Evaluates the hypergeometric probability function.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float imsls_f_hypergeometric_pdf (int k, int n, int m, int l)
The type double function is imsls_d_hypergeometric_pdf.
Required Arguments
int k
(Input)
Argument for which the hypergeometric probability
function is to be evaluated.
int n
(Input)
Sample size. n must be greater than
zero and greater than or equal to k.
int m
(Input)
Number of defectives in the lot.
int l
(Input)
Lot size. l must be greater than
or equal to n
and m.
Return Value
The probability that a hypergeometric random variable takes a value equal to k. This value is the probability that exactly k defectives occur in a sample of size n drawn from a lot of size l that contains m defectives.
Description
The function imsls_f_hypergeometic_pdf evaluates the probability function of a hypergeometric random variable with parameters n, l, and m. The hypergeometric random variable X can be thought of as the number of items of a given type in a random sample of size n that is drawn without replacement from a population of size l containing m items of this type. The probability function is
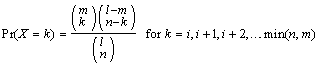
where i = max(0, n − l + m). imsls_f_hypergeometic_pdf evaluates the expression using log gamma functions.
Example
Suppose X is a hypergeometric random variable with n = 100, l = 1000, and m = 70. In this example, we evaluate the probability function at 7.
#include <imsls.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int k=7, n = 100, l = 1000, m = 70;
float pr;
pr = imsls_f_hypergeometric_pdf(k, n, m, l);
printf("The probability that X is equal to "
"%d is %6.4f\n", k, pr);
}
Output
The probability that X is equal to 7 is 0.1628
