Usage Notes
Unconstrained Minimization
The unconstrained minimization problem can be stated as follows:
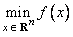
where f : Rn ® R is continuous and has derivatives of all orders required by the algorithms. The functions for unconstrained minimization are grouped into three categories: univariate functions, multivariate functions, and nonlinear least-squares functions.
For the univariate functions, it is assumed that the function is unimodal within the specified interval. For discussion on unimodality, see Brent (1973).
A quasi-Newton method is used for the multivariate function imsl_f_min_uncon_multivar. The default is to use a finite-difference approximation of the gradient of f(x). Here, the gradient is defined to be the vector

However, when the exact gradient can be easily provided, the keyword IMSL_GRAD should be used.
The nonlinear least-squares function uses a modified Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm. The most common application of the function is the nonlinear data-fitting problem where the user is trying to fit the data with a nonlinear model.
These functions are designed to find only a local minimum point. However, a function may have many local minima. Try different initial points and intervals to obtain a better local solution.
Double-precision arithmetic is recommended for the functions when the user provides only the function values.
Linearly Constrained Minimization
The linearly constrained minimization problem can be stated as follows:
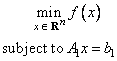
where f : Rn ® R, A1 and A2 are coefficient matrices, and
b1 and b2 are vectors. If
f(x) is linear, then the problem is a linear programming
problem. If f(x) is quadratic,
the problem is a quadratic
programming problem.
The function imsl_f_linear_programming uses an active set strategy to solve linear programming problems, and is intended as a replacement for the function imsl_f_lin_prog. The two functions have similar interfaces, which should help facilitate migration from imsl_f_lin_prog to imsl_f_linear_programming. In general, the function imsl_f_linear_programming should be expected to perform more efficiently than imsl_f_lin_prog. Both imsl_f_linear_programming and imsl_f_lin_prog are intended for use with small- to medium-sized linear programming problems. No sparsity is assumed since the coefficients are stored in full matrix form.
The function imsl_f_quadratic_prog is designed to solve convex quadratic programming problems using a dual quadratic programming algorithm. If the given Hessian is not positive definite, then imsl_f_quadratic_prog modifies it to be positive definite. In this case, output should be interpreted with care because the problem has been changed slightly. Here, the Hessian of f(x) is defined to be the n ´ n matrix
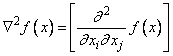
Nonlinearly Constrained Minimization
The nonlinearly constrained minimization problem can be stated as follows:

where f : Rn ® R and gi : Rn ® R, for i = 1, 2, ¼, m.
The function imsl_f_constrained_nlp uses a sequential equality constrained quadratic programming algorithm to solve this problem. A more complete discussion of this algorithm can be found in the documentation.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |