This function evaluates the hypergeometric probability density function.
Function Return Value
HYPPR — Function
value, the probability that a hypergeometric random variable takes a value equal
to K.
(Output)
HYPPR is the
probability that exactly K defectives occur in
a sample of size N drawn from a lot of
size L that
contains M
defectives.
See Comment 1.
Required Arguments
K — Argument for which the hypergeometric probability function is to be evaluated. (Input)
N — Sample
size. (Input)
N must be greater than
zero and greater than or equal to K.
M — Number of defectives in the lot. (Input)
L — Lot
size. (Input)
L must be greater than
or equal to N
and M.
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: HYPPR (K, N, M, L)
Specific: The specific interface names are S_HYPPR and D_HYPPR.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: HYPPR (K, N, M, L)
Double: The double precision name is DHYPPR.
Description
The function HYPPR evaluates the probability density function of a hypergeometric random variable with parameters n, l, and m. The hypergeometric random variable X can be thought of as the number of items of a given type in a random sample of size n that is drawn without replacement from a population of size l containing m items of this type. The probability density function is
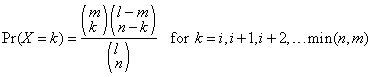
where i = max(0, n − l + m). HYPPR evaluates the expression using log gamma functions.
Comments
1. If the generic version of this function is used, the immediate result must be stored in a variable before use in an expression. For example:
X = HYPPR(K, N, M, L)
Y = SQRT(X)
must be used rather than
Y = SQRT(HYPPR(K, N, M, L))
If this is too much of a restriction on the programmer, then the specific name can be used without this restriction.
2. Informational errors
Type Code
1 5 The input argument, K, is less than zero.
1 6 The input argument, K, is greater than the sample size.
Example
Suppose X is a hypergeometric random variable with N = 100, L = 1000, and M = 70. In this example, we evaluate the probability function at 7.
USE UMACH_INT
USE HYPPR_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER K, L, M, N, NOUT
REAL PR
!
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
K = 7
N = 100
L = 1000
M = 70
PR = HYPPR(K,N,M,L)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) PR
99999 FORMAT (' The probability that X is equal to 7 is ', F6.4)
END
Output
The probability that X is equal to 7 is 0.1628
|
PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |