Integrates a smooth function using a nonadaptive rule.
Required Arguments
F — User-supplied
FUNCTION to be
integrated. The form is F(X),
where
X – Independent
variable.
(Input)
F – The function
value. (Output)
F must be declared
EXTERNAL in the
calling program.
A — Lower limit of integration. (Input)
B — Upper limit of integration. (Input)
RESULT — Estimate of the integral from A to B of F. (Output)
Optional Arguments
ERRABS — Absolute
accuracy desired. (Input)
Default: ERRABS = 1.e-3 for single precision and
1.d-8 for double precision.
ERRREL — Relative
accuracy desired. (Input)
Default: ERRREL = 1.e-3 for single precision and
1.d-8 for double precision.
ERREST — Estimate of the absolute value of the error. (Output)
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: CALL QDNG (F, A, B, RESULT [,…])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_QDNG and D_QDNG.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: CALL QDNG (F, A, B, ERRABS, ERRREL, RESULT, ERREST)
Double: The double precision name is DQDNG.
Description
The routine QDNG is designed to integrate smooth functions. This routine implements a nonadaptive quadrature procedure based on nested Paterson rules of order 10, 21, 43, and 87. These rules are positive quadrature rules with degree of accuracy 19, 31, 64, and 130, respectively. The routine QDNG applies these rules successively, estimating the error, until either the error estimate satisfies the user-supplied constraints or the last rule is applied. The routine QDNG is based on the routine QNG by Piessens et al. (1983).
This routine is not very robust, but for certain smooth functions it can be efficient. If QDNG should not perform well, we recommend the use of the IMSL routine QDAGS.
Comments
1.
Informational
error
Type
Code
4 1 The maximum number of steps allowed have been taken. The integral is too difficult for QDNG.
2.
If EXACT is the
exact value, QDNG attempts to find
RESULT such that
ABS(EXACT − RESULT).LE.MAX(ERRABS, ERRREL * ABS(EXACT)). To specify
only a relative error, set ERRABS to zero.
Similarly, to specify only an absolute error, set ERRREL to zero.
3. This routine is designed for efficiency, not robustness. If the above error is encountered, try QDAGS.
Example
The value of
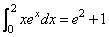
is estimated. The values of the actual and estimated error are machine dependent.
USE QDNG_INT
USE UMACH_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER NOUT
REAL A, ABS, B, ERRABS, ERREST, ERROR, EXACT, EXP, &
F, RESULT
INTRINSIC ABS, EXP
EXTERNAL F
! Get output unit number
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
! Set limits of integration
A = 0.0
B = 2.0
! Set error tolerances
ERRABS = 0.0
CALL QDNG (F, A, B, RESULT, ERRABS=ERRABS, ERREST=ERREST)
! Print results
EXACT = 1.0 + EXP(2.0)
ERROR = ABS(RESULT-EXACT)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) RESULT, EXACT, ERREST, ERROR
99999 FORMAT (' Computed =', F8.3, 13X, ' Exact =', F8.3, /, /, &
' Error estimate =', 1PE10.3, 6X, 'Error =', 1PE10.3)
END
!
REAL FUNCTION F (X)
REAL X
REAL EXP
INTRINSIC EXP
F = X*EXP(X)
RETURN
END
Output
Computed =
8.389
Exact = 8.389
Error estimate =
5.000E-05 Error = 9.537E-07
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |