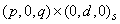[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [ I ] [J] [K] [L] [M]
[N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
Function Purpose Statement
A
|
Performs an Anderson-Darling test for normality. | |
|
Analyzes a one-way classification model with covariates. | |
|
Analyzes a balanced complete experimental design for a fixed, random, or mixed model. | |
|
Analyzes a balanced factorial design with fixed effects. | |
|
Analyzes a completely nested random model with possibly unequal numbers in the subgroups. | |
|
Analyzes a one-way classification model. | |
|
Computes least-square estimates of parameters for an ARMA model. | |
|
Computes forecasts and their associated probability limits for an ARMA model. | |
|
Reads freely-formatted ASCII files. | |
|
Computes the sample autocorrelation function of a stationary time series. | |
|
Automatically identifies
time series outliers, determines parameters of a multiplicative
seasonal ARIMA | |
|
Estimates structural breaks in non-stationary univariate time series. | |
|
Automatic selection and fitting of a univariate autoregressive time series model. |
B
|
Evaluates the complete beta function. | |
|
Evaluates the beta probability distribution function. | |
|
Evaluates the real incomplete beta function. | |
|
Evaluates the inverse of the beta distribution function. | |
|
Evaluates the binomial distribution function. | |
|
Evaluates the binomial coefficient. | |
|
Evaluates the binomial probability function. | |
|
Evaluates the bivariate normal distribution function. | |
|
Performs a Box-Cox transformation. |
C
|
Given an input array of deviate values, generates a canonical correlation array. | |
|
Analyzes categorical data using logistic, Probit, Poisson, and other generalized linear models. | |
|
Evaluates the chi-squared distribution function. | |
|
Evaluates the inverse of the chi-squared distribution function. | |
|
Performs a chi-squared test for normality. | |
|
Performs a chi-squared goodness-of-fit test. | |
|
Performs a hierarchical cluster analysis given a distance matrix. | |
|
Performs a K-means (centroid) cluster analysis. | |
|
Computes cluster membership for a hierarchical cluster tree. | |
|
Performs a Cochran Q test for related observations. | |
|
Calculates the complement of the chi-squared distribution. | |
|
Calculates the complement of the F distribution function | |
|
Evaluates the complementary noncentral F cumulative distribution function (CDF). | |
|
Calculates the complement of the Student's t distribution function. | |
|
Performs a chi-squared analysis of a two-way contingency table. | |
|
Sets up table to generate pseudorandom numbers from a general continuous distribution. | |
|
Computes the sample variance-covariance or correlation matrix. | |
|
Performs the Cox and Stuart’ sign test for trends in location and dispersion. | |
|
Analyzes data from balanced and unbalanced completely randomized experiments. | |
|
Computes the sample cross-correlation function of two stationary time series | |
|
Releases NVIDIA memory allocated by the IMSL C Numerical Library. | |
|
Get parameters used by the specified function to determine if the NVIDIA CUDA Toolkit algorithm will be used. | |
|
Set parameters used by the specified function to determine if the NVIDIA CUDA Toolkit algorithm will be used. | |
|
Performs a Cramer-von-Mises test for normality. |
D
|
Retrieves a commonly analyzed data set. | |
|
Differences a seasonal or nonseasonal time series. | |
|
Sets up a table to generate pseudorandom numbers from a general discrete distribution. | |
|
Performs discriminant function analysis. | |
|
Computes a matrix of dissimilarities (or similarities) between the columns (or rows) of a matrix. |
E
|
Computes empirical quantiles. |
| ||
|
Returns the code corresponding to the error message from the last function called. |
| ||
|
Gets the text of the error message from the last function called. |
| ||
|
Sets various error handling options. |
| ||
|
Gets the type corresponding to the error message from the last function called. |
| ||
|
Estimates missing values in a time series. |
| ||
|
Computes exact probabilities in a two-way contingency table, using the total enumeration method. | |||
|
Computes exact probabilities in a two-way contingency table using the network algorithm. | |||
F
|
Extracts initial factor-loading estimates in factor analysis. | |
|
Calculate the False Discovery Rate (FDR) q-values corresponding to a set of p-values from multiple simultaneous hypothesis tests. | |
|
Computes a shuffled Faure sequence | |
|
Closes a file opened by imsls_fopen. | |
|
Opens a file using the C runtime library used by the IMSL C Stat Library. | |
|
Frees memory returned from an IMSL C Stat Library function. | |
|
Performs Friedman’s test for a randomized complete block design. |
G
|
Codes and decodes binary information from phenotypes to a chromosome. | |||
|
Returns a new copy of an existing chromosome. | |||
|
Returns a new copy of an existing individual. | |||
|
Returns a new copy of an existing population. | |||
|
Copies the contents of one chromosome into another chromosome. | |||
|
Copies the contents of one individual into another individual. | |||
|
Copies the contents of one population into another population. | |||
|
Decodes an individual’s chromosome into its binary, nominal, integer and real phenotypes. | |||
|
Encodes an individual’s binary, nominal, integer and real phenotypes into its chromosome. | |||
|
Frees memory allocated to an existing individual | |||
|
Frees memory allocated to an existing population. | |||
|
Adds individuals to an existing population. | |||
|
Creates an Imsls_f_individual data structure from user supplied phenotypes. | |||
|
Creates a new population by merging two populations with identical chromosome structures. | |||
|
Performs the mutation operation on an individual’s chromosome. |
| ||
|
Creates an Imsls_f_population data structure from user supplied individuals. |
| ||
|
Creates an Imsls_f_population data structure from randomly generated individuals. |
| ||
|
Evaluates the real gamma functions. |
| ||
|
Evaluates the gamma distribution function. |
| ||
|
Evaluates the incomplete gamma function. |
| ||
|
Evaluates the inverse of the gamma distribution function. |
| ||
|
Computes estimates of the parameters of a GARCH (p, q) model |
| ||
|
Optimizes a user defined fitness function using a tailored genetic algorithm. |
| ||
H
|
Conducts Bartlett’s and Levene’s tests of the homogeneity of variance assumption in analysis of variance. | |
|
Calculates parameters and forecasts using the Holt-Winters Multiplicative or Additive forecasting method for seasonal data. | |
|
Evaluates the hypergeometric distribution function. | |
|
Evaluates the hypergeometric probability function. | |
|
Constructs a completely testable hypothesis. | |
|
Sums of cross products for a multivariate hypothesis. | |
|
Tests for the multivariate linear hypothesis. |
I
|
Locate and optionally replace dependent variable missing values with nearest neighbor estimates |
| ||
|
Initializes the IMSL C Stat Library. |
| ||
|
| |||
J
K
|
Performs Kalman filtering and evaluates the likelihood function for the state-space model. |
| ||
|
Computes Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival probabilities in stratified samples. |
| ||
|
Performs a Kolmogorov-Smirnov’s one-sample test for continuos distributions. | |||
|
Performs a Kolmogorov-Smirnov’s two-sample test. | |||
|
Performs a Kruskal-Wallis’s test for identical population medians. | |||
|
Performs k-sample trends test against ordered alternatives. | |||
L
|
Performs lack-of-fit test for an univariate time series or transfer function given the appropriate correlation function. | |
|
Analyzes data from latin-square experiments. | |
|
Analyzes balanced and partially-balanced lattice experiments. | |
|
Produces population and cohort life tables. | |
|
Performs a Lilliefors test for normality. | |
|
Fits a multiple linear regression model using criteria other than least squares. | |
|
Evaluates the log of the real beta function. | |
|
Evaluates the logarithm of the absolute value of the gamma function. | |
|
Fit a binomial or multinomial logistic regression model using iteratively reweighted least squares. | |
|
Predict a binomial or multinomial outcome given an estimated model and new values of the independent variables. |
M
|
|
Returns information describing the computer's floating-point arithmetic. | |||||||
|
|
Returns integer information describing the computer's arithmetic. | |||||||
|
|
Computes the transpose of a matrix, a matrix-vector product, a matrix-matrix product, a bilinear form, or any triple product. | |||||||
|
|
Exact maximum likelihood estimation of the parameters in a univariate ARMA (autoregressive, moving average) time series model. | |||||||
|
|
Calculates maximum likelihood estimates for the parameters of one of several univariate probability distributions. | |||||||
|
|
Trains a multilayered feedforward neural network for classification. |
| ||||||
|
|
Initializes weights for multilayered feedforward neural networks prior to network training using one of four user selected methods. |
| ||||||
|
|
Creates a multilayered feedforward neural network. |
| ||||||
|
|
Calculates forecasts for trained multilayered feedforward neural networks. |
| ||||||
|
Frees memory allocated for an Imsls_f_NN_Network data structure. |
| |||||||
|
Initializes a data structure for training a neural network. |
| |||||||
|
IRetrieves a neural network from a file previously saved. |
| |||||||
|
Trains a multilayered feedforward neural network. |
| |||||||
|
Writes a trained neural network to an ASCII file. |
| |||||||
|
Calculates classifications for trained multilayered feedforward neural networks. |
| |||||||
|
Computes the multichannel cross-correlation function of two mutually stationary multichannel time series. |
| |||||||
|
Performs Student-Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons test. |
| |||||||
|
Computes Mardia’s multivariate measures of skewness and kurtosis and tests for multivariate normality. |
| |||||||
|
Computes the cumulative distribution function for the multivariate normal distribution. |
| |||||||
N
|
Classifies unknown patterns using a previously trained Naïve Bayes classifier | |||||||
|
Trains a Naïve Bayes classifier. | |||||||
|
Frees memory allocated to an Imsls_f_nb_classifier data structure. | |||||||
|
Retrieves a Naive Bayes Classifier previously filed using imsls_f_nb_classifier_write. | |||||||
|
Writes a Naive Bayes Classifier to an ASCII file for later retrieval using imsls_f_nb_classifier_read. | |||||||
|
Performs the Noether’s test for cyclical trend. |
| ||||||
|
|
Evaluates the noncentral beta cumulative distribution function (CDF). |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the inverse of the noncentral beta cumulative distribution function (CDF). |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the noncentral beta probability density function (PDF). |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the noncentral chi-squared distribution function. |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the inverse of the noncentral chi-squared function. |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the noncentral chi-squared probability density function. |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the noncentral F cumulative distribution function. |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the inverse of the noncentral F cumulative distribution function. |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the noncentral F probability density function. |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the noncentral Student’s t distribution function. |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the inverse of the noncentral Student’s t distribution function. |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the noncentral Student's t probability density function. |
| |||||
|
|
Fits a nonlinear regression model using Powell's algorithm. |
| |||||
|
|
Fits a nonlinear regression model. |
| |||||
|
|
Performs nonparametric hazard rate estimation using kernel functions and quasi-likelihoods. |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the standard normal (Gaussian) distribution function. |
| |||||
|
|
Evaluates the inverse of the standard normal (Gaussian) distribution function. |
| |||||
|
|
Computes statistics for mean and variance inferences using a sample from a normal population. |
| |||||
|
|
Computes statistics for mean and variance inferences using samples from two normal population. |
| |||||
O
|
Sets various OpenMP options. | |
|
Sets the output file or the error message output file. |
P
|
Sets or retrieves the page width or length. | |
|
Computes the sample partial autocorrelation function of a stationary time series. | |
|
Computes partial covariances or partial correlations from the covariance or correlation matrix. | |
|
Permutes the rows or columns of a matrix. | |
|
Rearranges the elements of a vector as specified by a permutation. | |
|
Performs partial least squares regression for one or more response variables and one or more predictor variables. | |
|
Evaluates the Poisson distribution function. | |
|
Evaluates the Poisson probability function. | |
|
Computes predicted values, confidence intervals, and diagnostics after fitting a polynomial regression model. | |
|
Performs a polynomial least-squares regression. | |
|
Computes a pooled variance-covariance from the observations. | |
|
Computes principal components. | |
|
Analyzes time event data via the proportional hazards model. | |
|
|
Q
R
|
Generates pseudorandom ARMA process numbers. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a beta distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom binomial numbers. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a Cauchy distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a chi-squared distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a standard exponential distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom mixed numbers from a standard exponential distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a standard gamma distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a general continuous distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a general discrete distribution using an alias method or optionally a table lookup method. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a geometric distribution. | |
|
Retrieves the current table used in the GFSR generator. | |
|
Sets the current table used in the GFSR generator. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a hypergeometric distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a logarithmic distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a lognormal distribution. | |
|
Initializes the 32-bit Mersenne Twister generator using an array. | |
|
Retrieves the current table used in the 32-bit Mersenne Twister generator. | |
|
Sets the current table used in the 32-bit Mersenne Twister generator. | |
|
Initializes the 64-bit Mersenne Twister generator using an array. | |
|
Retrieves the current table used in the 64-bit Mersenne Twister generator. | |
|
Sets the current table used in the 64-bit Mersenne Twister generator. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a multinomial distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a multivariate distribution determined from a given sample. | |
|
Given a Cholesky factorization of a correlation matrix, generates pseudorandom numbers from a Gaussian Copula distribution. | |
|
