This function evaluates the derivative of a function defined on a rectangular three-dimensional grid using quadratic interpolation.
Function Return Value
QD3DR — Value of the appropriate derivative of the function at (X, Y, Z). (Output)
Required Arguments
IXDER — Order of the x-derivative. (Input)
IYDER — Order of the y-derivative. (Input)
IZDER — Order of the z-derivative. (Input)
X — x-coordinate of the point at which the function is to be evaluated. (Input)
Y — y-coordinate of the point at which the function is to be evaluated. (Input)
Z — z-coordinate of the point at which the function is to be evaluated. (Input)
XDATA — Array of
length NXDATA
containing the location of the data points in the
x-direction. (Input)
XDATA must be
increasing.
YDATA — Array of
length NYDATA
containing the location of the data points in the
y-direction. (Input)
YDATA must be
increasing.
ZDATA — Array of
length NZDATA
containing the location of the data points in the
z-direction. (Input)
ZDATA must be
increasing.
FDATA — Array of
size NXDATA by
NYDATA by NZDATA containing
function values. (Input)
FDATA(I, J, K) is the value of the
function at (XDATA(I), YDATA(J), ZDATA(K)).
Optional Arguments
NXDATA — Number
of data points in the x-direction. (Input)
NXDATA must be at
least three.
Default: NXDATA = size (XDATA,1).
NYDATA — Number
of data points in the y-direction. (Input)
NYDATA must be at
least three.
Default: NYDATA = size (YDATA,1).
NZDATA — Number
of data points in the z-direction. (Input)
NZDATA must be at
least three.
Default: NZDATA = size (ZDATA,1).
LDF — Leading
dimension of FDATA exactly as
specified in the dimension statement of the calling program. (Input)
LDF must be
at least as large as NXDATA.
Default:
LDF = size
(FDATA,1).
MDF — Middle
(second) dimension of FDATA exactly as
specified in the dimension statement of the calling program. (Input)
MDF must be
at least as large as NYDATA.
Default:
MDF = size
(FDATA,2).
CHECK — Logical
variable that is .TRUE. if checking of
XDATA, YDATA, and ZDATA is required or
.FALSE. if
checking is not required. (Input)
Default: CHECK = .TRUE.
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: QD3DR (IXDER, IYDER, IZDER, X, Y, Z, XDATA, YDATA, ZDATA, FDATA [,…])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_QD3DR and D_QD3DR.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: QD3DR (IXDER, IYDER, IZDER, X, Y, Z, NXDATA, XDATA, NYDATA, YDATA, NZDATA, ZDATA, FDATA, LDF, MDF, CHECK)
Double: The double precision function name is DQD3DR.
Description
The function QD3DR interpolates a table of values, using quadratic polynomials, returning an approximation to the partial derivatives of the tabulated function. Let
(xi, yj, zk, fijk)
for i = 1, …, nx, j = 1, …, ny, and k = 1, …, nz be the tabular data. Given a point (x, y, z) at which an interpolated value is desired, we first find the nearest interior grid point (xi, yj, zk). A trivariate quadratic interpolant q is then formed. Ten points are needed for this purpose. Seven points have the form
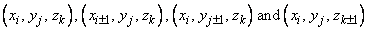
The last three points are drawn from the vertices of the octant containing (x, y, z). There are four of these vertices remaining, and we choose to exclude the vertex farthest from the center. This has the slightly deleterious effect of not reproducing the tabular data at the eight exterior corners of the table. The value q(p,r,t)(x, y, z) is returned by QD3DR, where p = IXDER, r = IYDER, and t = IZDER.
Comments
1. Informational errors
Type Code
4 9 The XDATA values must be strictly increasing.
4 10 The YDATA values must be strictly increasing.
4 11 The ZDATA values must be strictly increasing.
2. Because quadratic interpolation is used, if the order of any derivative is greater than two, then the returned value is zero.
Example
In this example, the derivatives of sin(x + y + z) at x = y = z = π/5 are approximated by using QD3DR on a grid of size 21 × 42 × 18 equally spaced values on the cube [0, 2]3.
USE IMSL_LIBRARIES
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER LDF, MDF, NXDATA, NYDATA, NZDATA
PARAMETER (NXDATA=21, NYDATA=42, NZDATA=18, LDF=NXDATA,&
MDF=NYDATA)
!
INTEGER I, IXDER, IYDER, IZDER, J, K, NOUT
REAL F, FDATA(NXDATA,NYDATA,NZDATA), FLOAT, FU,&
FUNC, PI, Q, SIN, X, XDATA(NXDATA), Y,&
YDATA(NYDATA), Z, ZDATA(NZDATA)
INTRINSIC FLOAT, SIN
EXTERNAL FUNC
! Define function
F(X,Y,Z) = SIN(X+Y+Z)
! Set up X-grid
DO 10 I=1, NXDATA
XDATA(I) = 2.0*(FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(NXDATA-1))
10 CONTINUE
! Set up Y-grid
DO 20 J=1, NYDATA
YDATA(J) = 2.0*(FLOAT(J-1)/FLOAT(NYDATA-1))
20 CONTINUE
! Set up Z-grid
DO 30 K=1, NZDATA
ZDATA(K) = 2.0*(FLOAT(K-1)/FLOAT(NZDATA-1))
30 CONTINUE
! Evaluate function on grid
DO 40 I=1, NXDATA
DO 40 J=1, NYDATA
DO 40 K=1, NZDATA
FDATA(I,J,K) = F(XDATA(I),YDATA(J),ZDATA(K))
40 CONTINUE
! Get output unit number
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
! Write heading
WRITE (NOUT,99999)
! Get value for PI and set X, Y, and Z
PI = CONST('PI')
X = PI/5.0
Y = PI/5.0
Z = PI/5.0
! Compute derivatives at (X,Y,Z)
! and print results
DO 50 IXDER=0, 1
DO 50 IYDER=0, 1
DO 50 IZDER=0, 1
Q = QD3DR(IXDER,IYDER,IZDER,X,Y,Z,XDATA,YDATA,ZDATA,FDATA)
FU = FUNC(IXDER,IYDER,IZDER,X,Y,Z)
WRITE (NOUT,99998) X, Y, Z, IXDER, IYDER, IZDER, FU, Q,&
(FU-Q)
50 CONTINUE
!
99998 FORMAT (3F7.4, 3I5, 4X, F7.4, 8X, 2F10.4)
99999 FORMAT (39X, '(IDX,IDY,IDZ)', /, 6X, 'X', 6X, 'Y', 6X,&
'Z', 3X, 'IDX', 2X, 'IDY', 2X, 'IDZ', 2X, 'F ',&
'(X,Y,Z)', 3X, 'QD3DR', 5X, 'ERROR')
END
!
REAL FUNCTION FUNC (IX, IY, IZ, X, Y, Z)
INTEGER IX, IY, IZ
REAL X, Y, Z
!
REAL COS, SIN
INTRINSIC COS, SIN
!
IF (IX.EQ.0 .AND. IY.EQ.0 .AND. IZ.EQ.0) THEN
! Define (0,0,0) derivative
FUNC = SIN(X+Y+Z)
ELSE IF (IX.EQ.0 .AND. IY.EQ.0 .AND. IZ.EQ.1) THEN
! Define (0,0,1) derivative
FUNC = COS(X+Y+Z)
ELSE IF (IX.EQ.0 .AND. IY.EQ.1 .AND. IZ.EQ.0) THEN
! Define (0,1,0,) derivative
FUNC = COS(X+Y+Z)
ELSE IF (IX.EQ.0 .AND. IY.EQ.1 .AND. IZ.EQ.1) THEN
! Define (0,1,1) derivative
FUNC = -SIN(X+Y+Z)
ELSE IF (IX.EQ.1 .AND. IY.EQ.0 .AND. IZ.EQ.0) THEN
! Define (1,0,0) derivative
FUNC = COS(X+Y+Z)
ELSE IF (IX.EQ.1 .AND. IY.EQ.0 .AND. IZ.EQ.1) THEN
! Define (1,0,1) derivative
FUNC = -SIN(X+Y+Z)
ELSE IF (IX.EQ.1 .AND. IY.EQ.1 .AND. IZ.EQ.0) THEN
! Define (1,1,0) derivative
FUNC = -SIN(X+Y+Z)
ELSE IF (IX.EQ.1 .AND. IY.EQ.1 .AND. IZ.EQ.1) THEN
! Define (1,1,1) derivative
FUNC = -COS(X+Y+Z)
ELSE
FUNC = 0.0
END IF
RETURN
END
Output
(IDX,IDY,IDZ)
X
Y Z IDX IDY IDZ
F (X,Y,Z)
QD3DR ERROR
0.6283 0.6283 0.6283
0 0 0
0.9511
0.9511 -0.0001
0.6283 0.6283 0.6283
0 0 1
-0.3090
-0.3080 -0.0010
0.6283 0.6283 0.6283
0 1 0
-0.3090
-0.3088 0.0002
0.6283 0.6283 0.6283
0 1 1
-0.9511
-0.9587 0.0077
0.6283 0.6283 0.6283
1 0 0 -0.3090
-0.3078
-0.0012
0.6283 0.6283 0.6283 1
0 1
-0.9511
-0.9348 -0.0162
0.6283 0.6283 0.6283
1 1 0
-0.9511
-0.9613 0.0103
0.6283 0.6283 0.6283
1 1 1
0.3090
0.0000 0.3090
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |