Exact maximum likelihood estimation of the parameters in a univariate ARMA (autoregressive, moving average) time series model.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float *imsls f max_arma (int n_obs, float w[], int p, int q,…,0)
The type double function is imsls_d_max_arma.
Required Arguments
int n_obs
(Input)
Number of observations in the time series.
float w[] (Input)
Array
of length n_obs
containing the time series.
int p
(Input)
Non-negative number of autoregressive parameters.
int q
(Input)
Non-negative number of moving average parameters.
Return Value
Pointer to an array of length 1+p+q with the estimated constant, AR and MA parameters. If no value can be computed, NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
float
*imsls_f_max_arma
(int
n_obs,
float w[],
int p,
int q,
IMSLS_INITIAL_ESTIMATES, float
init_ar[] float
init_ma[],
IMSLS_PRINT_LEVEL, int
iprint,
IMSLS_MAX_ITERATIONS, int
maxit,
IMSLS_LOG_LIKELIHOOD, float
*log_likeli,
IMSLS_VAR_NOISE, float
*avar,
IMSLS_ARMA_INFO,
Imsls_f_arma **arma_info,
IMSLS_MEAN_ESTIMATE, float
*w_mean,
IMSLS_RESIDUAL, float
**residuals,
IMSLS_RESIDUAL_USER, float
residuals[],
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, float
*constant, float
ar[], float
ma[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_INITIAL_ESTIMATES,
float init
ar[], float init ma[]
(Input)
If specified, init ar is an
array of length p containing
preliminary estimates of the autoregressive parameters, and init ma is an
array of length q containing
preliminary estimates of the moving average parameters; otherwise, they are
computed internally. If p=0 or q=0, then the
corresponding arguments are ignored.
IMSLS_PRINT_LEVEL,
int iprint
(Input)
Printing option:
0 — No printing.
1 — Prints final
results only.
2 — Prints intermediate and final results.
Default:
iprint = 0
IMSLS_MAX_ITERATIONS,
int maxit
(Input)
Maximum number of
estimation iterations.
Default: maxit = 300
IMSLS_VAR_NOISE,
float *avar
(Output)
Estimate of innovation variance.
IMSLS_LOG_LIKELIHOOD,
float *log_likeli
(Output)
Value of -2*(ln(likelihood)) for
the fitted model.
IMSLS_ARMA_INFO,
Imsls_f_arma **arma_info
(Output)
Address of a pointer to an internally allocated structure of
type Imsls_f_arma that contains information
necessary in the call to imsls_f_arma_forecast.
IMSLS_MEAN_ESTIMATE,
float *w_mean
(Input/Output)
Estimate of the mean of the time series w. On return, w_mean contains an
update of the mean.
Default: Time series w is centered about
its sample mean.
IMSLS_RESIDUAL,
float **residuals
(Output)
Address of a pointer to an internally allocated array of
length n_obs
containing the residuals of the requested ARMA fit.
IMSLS_RESIDUAL_USER,
float residuals[]
(Output)
Storage array residuals is provided
by the user. See IMSLS_RESIDUAL.
IMSLS_RETURN_USER,
float *constant, float
ar[],
float ma[]
(Output)
If specified,
constant is the
constant parameter estimate, ar is an array of
length p
containing the final autoregressive parameter estimates, and ma is an array of
length q
containing the final moving average parameter estimates.
Description
The function imsls_f_max_arma is derived from the maximum likelihood estimation algorithm described by Akaike, Kitagawa, Arahata and Tada (1979), and the XSARMA routine published in the TIMSAC-78 Library.
Using the notation developed in the Time Domain Methodology
at the beginning of this chapter, the stationary time series 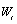 with mean
with mean 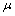 can be represented by the
nonseasonal autoregressive moving average (ARMA) model by the following
relationship:
can be represented by the
nonseasonal autoregressive moving average (ARMA) model by the following
relationship:
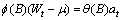
where
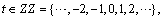
B is the backward shift operator defined by 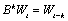 ,
,
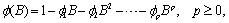
and
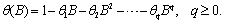
Function imsls_f_max_arma
estimates the AR coefficients 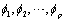 and the MA coefficients
and the MA coefficients 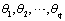 using maximum likelihood estimation.
using maximum likelihood estimation.
Function imsls_f_max_arma checks the initial estimates for both the autoregressive and moving average coefficients to ensure that they represent a stationary and invertible series respectively.
If
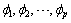
are the initial estimates for a stationary series then all (complex) roots of the following polynomial will fall outside the unit circle:
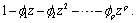
Initial values for the AR and MA coefficients can be supplied by vectors init_ar and init_ma. Otherwise, estimates are computed internally by the method of moments. imsls_f_max_arma computes the roots of the associated polynomials. If the AR estimates represent a non-stationary series, imsls_f_max_arma issues a warning message and replaces init_ar with initial values that are stationary. If the MA estimates represent a non-invertible series, imsls_f_max_arma issues a terminal error, and new initial values have to be sought.
imsls_f_max_arma also validates the final estimates of the AR coefficients to ensure that they too represent a stationary series. This is done to guard against the possibility that the internal log-likelihood optimizer converged to a non-stationary solution. If non-stationary estimates are encountered, imsls_f_max_arma issues a fatal error message. Functions imsls_error_options and imsls_error_code (see Chapter 15, Utilities) can be used to verify that the stationarity condition was met.
For model selection, the ARMA model with the minimum value for AIC might be preferred,
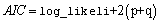
Function imsls_f_max_arma can also handle white noise processes, i.e. ARMA(0,0) Processes.
Examples
Example 1
Consider the Wolfer Sunspot data (Anderson 1971, p. 660) consisting of the number of sunspots observed each year from 1770 through 1869. In this example, imsls_f_max_arma is used to fit the following ARMA(2,1) model:
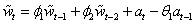 ,
,
with 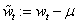 ,
, 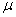 the sample mean of the time
series
the sample mean of the time
series 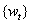 .
.
For these data, imsls_f_max_arma calculated the following model:
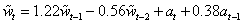 .
.
Defining the overall constant 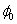 by
by 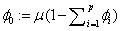 , we obtain the following equivalent
representations:
, we obtain the following equivalent
representations:
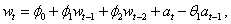
and
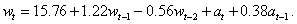
#include <imsls.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
int n_obs = 100;
int p = 2, q = 1;
float z[176][2];
float w[100];
float *parameters = NULL;
float avar, log_likeli;
/* get wolfer sunspot data */
imsls_f_data_sets (2, IMSLS_X_COL_DIM, 2,
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, z,
0);
for (i=0; i<n_obs; i++)
w[i] = z[21+i][1];
parameters = imsls_f_max_arma (n_obs, w, p, q,
IMSLS_MAX_ITERATIONS, 12000,
IMSLS_VAR_NOISE, &avar,
IMSLS_LOG_LIKELIHOOD, &log_likeli,
0);
printf("AR estimates are %11.4f and %11.4f.\n",
parameters[1], parameters[2]);
printf("MA estimate is %11.4f.\n", parameters[3]);
printf("Constant estimate is %11.4f.\n", parameters[0]);
printf("-2*ln(Maximum Log Likelihood) = %11.4f.\n", log_likeli);
printf("White noise variance = %11.4f.\n", avar);
if (parameters)
{
imsls_free(parameters);
parameters = NULL;
}
}
Output
AR estimates are 1.2245 and -0.5601.
MA estimate is -0.3831.
Constant estimate is 15.7624.
-2*ln(Maximum Log Likelihood) = 539.5839.
White noise variance = 214.5123.
Example 2
This example is the same as Example 1, but now initial values for the AR and MA parameters are explicitly given.
#include <imsls.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
int n_obs = 100;
int p = 2, q = 1;
float z[176][2];
float w[100];
float parameters[4];
float avar, log_likeli;
float init_ar[2] = {1.244e0, -0.575e0};
float init_ma[1] = {-0.1241e0};
/* get wolfer sunspot data */
imsls_f_data_sets (2, IMSLS_X_COL_DIM, 2,
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, z,
0);
for (i=0; i<n_obs; i++)
w[i] = z[21+i][1];
imsls_f_max_arma (n_obs, w, p, q,
IMSLS_MAX_ITERATIONS, 12000,
IMSLS_VAR_NOISE, &avar,
IMSLS_LOG_LIKELIHOOD, &log_likeli,
IMSLS_INITIAL_ESTIMATES, init_ar, init_ma,
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, ¶meters[0], ¶meters[1],
¶meters[3],
0);
printf("AR estimates are %11.4f and %11.4f.\n",
parameters[1], parameters[2]);
printf("MA estimate is %11.4f.\n", parameters[3]);
printf("Constant estimate is %11.4f.\n", parameters[0]);
printf("-2*ln(Maximum Log Likelihood) = %11.4f.\n", log_likeli);
printf("White noise variance = %11.4f.\n", avar);
}
Output
AR estimates are 1.2252 and -0.5607.
MA estimate is -0.3828.
Constant estimate is 15.7587.
-2*ln(Maximum Log Likelihood) = 539.5839.
White noise variance = 214.5083.