Given a Cholesky factorization of a correlation matrix, generates pseudorandom numbers from a Student’s t Copula distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a negative binomial distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a normal, N (μ, σ2), distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a multivariate normal distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a nonhomogeneous Poisson process. | |
|
Selects the uniform (0, 1) multiplicative congruential pseudorandom number generator. | |
|
Retrieves the uniform (0, 1) multiplicative congruential pseudorandom number generator. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom order statistics from a standard normal distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom order statistics from a uniform (0, 1) distribution | |
|
Generates a pseudorandom orthogonal matrix or a correlation matrix. | |
|
Generates a pseudorandom permutation. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a Poisson distribution. | |
|
Generates a simple pseudorandom sample from a finite population. | |
|
Generates a simple pseudorandom sample of indices. | |
|
Retrieves the current value of the seed used in the IMSL random number generators. | |
|
Initializes a random seed for use in the IMSL random number generators. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom points on a unit circle or K-dimensional sphere. | |
|
Sets up a table to generate pseudorandom numbers from a general discrete distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom Student's t. | |
|
Retrieves a seed for the congruential generators that do not do shuffling that will generate random numbers beginning 100,000 numbers farther along. | |
|
Retrieves the current table used in the shuffled generator. | |
|
Sets the current table used in the shuffled generator. | |
|
Generates a pseudorandom two-way table. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a triangular distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a uniform (0, 1) distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a discrete uniform distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a von Mises distribution. | |
|
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a Weibull distribution. | |
|
Performs a test for randomness. | |
|
Computes the ranks, normal scores, or exponential scores for a vector of observations. | |
|
Analyzes data from balanced and unbalanced randomized complete-block experiments. | |
|
Fits a multiple linear regression model using least squares. | |
|
Fits a univariate, non-seasonal ARIMA time series model with the inclusion of one or more regression variables. | |
|
Computes predicted values, confidence intervals, and diagnostics after fitting a regression model. | |
|
Selects the best multiple linear regression models. | |
|
Builds multiple linear regression models using forward selection, backward selection or stepwise selection. | |
|
Produces summary statistics for a regression model given the information from the fit. | |
|
Generates regressors for a general linear model. | |
|
Computes a robust estimate of a covariance matrix and mean vector. |
S
|
Scales or unscales continuous data prior to its use in neural network training, testing, or forecasting. | |
|
Estimates the optimum seasonality parameters for a time series using an autoregressive model, AR(p), to represent the time series. | |
|
Performs the Shapiro-Wilk test for normality. | |
|
Performs a sign test. | |
|
Computes basic univariate statistics. | |
|
Sorts observations by specified keys, with option to tally cases into a multi-way frequency table. | |
|
Analyzes a wide variety of split-plot experiments with fixed, mixed or random factors. | |
|
Analyzes data from split-split-plot experiments. | |
|
Analyzes data from strip-plot experiments. | |
|
Analyzes data from strip-split-plot experiments. | |
|
Estimates using various parametric models. | |
|
Analyzes survival data using a generalized linear model. |
T
|
Evaluates the Student's t distribution function. | |
|
Evaluates the inverse of the Student's t distribution function. | |
|
Tallies observations into one-way frequency table. | |
|
Tallies observations into a two-way frequency table. | |
|
Computes tie statistics for a sample of observations. | |
|
Converts time series data sorted with nominal classes in decreasing chronological order to useful format for processing by a neural network. | |
|
Converts time series data to the format required for processing by a neural network. | |
|
Computes forecasts, their associated probability limits
and | |
|
Detects and determines outliers and simultaneously estimates the model parameters in a time series whose underlying outlier free series follows a general seasonal or nonseasonal ARMA model. |
U
|
Converts nominal data into a series of binary encoded columns for input to a neural network. | |
|
Converts ordinal data into percentages. |
V
|
Returns integer information describing the version of the library, license number, operating system, and compiler. |
W
|
Performs a Wilcoxon rank sum test. | |
|
Performs a Wilcoxon sign rank test. | |
|
Prints a rectangular matrix (or vector) stored in contiguous memory locations. | |
|
Sets or retieves an option for printing a matrix. | |
|
|
X
Y
Z