Calculates forecasts for trained multilayered feedforward neural networks.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float
*imsls_f_mlff_network_forecast (Imsls_f_NN_Network
*ff_net,
int n_categorical, int n_continuous,
int
categorical[], float
continuous[], ..., 0)
The type double function is imsls_d_mlff_network_forecast.
Return Value
Pointer to an array of size n_outputs
containing the forecasts, where n_outputs
is the number of output perceptrons in the network.
n_outputs
=
ff_net->layers[ff_net->n_layers-1].n_nodes.
Required Arguments
Imsls_f_NN_Network *ff_net
(Input)
Pointer to a structure of type Imsls_f_NN_Network containing
the trained feedforward network. See imsls_f_mlff_network.
int
n_categorical (Input)
Number of categorical attributes.
int
n_continuous (Input)
Number of continous attributes.
int
categorical[] (Input)
Array of size n_categorical
containing the categorical input variables.
float
continuous[] (Input)
Array of size n_continuous
containing the continuous input variables.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
float
*imsls_f_mlff_network_forecast (Imsls_f_NN_Network
*ff_net,
int
n_categorical,
int n_continuous, int
categorical[],
float
continuous[],
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, float
forecasts[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_RETURN_USER,
float forecasts[]
(Output)
If specified, the forecasts for the trained network is stored in
array forecasts
of size n_outputs, where n_outputs is the
number of perceptrons in the network.
n_outputs = ff_net->layers[ff_net->n_layers
-1].n_nodes.
Description
Function imsls_f_mlff_network calculates a forecast for a previously trained multilayered feedforward neural network using the same network structure and scaling applied during the training. The structure Imsls_f_NN_Network describes the network structure used to originally train the network. The weights, which are the key output from training, are used as input to this routine. The weights are stored in the Imsls_f_NN_Network structure.
In addition, two one-dimensional arrays are used to describe the values of the categorical and continuous attributes that are to be used as network inputs for calculating the forecast.
Function imsls_f_mlff_network returns a forecast, calculated using the network input attributes provided.
Training Data
Neural network training data consist of the following three types of data:
1. categorical input attribute data
2. continuous input attribute data
3. continuous output data
The first data type contains the encoding of any nominal input attributes. If binary encoding is used, this encoding consists of creating columns of zeros and ones for each class value associated with every nominal attribute. If only one attribute is used for input, then the number of columns is equal to the number of classes for that attribute. If more columns appear in the data, then each nominal attribute is associated with several columns, one for each of its classes.
Each column consists of zeros, if that classification is not associated with this case, otherwise, one if that classification is associated. Consider an example with one nominal variable and two classes: male and female (male, male, female, male, female). With binary encoding, the following matrix is sent to the training engine to represent this data:

Continuous input and output data are passed to the training engine using two double precision arrays: continuous and outputs. The number of rows in each of these matrices is n_observations. The number of columns in continuous and outputs, corresponds to the number of input and output variables, respectively.
Network Configuration
The configuration of the network consists of a description of the number of perceptrons for each layer, the number of hidden layers, the number of inputs and outputs, and a description of the linkages among the perceptrons. This description is passed into this training routine through the structure Imsls_f_NN_Network. See imsls_f_mlff_network.
Forecast Calculation
The forecast is calculated from the input attributes, network structure and weights provided in the structure Imsls_f_NN_Network.
Examples
Example 1
This example trains a two-layer network using 90 training patterns from one nominal and one continuous input attribute. The nominal attribute has three classifications which are encoded using binary encoding. This results in three binary network input columns. The continuous input attribute is scaled to fall in the interval [0,1].
The network training targets were generated using the relationship:
Y = 10*X1 + 20*X2 + 30*X3 + 2.0*X4,
where X1, X2, X3 are the three binary columns, corresponding to the categories 1-3 of the nominal attribute, and X4 is the scaled continuous attribute.
The structure of the network consists of four input nodes ands two layers, with three perceptrons in the hidden layer and one in the output layer. The following figure illustrates this structure:
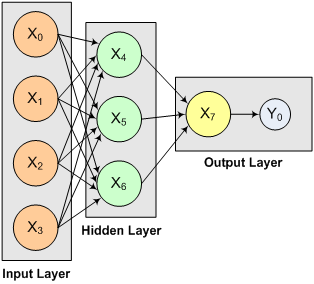
Figure 13- 12: A 2-layer, Feedforward Network with 4 Inputs and 1 Output
There are a total of 100 outputs. Training the first 90 and forecasting the 10 and compare the forecasted values with the actual outputs.
