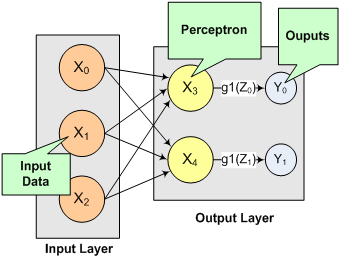
Figure 13- 8: A Single-Layer Feedforward Neural Net
#include "imsls.h"
void main()
{
Imsls_f_NN_Network *ffnet;
float *stats;
int n_obs= 100, n_cat=2, n_cont=1;
/* Data for categorical,continuous, and output omitted
See
imsls_f_mlff_network_trainer Example 1 for a complete
source code example */
…
ffnet = imsls_f_mlff_network_init(3,2);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_ALL, 0);
stats = imsls_f_mlff_network_trainer(ffnet, n_obs, n_cat, n_cont,
categorical,continuous, output,0);
imsls_f_mlff_network_free(ffnet);
}
Example 2
This code fragment creates a two-layer feedforward network with four inputs, one hidden layer with three perceptrons and two outputs.
Since the default activation function is linear for output and logistic for the hidden layers, to create a network that uses only linear activation you must specify the linear activation for each hidden layer in the network. This code fragment demonstrates how to change the activation function and bias values for hidden and output layer perceptrons as shown in Figure 13- 9 below.
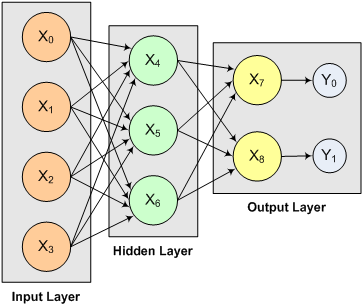
Figure 13- 9: A 2-layer, Feedforward Network with 4 Inputs and 2 Outputs
#include "imsls.h"
void main()
{
Imsls_f_NN_Network *ffnet;
float *stats;
int n_obs= 100, n_cat=5, n_cont=1;
int hidActFcn[3] ={IMSLS_LINEAR, IMSLS_LINEAR, IMSLS_LINEAR};
int outbias[1] = {1.0};
int hidbias[3] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
/* Data for categorical,continuous, and output Omitted
See imsls_f_mlff_network_trainer Example 1 for a complete
source code example */
…
ffnet = imsls_f_mlff_network_init(4,2);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_CREATE_HIDDEN_LAYER, 3,
IMSLS_ACTIVATION_FCN, 1, &hidActFcn,
IMSLS_BIAS, 2, &outbias,
IMSLS_LINK_ALL, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_BIAS, 1, &hidbias, 0);
stats = imsls_f_mlff_trainer(ffnet, n_obs, n_cat, n_cont,
categorical,continuous, output,
0);
imsls_f_mlff_network_free(ffnet);
}
Example 3
This example creates a three-layer feedforward network with six input nodes and they are not all connected to every node in the first hidden layer.
Note also that the four perceptrons in the first hidden layer are not connected to every node in the second hidden layer, and the perceptrons in the second hidden layer are not all connected to the two outputs.
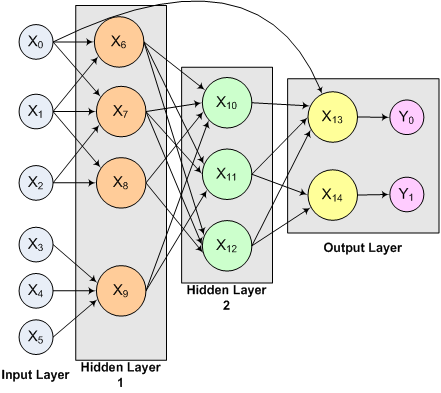
Figure 13- 10: This network uses
a total of nine perceptrons to produce two forecasts
from six input
attributes.
Links among the input nodes and perceptrons can be created using one of several approaches. If all inputs are connected to every perceptron in the first hidden layer, and if all perceptrons are connected to every perceptron in the following layer, which is a standard architecture for feed forward networks, then a call to the IMSLS_LINK_ALL method can be used to create these links.
However, this example does not use that standard configuration. Some links are missing. The keyword IMSLS_LINK_NODE can be used is to construct individual links or an alternative approach is to first create all links and then remove those that are not needed. The code fragment below illustrates this approach.
#include "imsls.h"
void main()
{
Imsls_f_NN_Network *ffnet;
float *stats;
int n_obs= 100, n_cat=4, n_cont=2;
ffnet =
imsls_f_mlff_network_init(6,2);
/* Create 2 hidden layers
and link all nodes 0 */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_CREATE_HIDDEN_LAYER, 4, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_CREATE_HIDDEN_LAYER, 3,
IMSLS_LINK_ALL, 0);
/* Remove unwanted links from Input 0 */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,8,0, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,9,0, 0);
/* Remove unwanted links from Input 1 */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,9,1, 0);
/* Remove unwanted links from Input 2 */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,6,2, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,9,2, 0);
/* Remove unwanted links from Input 3*/
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,6,3, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,7,3, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,8,3, 0);
/* Remove unwanted links from Input 4 */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,6,4, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,7,4, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,8,4, 0);
/* Remove unwanted links from Input 5 */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,6,5, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,7,5, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,8,5, 0);
/* Add link from Input 0 to Output Perceptron 0 */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_NODE,13,0, 0);
/* Remove unwanted links between hidden Layer 1 and hidden layer 2 */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,11,8, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,10,9, 0);
/* Remove unwanted links between hidden Layer 2 and output layer */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,14,10, 0);
stats = imsls_f_network_trainer(ffnet, n_obs, n_cat, n_cont,
categorical,continuous, output,
0);
imsls_f_mlff_network_free(ffnet);
}
Another approach is to use keywords LINK_NODE and LINK_LAYER to combine links between the two hidden layers, create individual links, and remove the links that are not needed. The following code fragment illustrates this approach:
#include "imsls.h"
void main()
{
Imsls_f_NN_Network *ffnet;
double *stats;
int n_obs= 100, n_cat=4, n_cont=2;
/* Data for categorical,continuous, and output Omitted
See imsls_network_trainer
Example 1 for complete
source code
example */
…
ffnet = imsls_f_mlff_network_init(6,2);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_CREATE_HIDDEN_LAYER, 4, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_CREATE_HIDDEN_LAYER, 3, 0);
/* Link input attributes to first hidden layer */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_NODE,6,0, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_NODE,7,0, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_NODE,6,1, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_NODE,7,1, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_NODE,8,1, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_NODE,7,2, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_NODE,8,2, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_NODE,9,3, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_NODE,9,4, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_NODE,9,5, 0);
/* Link hidden layer 1 to hidden layer 2 then remove unwanted links */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_LAYER,2,1, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,11,8, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,10,9, 0);
/* Link hidden layer 2 to output layer then remove unwanted links */
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_LINK_LAYER,3,2, 0);
imsls_f_mlff_network(ffnet, IMSLS_REMOVE_LINK,14,10, 0);
stats = imsls_f_mlff_network_trainer(ffnet, n_obs, n_cat, n_cont,
categorical,continuous, output,
0);
imsls_f_mlff_network_free(ffnet);
}
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |