This function evaluates the exponential integral for arguments greater than zero and the Cauchy principal value of the integral for arguments less than zero.
Function Return Value
E1 — Function value. (Output)
Required Arguments
X — Argument for which the integral is to be evaluated. (Input)
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: E1 (X)
Specific: The specific interface names are S_E1 and D_E1.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: E1 (X)
Double: The double precision function name is DE1.
Description
The alternate definition of the exponential integral, E1(x), is
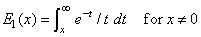
The path of integration must exclude the origin and not cross the negative real axis.
The argument x must be large enough that e−x does not overflow, and x must be small enough to insure that e−x/x does not underflow.
Comments
Informational error
Type Code
3 2 The function underflows because X is too large.
Example
In this example, E1 (1.3) is computed and printed.
USE E1_INT
USE UMACH_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
! Declare variables
INTEGER NOUT
REAL VALUE, X
! Compute
X = 1.3
VALUE = E1(X)
! Print the results
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) X, VALUE
99999 FORMAT (' E1(', F6.3, ') = ', F6.3)
END
Output
E1( 1.300) = 0.135
|
PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |