| Bond Class |
Namespace: Imsl.Finance
Assembly: ImslCS (in ImslCS.dll) Version: 6.5.2.0
The Bond type exposes the following members.
| Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Accrint |
Returns the interest which has accrued on a security that pays
interest periodically.
| |
| Accrintm |
Returns the interest which has accrued on a security that pays
interest at maturity.
| |
| Amordegrc |
Returns the depreciation for each accounting Frequency.
| |
| Amorlinc |
Returns the depreciation for each accounting Frequency.
| |
| Convexity |
Returns the convexity for a security.
| |
| Coupdaybs |
Returns the number of days starting with the beginning of the coupon
period and ending with the settlement date.
| |
| Coupdays |
Returns the number of days in the coupon period containing the
settlement date.
| |
| Coupdaysnc |
Returns the number of days starting with the settlement date and
ending with the next coupon date.
| |
| Coupncd |
Returns the first coupon date which follows the settlement date.
| |
| Coupnum |
Returns the number of coupons payable between the settlement
date and the maturity date.
| |
| Couppcd |
Returns the coupon date which immediately precedes the settlement
date.
| |
| Disc |
Returns the implied interest rate of a discount bond.
| |
| Duration |
Returns the Macauley's duration of a security where the security has
periodic interest payments.
| |
| Equals | Determines whether the specified object is equal to the current object. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| GetHashCode | Serves as a hash function for a particular type. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| GetType | Gets the Type of the current instance. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| Intrate |
Returns the interest rate of a fully invested security.
| |
| Mduration |
Returns the modified Macauley duration for a security with an assumed
par value of $100.
| |
| Price |
Returns the price, per $100 face value, of a security that pays
periodic interest.
| |
| Pricedisc |
Returns the price of a discount bond given the discount rate.
| |
| Pricemat |
Returns the price, per $100 face value, of a discount bond.
| |
| Priceyield |
Returns the price of a discount bond given the yield.
| |
| Received |
Returns the amount one receives when a fully invested security reaches
the maturity date.
| |
| Tbilleq |
Returns the bond-equivalent yield of a Treasury bill.
| |
| Tbillprice |
Returns the price, per $100 face value, of a Treasury bill.
| |
| Tbillyield |
Returns the yield of a Treasury bill.
| |
| ToString | Returns a string that represents the current object. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| Yearfrac |
Returns the fraction of a year represented by the number of whole days
between two dates.
| |
| Yield |
Returns the yield of a security that pays periodic interest.
| |
| Yielddisc |
Returns the annual yield of a discount bond.
| |
| Yieldmat |
Returns the annual yield of a security that pays interest at
maturity.
|
Definitions
rate is an annualized rate of return based on the par value of the bills.
yield is an annualized rate based on the purchase price and reflects the actual yield to maturity.
coupons are interest payments on a bond.
redemption is the amount a bond pays at maturity.
frequency is the number of times a year that a bond makes interest payments.
basis is the method used to calculate dates. For example, sometimes computations are done assuming 360 days in a year.
issue is the day a bond is first sold.
settlement is the day a purchaser aquires a bond.
maturity is the day a bond's principal is repaid.
Discount Bonds
Discount bonds, also called zero-coupon bonds, do not pay interest during the life of the security, instead they sell at a discount to their value at maturity. The discount bond methods all have settlement, maturity, basis and redemption as arguments. In the following list these common arguments are ommitted.
- price = Pricedisc(rate)
- price = Priceyield(yield)
- price = Pricemat(issue, rate, yield)
- rate = Disc(price)
- yield = Yielddisc(price)
A related method is Accrintm, which returns the interest that has accumulated on the discount bond.
Treasury Bills
US Treasury bills are a special case of discount bonds. The basis is fixed for treasury bills and the redemption value is assumed to be $100. So these functions have only settlement and maturity as common arguments.
- price = Tbillprice(rate)
- yield = Tbillyield(Price)
- yield = Tbilleq(rate)
Interest Paying Bonds
Most bonds pay interest periodically. The interest paying bond methods all have settlement, maturity, basis and frequency as arguments. Again supressing the common arguments,
- price = Price(rate, yield, redemption)
- yield = Yield(rate, Price, redemption)
- redemption = Received(Price, rate)
A related method is Accrint, which returns the interest that has accumulated at settlement from the previous coupon date.
Coupon days
In this diagram, the settlement date is shown as a hollow circle and the adjacent coupon dates are shown as filled circles.
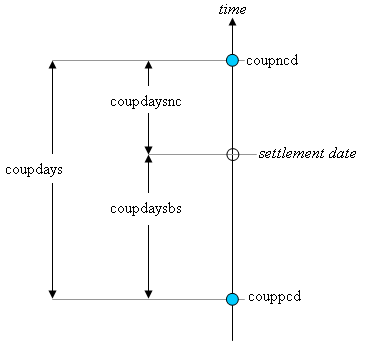
- Coupppcd is the coupon date immediately prior to the settlement date.
- Coupncd is the coupon date immediately after the settlement date.
- Coupdaybs is the number of days from the immediately prior coupon date to the settlement date.
- Coupdaysnc is the number of days from the settlement date to the next Coupon date.
- Coupdays is the number of days between these two coupon dates.
A related method is Coupnum, which returns the number of coupons payable between settlement and maturity.
Another related method is Yearfrac, which returns the fraction of the year between two days.
Duration
Duration is used to measure the sensitivity of a bond to changes in interest rates. Convexity is a measure of the sensitivity of duration.