#include "imsls.h"
#include <stdio.h>
void
main ()
{
static int categorical[300] = {
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1
};
static float continuous[100] = {
4.007054658, 7.10028447, 4.740350984, 5.714553211, 6.205437459,
2.598930065, 8.65089967, 5.705787357, 2.513348184, 2.723795955,
4.1829356, 1.93280416, 0.332941608, 6.745567628, 5.593588463,
7.273544478, 3.162117939, 4.205381208, 0.16414745, 2.883418275,
0.629342241, 1.082223406, 8.180324708, 8.004894314, 7.856215418,
7.797143157, 8.350033996, 3.778254431, 6.964837082, 6.13938006,
0.48610387, 5.686627923, 8.146173848, 5.879852653, 4.587492779,
0.714028533, 7.56324211, 8.406012623, 4.225261454, 6.369220241,
4.432772218, 9.52166984, 7.935791508, 4.557155333, 7.976015058,
4.913538616, 1.473658514, 2.592338905, 1.386872932, 7.046051685,
1.432128376, 1.153580985, 5.6561491, 3.31163251, 4.648324851,
5.042514515, 0.657054195, 7.958308093, 7.557870384, 7.901990083,
5.2363088, 6.95582150, 8.362167045, 4.875903563, 1.729229471,
4.380370223, 8.527875685, 2.489198107, 3.711472959, 4.17692681,
5.844828801, 4.825754155, 5.642267843, 5.339937786, 4.440813223,
1.615143829, 7.542969339, 8.100542684, 0.98625265, 4.744819569,
8.926039258, 8.813441887, 7.749383991, 6.551841576, 8.637046998,
4.560281415, 1.386055087, 0.778869034, 3.883379045, 2.364501589,
9.648737525, 1.21754765, 3.908879368, 4.253313879, 9.31189696,
3.811953836, 5.78471629, 3.414486452, 9.345413015, 1.024053777
};
static float output[100] = {
18.01410932, 24.20056894, 19.48070197, 21.42910642, 22.41087492,
15.19786013, 27.30179934, 21.41157471, 15.02669637, 15.44759191,
18.3658712, 13.86560832, 10.66588322, 23.49113526, 21.18717693,
24.54708896, 16.32423588, 18.41076242, 10.3282949, 15.76683655,
11.25868448, 12.16444681, 26.36064942, 26.00978863, 25.71243084,
25.59428631, 26.70006799, 17.55650886, 23.92967416, 22.27876012,
10.97220774, 21.37325585, 26.2923477, 21.75970531, 19.17498556,
21.42805707, 35.12648422, 36.81202525, 28.45052291, 32.73844048,
28.86554444, 39.04333968, 35.87158302, 29.11431067, 35.95203012,
29.82707723, 22.94731703, 25.18467781, 22.77374586, 34.09210337,
22.86425675, 22.30716197, 31.3122982, 26.62326502, 29.2966497,
30.08502903, 21.31410839, 35.91661619, 35.11574077, 35.80398017,
30.4726176, 33.91164302, 36.72433409, 29.75180713, 23.45845894,
38.76074045, 47.05575137, 34.97839621, 37.42294592, 38.35385362,
41.6896576, 39.65150831, 41.28453569, 40.67987557, 38.88162645,
33.23028766, 45.08593868, 46.20108537, 31.9725053, 39.48963914,
47.85207852, 47.62688377, 45.49876798, 43.10368315, 47.274094,
39.1205628, 32.77211017, 31.55773807, 37.76675809, 34.72900318,
49.29747505, 32.4350953, 37.81775874, 38.50662776, 48.62379392,
37.62390767, 41.56943258, 36.8289729, 48.69082603, 32.04810755
};
/* 2D Array Definitions */
#define CATEGORICAL(i,j) categorical[i*n_cat+j]
#define CATEGORICALOBS(i,j) categoricalObs[i*n_cat+j]
Imsls_f_NN_Network *ffnet;
float *stats;
int n_obs = 100, n_cat = 3, n_cont = 1;
int i, j;
float *forecasts;
/* for forecasting */
int categoricalObs[3] = { 0, 0, 0 };
float continuousObs[1] = { 0 };
float x, y;
float forecast[5];
float *cont;
/* Scale continuous attribute to the interval [0, 1] */
cont = imsls_f_scale_filter (n_obs, continuous, 1,
IMSLS_SCALE_LIMITS, 0.0, 10.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0);
ffnet = imsls_f_mlff_network_init (4, 1);
imsls_f_mlff_network (ffnet,
IMSLS_CREATE_HIDDEN_LAYER, 3, IMSLS_LINK_ALL, 0);
for (i = 0; i < ffnet->n_links; i++)
{
/* hidden layer 1 */
if (ffnet->nodes[ffnet->links[i].to_node].layer_id == 1)
{
ffnet->links[i].weight = .25;
}
/* output layer */
if (ffnet->nodes[ffnet->links[i].to_node].layer_id == 2)
{
ffnet->links[i].weight = .33;
}
}
imsls_random_seed_set (12345);
stats = imsls_f_mlff_network_trainer (ffnet, n_obs - 10, n_cat,
n_cont, categorical, continuous, output,
0);
printf ("Predictions for Observations 90 to 100: \n");
for (i = 90; i < 100; i++)
{
continuousObs[0] = continuous[i];
for (j = 0; j < n_cat; j++)
{
CATEGORICALOBS (0, j) = CATEGORICAL (i, j);
}
forecasts = imsls_f_mlff_network_forecast (ffnet, n_cat, n_cont,
categoricalObs,
continuousObs, 0);
x = output[i];
y = forecasts[0];
printf
("observation[%d] %8.4f Prediction %8.4f Residual %8.4f \n",
i, x, y, x - y);
}
imsls_f_mlff_network_free (ffnet);
#undef CATEGORICAL
#undef CATEGORICALOBS
}
Output
NOTE: Because multiple optima are possible during training, the output of this example can vary by platform.
Predictions for Observations 90 to 100:
observation[90] 49.2975 Prediction 43.8761 Residual 5.4213
observation[91] 32.4351 Prediction 23.6643 Residual 8.7708
observation[92] 37.8178 Prediction 30.4261 Residual 7.3916
observation[93] 38.5066 Prediction 31.2768 Residual 7.2298
observation[94] 48.6238 Prediction 43.1369 Residual 5.4869
observation[95] 37.6239 Prediction 30.1860 Residual 7.4379
observation[96] 41.5694 Prediction 35.0006 Residual 6.5688
observation[97] 36.8290 Prediction 29.1978 Residual 7.6311
observation[98] 48.6908 Prediction 43.2108 Residual 5.4800
observation[99] 32.0481 Prediction 23.1740 Residual 8.8742
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |