| RandomNextExponentialMix Method |
Generate a pseudorandom number from a mixture of two exponential
distributions.
Namespace: Imsl.Stat
Assembly: ImslCS (in ImslCS.dll) Version: 6.5.2.0
Parameters
- theta1
- Type: SystemDouble
A double which specifies the mean of the exponential distribution that has the larger mean. - theta2
- Type: SystemDouble
A double which specifies the mean of the exponential distribution that has the smaller mean. theta2 must be positive and less than or equal to theta1. - p
- Type: SystemDouble
A double which specifies the mixing parameter. It must satisfy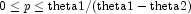 .
.
Return Value
Type: DoubleA double which specifies a pseudorandom number from a mixture of the two exponential distributions.
The probability density function is
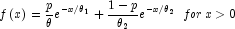
where ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
In the case of a convex mixture, that is, the case ![]() , the mixing parameter p is interpretable as a
probability; and NextExponentialMix with probability p
generates an exponential deviate with mean
, the mixing parameter p is interpretable as a
probability; and NextExponentialMix with probability p
generates an exponential deviate with mean
![]() , and with probability 1 - p
generates an exponential with mean
, and with probability 1 - p
generates an exponential with mean ![]() .
When p is greater than 1, but less than
.
When p is greater than 1, but less than
![]() , then either an
exponential deviate with mean
, then either an
exponential deviate with mean ![]() or the
sum of two exponentials with means
or the
sum of two exponentials with means ![]() and
and
![]() is generated. The probabilities are
is generated. The probabilities are
![]() and
1 - q, respectively, for the single exponential and the sum of
the two exponentials.
and
1 - q, respectively, for the single exponential and the sum of
the two exponentials.