gamma¶
Evaluates the real gamma function.
Synopsis¶
gamma (x)
Required Arguments¶
- float
x(Input) - Point at which the gamma function is to be evaluated.
Return Value¶
The value of the gamma function Γ(x).
Description¶
The gamma function, Γ(x), is defined to be
\[\mathit{\Gamma}(x) = \int_{0}^{\infty} t^{x-1} e^{-t} dt\]
For x < 0, the above definition is extended by analytic continuation.
The gamma function is not defined for integers less than or equal to zero. It underflows for x << 0 and overflows for large x. It also overflows for values near negative integers.
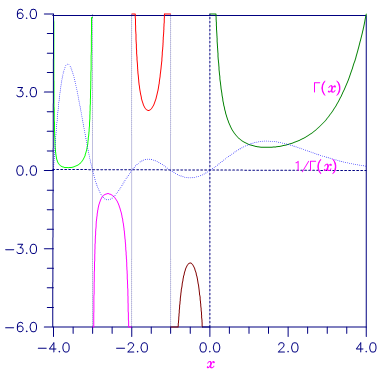
Figure 15.2 — Plot of Γ(x) and 1/Γ(x)
Example¶
In this example, Γ(1.5) is computed and printed.
from __future__ import print_function
from pyimsl.stat.gamma import gamma
x = 1.5
ans = gamma(x)
print("Gamma(%f) = %f\n" % (x, ans))
Output¶
Gamma(1.500000) = 0.886227
Alert Errors¶
IMSLS_SMALL_ARG_UNDERFLOW |
The argument x must be large
enough that Γ(x) does not
underflow. The underflow limit occurs
first for arguments close to large
negative half integers. Even though
other arguments away from these half
integers may yield
machine-representable values of
Γ(x), such arguments are
considered illegal. |
Warning Errors¶
IMSLS_NEAR_NEG_INT_WARN |
The result is accurate to less than
one-half precision because x is too
close to a negative integer. |
Fatal Errors¶
IMSLS_ZERO_ARG_OVERFLOW |
The argument for the gamma function is too close to zero. |
IMSLS_NEAR_NEG_INT_FATAL |
The argument for the function is too close to a negative integer. |
IMSLS_LARGE_ARG_OVERFLOW |
The function overflows because x
is too large. |
IMSLS_CANNOT_FIND_XMIN |
The algorithm used to find \(\text{x}_{min}\) failed. This error should never occur. |
IMSLS_CANNOT_FIND_XMAX |
The algorithm used to find \(\text{x}_{max}\) failed. This error should never occur. |