Computes a two-dimensional iterated integral.
Required Arguments
F — User-supplied
FUNCTION to be
integrated. The form is F(X,Y),
where
X – First
argument of F.
(Input)
Y – Second
argument of F.
(Input)
F – The function value. (Output)
F must be declared
EXTERNAL in the
calling program.
A — Lower limit of outer integral. (Input)
B — Upper limit of outer integral. (Input)
G — User-supplied
FUNCTION to
evaluate the lower limits of the inner integral.
The form is G(X),
where
X – Only
argument of G.
(Input)
G – The function
value. (Output)
G must be declared
EXTERNAL in the
calling program.
H — User-supplied
FUNCTION to
evaluate the upper limits of the inner integral. The form is H(X),
where
X – Only
argument of H.
(Input)
H – The function
value. (Output)
H must be declared
EXTERNAL in the
calling program.
RESULT — Estimate of the integral from A to B of F. (Output)
Optional Arguments
ERRABS — Absolute
accuracy desired. (Input)
Default: ERRABS = 1.e-3 for
single precision and 1.d-8 for double precision.
ERRREL — Relative
accuracy desired. (Input)
Default: ERRREL = 1.e-3 for
single precision and 1.d-8 for double precision.
IRULE --- Choice
of quadrature rule. (Input)
Default: IRULE = 2.
The
Gauss-Kronrod rule is used with the following points:
|
IRULE |
Points |
|
1 |
7-15 |
|
2 |
10-21 |
|
3 |
15-31 |
|
4 |
20-41 |
|
5 |
25-51 |
|
6 |
30-61 |
If the function has a peak
singularity, use IRULE = 1. If
the function is oscillatory, use IRULE = 6.
ERREST — Estimate of the absolute value of the error. (Output)
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: CALL TWODQ (F, A, B, G, H, RESULT [,…])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_TWODQ and D_TWODQ.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: CALL TWODQ (F, A, B, G, H, ERRABS, ERRREL, IRULE, RESULT, ERREST)
Double: The double precision name is DTWODQ.
Description
The routine TWODQ approximates the two-dimensional iterated integral
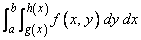
with the approximation returned in RESULT. An estimate of the error is returned in ERREST. The approximation is achieved by iterated calls to QDAG. Thus, this algorithm will share many of the characteristics of the routine QDAG. As in QDAG, several options are available. The absolute and relative error must be specified, and in addition, the Gauss-Kronrod pair must be specified (IRULE). The lower-numbered rules are used for less smooth integrands while the higher-order rules are more efficient for smooth (oscillatory) integrands.
Comments
1. Workspace may be explicitly provided, if desired, by use of T2ODQ/DT2ODQ. The reference is:
CALL T2ODQ (F, A, B, G, H, ERRABS, ERRREL, IRULE, RESULT, ERREST, MAXSUB, NEVAL, NSUBIN, ALIST, BLIST, RLIST, ELIST, IORD, WK, IWK)
The additional arguments are as follows:
MAXSUB —
Number of subintervals allowed. (Input)
A value of 250 is used
by TWODQ.
NEVAL — Number of evaluations of F. (Output)
NSUBIN — Number of subintervals generated in the outer integral. (Output)
ALIST — Array of length MAXSUB containing a list of the NSUBIN left endpoints for the outer integral. (Output)
BLIST — Array of length MAXSUB containing a list of the NSUBIN right endpoints for the outer integral. (Output)
RLIST — Array of length MAXSUB containing approximations to the NSUBIN integrals over the intervals defined by ALIST, BLIST, pertaining only to the outer integral. (Output)
ELIST — Array of length MAXSUB containing the error estimates of the NSUBIN values in RLIST. (Output)
IORD —
Array of length MAXSUB. (Output)
Let K be NSUBIN if NSUBIN.LE.(MAXSUB/2 + 2),
MAXSUB + 1
− NSUBIN otherwise.
Then the first K locations contain pointers to the error
estimates over the corresponding subintervals, such that ELIST(IORD(1)), …, ELIST(IORD(K)) form a
decreasing sequence.
WK — Work array of length 4 * MAXSUB, needed to evaluate the inner integral.
IWK — Work array of length MAXSUB, needed to evaluate the inner integral.
2.
Informational
errors
Type
Code
4 1 The maximum number of subintervals allowed has been reached.
3 2 Roundoff error, preventing the requested tolerance from being achieved, has been detected.
3 3 A degradation in precision has been detected.
3.
If EXACT is the
exact value, TWODQ attempts to find
RESULT such that
ABS(EXACT − RESULT).LE.MAX(ERRABS, ERRREL * ABS(EXACT)). To specify
only a relative error, set ERRABS to zero.
Similarly, to specify only an absolute error, set ERRREL to zero.
Example 1
In this example, we approximate the integral
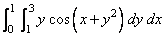
The value of the error estimate is machine dependent.
USE TWODQ_INT
USE UMACH_INT
IMPLICIT
NONE
INTEGER IRULE, NOUT
REAL A, B, ERRABS, ERREST, ERRREL, F, G, H, RESULT
EXTERNAL F, G, H
! Get output unit number
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
! Set limits of integration
A = 0.0
B = 1.0
! Set error tolerances
ERRABS = 0.0
ERRREL = 0.01
! Parameter for oscillatory function
IRULE = 6
CALL TWODQ (F, A, B, G, H, RESULT, ERRABS, ERRREL, IRULE, errest)
! Print results
WRITE (NOUT,99999) RESULT, ERREST
99999 FORMAT (' Result =', F8.3, 13X, ' Error estimate = ', 1PE9.3)
END
!
REAL FUNCTION F (X, Y)
REAL X, Y
REAL COS
INTRINSIC COS
F = Y*COS(X+Y*Y)
RETURN
END
!
REAL FUNCTION G (X)
REAL X
G = 1.0
RETURN
END
!
REAL FUNCTION H (X)
REAL X
H = 3.0
RETURN
END
Output
Result = -0.514 Error estimate = 3.065E-06
Additional Examples
Example 2
We modify the above example by assuming that the limits for the inner integral depend on x and, in particular, are g(x) = −2x and h(x) = 5x. The integral now becomes
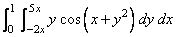
The value of the error estimate is machine dependent.
USE TWODQ_INT
USE
UMACH_INT
!
Declare F, G, H
INTEGER IRULE, NOUT
REAL A, B, ERRABS, ERREST, ERRREL, F, G, H, RESULT
EXTERNAL F, G, H
!
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
! Set limits of integration
A = 0.0
B = 1.0
! Set error tolerances
ERRABS = 0.001
ERRREL = 0.0
! Parameter for oscillatory function
IRULE = 6
CALL TWODQ (F, A, B, G, H, RESULT, ERRABS, ERRREL, IRULE, ERREST)
! Print results
WRITE (NOUT,99999) RESULT, ERREST
99999 FORMAT (' Computed =', F8.3, 13X, ' Error estimate = ', 1PE9.3)
END
REAL FUNCTION F (X, Y)
REAL X, Y
!
REAL COS
INTRINSIC COS
!
F = Y*COS(X+Y*Y)
RETURN
END
REAL FUNCTION G (X)
REAL X
!
G = -2.0*X
RETURN
END
REAL FUNCTION H (X)
REAL X
!
H = 5.0*X
RETURN
END
Output
Computed = -0.083 Error estimate = 2.095E-06
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |